Amino Acid Sequences containing Cysteine or Cystine Residues in
... carboxymethy1cellulose columns, and is known to have a high cystine content. No stringent repurification was applied to the samples used for sequence work and no peptide amino acid sequences were found in recovered peptides, other than those that related to the sequences given in this paper. For goo ...
... carboxymethy1cellulose columns, and is known to have a high cystine content. No stringent repurification was applied to the samples used for sequence work and no peptide amino acid sequences were found in recovered peptides, other than those that related to the sequences given in this paper. For goo ...
attachment of amino acids to tRNA
... tRNAs are 75-95 nt in length. There are 15 invariant and 8 semi-invariant residues. The position of invariant and semi-variant nucleosides play a role in either the secondary and tertiary structure. There are many modified bases, which sometimes accounting for 20% of the total bases in one tRNA mole ...
... tRNAs are 75-95 nt in length. There are 15 invariant and 8 semi-invariant residues. The position of invariant and semi-variant nucleosides play a role in either the secondary and tertiary structure. There are many modified bases, which sometimes accounting for 20% of the total bases in one tRNA mole ...
Functional analysis of a novel baculovirus envelope fusion protein
... nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV). Nowadays a lot more baculoviruses are studied because of their unique features and their potential use as biological insecticide. This will ultimately led to new discoveries with respect to baculoviral properties and applications. The research in this thesis focuses on ...
... nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV). Nowadays a lot more baculoviruses are studied because of their unique features and their potential use as biological insecticide. This will ultimately led to new discoveries with respect to baculoviral properties and applications. The research in this thesis focuses on ...
Picky nascent peptides do not talk to foreign ribosomes
... functionally important compartment where the structure of the nascent peptide is monitored and from which specific peptides can signal the ribosome to slow down its rate of elongation or even completely stop translation. The bestcharacterized manifestation of this feedback mechanism is nascent peptid ...
... functionally important compartment where the structure of the nascent peptide is monitored and from which specific peptides can signal the ribosome to slow down its rate of elongation or even completely stop translation. The bestcharacterized manifestation of this feedback mechanism is nascent peptid ...
Diacylglycerol kinases - University of Toronto Mississauga
... All DGKs have at least two cysteine-rich regions homologous to the C1A and C1B motifs of PKCs [26]. In theory, these domains may bind DAG, perhaps localizing DGKs to where DAG accumulates. However, no DGK C1 domain has so far been conclusively shown to bind DAG. In fact, structural predictions sugge ...
... All DGKs have at least two cysteine-rich regions homologous to the C1A and C1B motifs of PKCs [26]. In theory, these domains may bind DAG, perhaps localizing DGKs to where DAG accumulates. However, no DGK C1 domain has so far been conclusively shown to bind DAG. In fact, structural predictions sugge ...
Full Article - PDF - Journal of Biotech Research
... central loop. These domains have also been observed by Jiang et al. [30] and others [31, 32, 33, 34]. The inward and outward opening of the pore through the membrane is a major property of MFS transporter family proteins [28]. They have both the N- and C-termini located in the cytoplasmic matrix [35 ...
... central loop. These domains have also been observed by Jiang et al. [30] and others [31, 32, 33, 34]. The inward and outward opening of the pore through the membrane is a major property of MFS transporter family proteins [28]. They have both the N- and C-termini located in the cytoplasmic matrix [35 ...
Investigation of asparagine deamidation in a SOD1
... shift of -17 Da can be indicative of succinimide intermediate whose existence correlates with formation of Asp/isoAsp isomers and therefore may be useful in identification of the deamidation site. There are also two indirect proofs for the presence of isoAsp residue employed in this study: terminati ...
... shift of -17 Da can be indicative of succinimide intermediate whose existence correlates with formation of Asp/isoAsp isomers and therefore may be useful in identification of the deamidation site. There are also two indirect proofs for the presence of isoAsp residue employed in this study: terminati ...
A Calcium-Regulated Gatekeeper in Phloem Sieve Tubes
... the aquatic plant Pistia stratiotes using immunolabeling with antibodies to a calcium channel protein. These authors proposed that calcium channels become activated during wounding or pathogen attack, facilitating calcium influx into phloem tissues. McEuen et al. (1981) detected a calcium binding pr ...
... the aquatic plant Pistia stratiotes using immunolabeling with antibodies to a calcium channel protein. These authors proposed that calcium channels become activated during wounding or pathogen attack, facilitating calcium influx into phloem tissues. McEuen et al. (1981) detected a calcium binding pr ...
The Role of the Plant Nucleolus in Pre-mRNA Processing
... (Saez-Vasquez et al. 2004). In addition, the absence of nucleolin expression causes disruption of the structural organisation of the nucleolus (Pontvianne et al. 2007). Ribosomal RNAs contain numerous nucleotide modifications. The two major modifications in rRNA are 2′-O-ribose methylation and pseud ...
... (Saez-Vasquez et al. 2004). In addition, the absence of nucleolin expression causes disruption of the structural organisation of the nucleolus (Pontvianne et al. 2007). Ribosomal RNAs contain numerous nucleotide modifications. The two major modifications in rRNA are 2′-O-ribose methylation and pseud ...
Accommodating the bacterial decoding release factor as an
... implying these events involve RNA almost exclusively with the tRNA, mRNA and rRNA, all playing key roles. It is observations like these that have consolidated the concept that the ribosome is an ‘RNA machine’ [6]. However, each X-ray structure represents a fixed snapshot and it remains a theoretical ...
... implying these events involve RNA almost exclusively with the tRNA, mRNA and rRNA, all playing key roles. It is observations like these that have consolidated the concept that the ribosome is an ‘RNA machine’ [6]. However, each X-ray structure represents a fixed snapshot and it remains a theoretical ...
Evolution of Amino Acid Metabolism Inferred through Cladistic
... the pentose phosphate pathway), and the Krebs cycle. Because the Krebs cycle is the point of confluence of all other metabolic pathways, it is sometimes viewed as primitive. That view is, however, challenged by several lines of evidence. Molecules entering the Krebs cycle (oxo acids and acyl-CoAs) a ...
... the pentose phosphate pathway), and the Krebs cycle. Because the Krebs cycle is the point of confluence of all other metabolic pathways, it is sometimes viewed as primitive. That view is, however, challenged by several lines of evidence. Molecules entering the Krebs cycle (oxo acids and acyl-CoAs) a ...
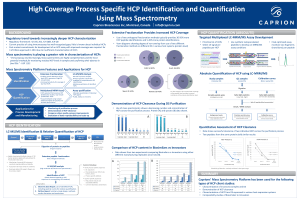
High Coverage Process Specific HCP Identification and
... • Data shows successful clearance of two individual HCPs across the purification process • Two peptides from the same protein yield similar results ...
... • Data shows successful clearance of two individual HCPs across the purification process • Two peptides from the same protein yield similar results ...
The phosphopantetheinyl transferases
... other central biosynthetic pathways in both primary and specialized metabolism. The essential enzymatic role of PPTases in general fatty acid biosynthesis was recognized in the groundbreaking work of Vagelos and Elovson.3 Since then, many other PPTases have been discovered to play the same role in a ...
... other central biosynthetic pathways in both primary and specialized metabolism. The essential enzymatic role of PPTases in general fatty acid biosynthesis was recognized in the groundbreaking work of Vagelos and Elovson.3 Since then, many other PPTases have been discovered to play the same role in a ...
Effect of Amino Acid Sequence and pH on Nanofiber
... peptides have the same amino acid composition, their amino acid sequences are different. EAK16-II has a charge sequence of - - + + - - + + at neutral pH, whereas, EAK16-IV has a charge sequence of - - - - + + + +. AFM images of these samples in aqueous solution are shown in Figure 2. A significant d ...
... peptides have the same amino acid composition, their amino acid sequences are different. EAK16-II has a charge sequence of - - + + - - + + at neutral pH, whereas, EAK16-IV has a charge sequence of - - - - + + + +. AFM images of these samples in aqueous solution are shown in Figure 2. A significant d ...
PPT
... The “universal genetic code” is universal. The genetic code is unambiguous. All DNA (and RNA) genomes encode the information to make proteins with only 20 amino acids. The “central dogma of molecular biology” (DNA RNA protein) describes the only flow of biological information. ...
... The “universal genetic code” is universal. The genetic code is unambiguous. All DNA (and RNA) genomes encode the information to make proteins with only 20 amino acids. The “central dogma of molecular biology” (DNA RNA protein) describes the only flow of biological information. ...
Metabolic rate depression in animals
... becomes intermittent, and kidney filtration rate is reduced. Organisms do not eat so the energetic costs of digestion, nutrient absorption, and peristalsis are eliminated. A substantial part of total energy savings comes from the suppression of these physiological activities. Metabolic rate is also i ...
... becomes intermittent, and kidney filtration rate is reduced. Organisms do not eat so the energetic costs of digestion, nutrient absorption, and peristalsis are eliminated. A substantial part of total energy savings comes from the suppression of these physiological activities. Metabolic rate is also i ...
Modulation of functional properties of bifunctional S- Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase/Ornithine decarboxylase of
... Tumor necrosis factor alpha ...
... Tumor necrosis factor alpha ...
Fibrous Proteins
... Biosynthesis and assembly of collagen (Con’t) 4. Addition of Asn-linked oligosaccharides to collagen 5. Initial glycosylation of hydroxylyine residues 6. Alignment of three polypeptide chains and formation of interchain disulfide bridges 7. Formation of triple helical procollagen 8. Transfer by end ...
... Biosynthesis and assembly of collagen (Con’t) 4. Addition of Asn-linked oligosaccharides to collagen 5. Initial glycosylation of hydroxylyine residues 6. Alignment of three polypeptide chains and formation of interchain disulfide bridges 7. Formation of triple helical procollagen 8. Transfer by end ...
... state, it will cost about 20 kJ/mole of instability since a hydrogen bond to water is broken during folding, but not reformed. (6 pts) Additional factors (1 pt for either, unless the main reason was missed and these are discussed at length.): The mutant protein will be stabilized by increased vdw in ...
GTPase domains ofras p21 oncogene protein and elongation factor
... and Fig. 3). The core residues (Fig. 3) include primarily residues in the interior strands of the P-sheet, in helix al, and in part of the loop regions in contact with the bound nucleotide. For ras p21, 32 of 166 residues are in the core; for EF-Tu, 35 of 177 are in the core. Of the 116 equivalent r ...
... and Fig. 3). The core residues (Fig. 3) include primarily residues in the interior strands of the P-sheet, in helix al, and in part of the loop regions in contact with the bound nucleotide. For ras p21, 32 of 166 residues are in the core; for EF-Tu, 35 of 177 are in the core. Of the 116 equivalent r ...
PDF
... and 1⫻Fix Buffer (Westerfield, 2000) at 4°C, blocked in 1⫻PBS/5% NGS/4 mg/ml BSA/0.5% Triton X-100 for 1 hour at room temperature, and incubated in primary antibody (diluted in blocking solution) overnight at 4°C. Embryos were then washed at room temperature for 1.5 hours in PBS containing 0.1% Twee ...
... and 1⫻Fix Buffer (Westerfield, 2000) at 4°C, blocked in 1⫻PBS/5% NGS/4 mg/ml BSA/0.5% Triton X-100 for 1 hour at room temperature, and incubated in primary antibody (diluted in blocking solution) overnight at 4°C. Embryos were then washed at room temperature for 1.5 hours in PBS containing 0.1% Twee ...
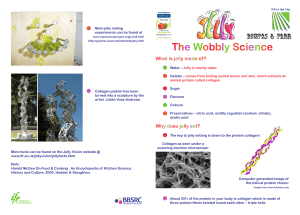
Jelly Facts - Institute of Food Research
... treatment with acids and alkalis. Bonds between collagen molecules (intermolecular bonds), bonds in the molecules (intramolecular bonds) and hydrogen bonds are broken down, making gelatin. When protein loses its shape it denatures. When the gelatin is heated and mixed with water the protein fibres c ...
... treatment with acids and alkalis. Bonds between collagen molecules (intermolecular bonds), bonds in the molecules (intramolecular bonds) and hydrogen bonds are broken down, making gelatin. When protein loses its shape it denatures. When the gelatin is heated and mixed with water the protein fibres c ...
Chapter2 Radiolabeled amino acids: basic aspects and
... precursors, amino acids can be crucial in metabolic cycles. For example, the amino acid methionine, derived from the diet, is part of the activated methyl cycle. In this important metabolic cycle, S-adenosylmethionine serves as a methyl group donor in many biosynthetic steps (3). Amino acid degradat ...
... precursors, amino acids can be crucial in metabolic cycles. For example, the amino acid methionine, derived from the diet, is part of the activated methyl cycle. In this important metabolic cycle, S-adenosylmethionine serves as a methyl group donor in many biosynthetic steps (3). Amino acid degradat ...
Production of recombinant EMA-1 protein and its
... with the same protein from different strains. There are more than 20 sequences of EMA-1 from different isolates deposited previously in the GenBank databank. All sequences are highly conserved, however the sequence of the protein EMA-1 from the ...
... with the same protein from different strains. There are more than 20 sequences of EMA-1 from different isolates deposited previously in the GenBank databank. All sequences are highly conserved, however the sequence of the protein EMA-1 from the ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.