PDF
... nucleotides. These triplets are known as codons. With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. That produces some redundancy in the code: most of the amino acids being encoded by more than one codon[12]. The genetic code can be expressed a ...
... nucleotides. These triplets are known as codons. With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. That produces some redundancy in the code: most of the amino acids being encoded by more than one codon[12]. The genetic code can be expressed a ...
Crabtree, Savage and Miller
... designed amplify single DNA fragment each when paired with the CP16 primer (Figure 1). The fragthat when amplified by these primers varied in size used together in single amplification reaction (four-primer reaction) the fragments could be easily separated and identified agarose gel. The four-primer ...
... designed amplify single DNA fragment each when paired with the CP16 primer (Figure 1). The fragthat when amplified by these primers varied in size used together in single amplification reaction (four-primer reaction) the fragments could be easily separated and identified agarose gel. The four-primer ...
Ph.D.™ Peptide Display Cloning System
... The following procedure is specific for the M13 cloning vector M13KE, but could easily be adapted for other phage (but NOT phagemid) vectors. 1. Design a library oligonucleotide following the convention in Figure 1. Bear in mind that the sequence VPFYSHS preceding the leader peptidase cleavage site ...
... The following procedure is specific for the M13 cloning vector M13KE, but could easily be adapted for other phage (but NOT phagemid) vectors. 1. Design a library oligonucleotide following the convention in Figure 1. Bear in mind that the sequence VPFYSHS preceding the leader peptidase cleavage site ...
Highlight of mutation GPS® technique
... A deletion is a mutation caused by loss of a DNA sequence. An insertion is a mutations caused by adding a piece of DNA into genome, which can occur naturally, or can be artificially created for research purposes in the lab mediated by virus, plasmid or transposons. Exogenous DNA insertion mutations ...
... A deletion is a mutation caused by loss of a DNA sequence. An insertion is a mutations caused by adding a piece of DNA into genome, which can occur naturally, or can be artificially created for research purposes in the lab mediated by virus, plasmid or transposons. Exogenous DNA insertion mutations ...
DATA ENCRYPTION USING BIO MOLECULAR INFORMATION
... from unauthorised users. The worst case of an attack within communication is complete control of the encryption system by illegitimate users. This happens by accessing the encryption algorithm to decrypt the data and access sensitive information. Cryptography relies on uncertainty in encoding the me ...
... from unauthorised users. The worst case of an attack within communication is complete control of the encryption system by illegitimate users. This happens by accessing the encryption algorithm to decrypt the data and access sensitive information. Cryptography relies on uncertainty in encoding the me ...
Using Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy, DNA
... optical paths. Each image is focused onto a separate half of the EMCCD to allow simultaneous dualcolor imaging. The entire TIRFM system is mounted on an optical table (Newport Corp.) to minimize vibrations and to facilitate alignment of optical components. Such TIRFM systems are capable of detecting ...
... optical paths. Each image is focused onto a separate half of the EMCCD to allow simultaneous dualcolor imaging. The entire TIRFM system is mounted on an optical table (Newport Corp.) to minimize vibrations and to facilitate alignment of optical components. Such TIRFM systems are capable of detecting ...
Biological information flow
... and GC boxes & other cisacting elements are recognized by proteins other than RNA polymerase. ...
... and GC boxes & other cisacting elements are recognized by proteins other than RNA polymerase. ...
POB3 Is Required for Both Transcription and Replication
... Spt16 levels and an spt16 mutation increase the production of some transcripts, notably the aberrant messages from transposon-disrupted alleles of HIS4 and LYS2 that lead to the Spt⫺ phenotype (Prendergast et al. 1990; Malone et al. 1991; Rowley et al. 1991; Lycan et al. 1994). However, the levels o ...
... Spt16 levels and an spt16 mutation increase the production of some transcripts, notably the aberrant messages from transposon-disrupted alleles of HIS4 and LYS2 that lead to the Spt⫺ phenotype (Prendergast et al. 1990; Malone et al. 1991; Rowley et al. 1991; Lycan et al. 1994). However, the levels o ...
Introduction
... PolyExpress™ reagent is capable to immobilize DNA migration during electrophoresis at very low concentration and form polyplexes within a few minutes at room temperature. Due to its biodegrable feature, the cationic polymer is rapidly degraded shortly after entering cells by endocytosis (Figure 1), ...
... PolyExpress™ reagent is capable to immobilize DNA migration during electrophoresis at very low concentration and form polyplexes within a few minutes at room temperature. Due to its biodegrable feature, the cationic polymer is rapidly degraded shortly after entering cells by endocytosis (Figure 1), ...
Ratio of DNA Concentrations
... ions that shield the negative charges on the two strands from one another. At low ionic strength, the mutually repulsive forces of the negative charges are strong enough to denature the DNA at a relatively low temperature. Renaturation of DNA, also known as annealing, is the reformation of complemen ...
... ions that shield the negative charges on the two strands from one another. At low ionic strength, the mutually repulsive forces of the negative charges are strong enough to denature the DNA at a relatively low temperature. Renaturation of DNA, also known as annealing, is the reformation of complemen ...
Report on tested replacement component for β
... using the SPRI method (Biopsrint, Qiagen). This was also reported by Pereira et al., 2011; they attributed this to a reduction human involvement in automated systems compared to the phenol-chloroform extraction method. While samples extracted using the CTAB buffer, followed by a phenol-chloroform ex ...
... using the SPRI method (Biopsrint, Qiagen). This was also reported by Pereira et al., 2011; they attributed this to a reduction human involvement in automated systems compared to the phenol-chloroform extraction method. While samples extracted using the CTAB buffer, followed by a phenol-chloroform ex ...
TEST REVIEW - Protein Synthesis – ANSWERS ON LAST PAGE
... ____ 13. Which type of ribonucleic acid combines with proteins to form a ribosome? a. mRNA c. sRNA b. tRNA d. rRNA ____ 14. What do these three statements describe? I. Instructions for translating information into proteins II. Alignment and sequence of genes on a chromosome III. Composed of nucleot ...
... ____ 13. Which type of ribonucleic acid combines with proteins to form a ribosome? a. mRNA c. sRNA b. tRNA d. rRNA ____ 14. What do these three statements describe? I. Instructions for translating information into proteins II. Alignment and sequence of genes on a chromosome III. Composed of nucleot ...
Student Guide - the BIOTECH Project
... 1. Label the PCR tube so that you can distinguish the samples in the tube. 2. Add 5 µl primer of each primer to each tube. If necessary, gently tap you tube on the counter to get all of the liquid to the bottom of the tube. 3. Add 10 µl GoTaq (green solution). Close the tubes and centrifuge briefly ...
... 1. Label the PCR tube so that you can distinguish the samples in the tube. 2. Add 5 µl primer of each primer to each tube. If necessary, gently tap you tube on the counter to get all of the liquid to the bottom of the tube. 3. Add 10 µl GoTaq (green solution). Close the tubes and centrifuge briefly ...
HiPer®Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Teaching
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis isextensively used in molecular biology for detecting variation at the DNA sequence level. Theprinciple of this analysis is to compare restriction digestion profiles of DNA samplesisolated from different individuals. RFLP functions as a molecu ...
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis isextensively used in molecular biology for detecting variation at the DNA sequence level. Theprinciple of this analysis is to compare restriction digestion profiles of DNA samplesisolated from different individuals. RFLP functions as a molecu ...
Plasmid pIP501 Encoded Transciptional Repressor CopR Binds to
... (site I and site II) on the same face of the DNA. In spite of identical sequence motifs in these sites, neighboring bases were contacted differently. Furthermore, we showed that CopR can dimerize in solution. We demonstrate by two independent methods that CopR binds the DNA as a dimer. We present da ...
... (site I and site II) on the same face of the DNA. In spite of identical sequence motifs in these sites, neighboring bases were contacted differently. Furthermore, we showed that CopR can dimerize in solution. We demonstrate by two independent methods that CopR binds the DNA as a dimer. We present da ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Hopewell Valley Regional School District
... Before it leaves the nucleus, RNA is edited. Splicing occurs by removing introns and fusing exons together. ...
... Before it leaves the nucleus, RNA is edited. Splicing occurs by removing introns and fusing exons together. ...
Nuclear Architecture, Chromosome Territories, Chromatin Dynamics
... We prepare a final volume of 12 µl hybridization solution, sufficient for 4 hybridizations (or 3 hybridizations on 15 x 15 mm cover slips respectively). Approximately 40 – 80 ng DNA/µl hybridization solution is used for non-repetitive (single copy) probes. Since exact measurement of DNA probe concen ...
... We prepare a final volume of 12 µl hybridization solution, sufficient for 4 hybridizations (or 3 hybridizations on 15 x 15 mm cover slips respectively). Approximately 40 – 80 ng DNA/µl hybridization solution is used for non-repetitive (single copy) probes. Since exact measurement of DNA probe concen ...
Restriction of M13 DNA by the restriction enzyme TaqI
... respect to the other. Each subunit recognizes a specific sequence on the DNA. Since the subunits are identical and antiparallel, so are the recognition sequences. As a result, recognition sites of commonly used restriction enzymes are palindromes. For example: EcoRI recognizes ...
... respect to the other. Each subunit recognizes a specific sequence on the DNA. Since the subunits are identical and antiparallel, so are the recognition sequences. As a result, recognition sites of commonly used restriction enzymes are palindromes. For example: EcoRI recognizes ...
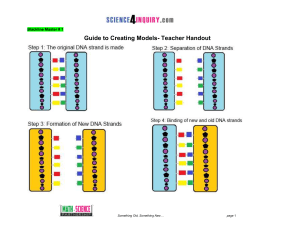
Activity Name - Science4Inquiry.com
... Something Old, Something New… You are a Molecular Biologist who is studying the process of DNA replication. Your task is to build a model that represents this process. Next you will investigate where DNA replication took place in the human body and explain why it occurred. This activity is divided u ...
... Something Old, Something New… You are a Molecular Biologist who is studying the process of DNA replication. Your task is to build a model that represents this process. Next you will investigate where DNA replication took place in the human body and explain why it occurred. This activity is divided u ...
251 Lab 2 Chrisine
... The gene that we choose is the mutS/hMSH2 DNA repair gene. In addition to following the readings and guided steps on pages 151 – 159, we will ask you to answer some questions related to your findings. First we give some background on this gene mutS is the name given to a prokaryotic (bacterial) defe ...
... The gene that we choose is the mutS/hMSH2 DNA repair gene. In addition to following the readings and guided steps on pages 151 – 159, we will ask you to answer some questions related to your findings. First we give some background on this gene mutS is the name given to a prokaryotic (bacterial) defe ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.