Lab 6: Electrophoresis
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
DNA Metallization Processes and Nanoelectronics
... arrangement of the basis is controlled by π stacking and then the Lewis base sites available for coordination to the metal (Pd, Pt, etc.) are limited to the exposed portion of the nucleobases found in the major groove (the N7 position of guanosine and adenosine). It is commonly thought that of these ...
... arrangement of the basis is controlled by π stacking and then the Lewis base sites available for coordination to the metal (Pd, Pt, etc.) are limited to the exposed portion of the nucleobases found in the major groove (the N7 position of guanosine and adenosine). It is commonly thought that of these ...
Boost Biology With Bats!
... - Print the required pages and cut out each template. - As you cut out each template glue each pair so that you have doubled sided sugars,phosphates,As,Ts,Gs,Cs (model should read from the back also) Important: There will be some trimming to size required, G base and C base mostly. - When cutting ...
... - Print the required pages and cut out each template. - As you cut out each template glue each pair so that you have doubled sided sugars,phosphates,As,Ts,Gs,Cs (model should read from the back also) Important: There will be some trimming to size required, G base and C base mostly. - When cutting ...
Pol /Primase, Pol ε Pol ε α MIT Department of Biology 7.28, Spring
... dependent on a primer/template junction. A mutation in the Primase subunit eliminates its ability to make the RNA primer, therefore there is no primer/template junction and the complex is no longer stable in high salt. (E) Based on your hypothesis and your knowledge of DNA polymerases, what other fa ...
... dependent on a primer/template junction. A mutation in the Primase subunit eliminates its ability to make the RNA primer, therefore there is no primer/template junction and the complex is no longer stable in high salt. (E) Based on your hypothesis and your knowledge of DNA polymerases, what other fa ...
doc BIOL 200 final notes
... Duplex DNA is unwound + Daughter strands are formed at DNA Replication fork - At replication origins ORI: usually A-T rich; replication fork - helicase unwinds parental DNA strands - primase, a specialized RNA polymerase, forms a short RNA primer complementary to unwound template strands - DNA pol t ...
... Duplex DNA is unwound + Daughter strands are formed at DNA Replication fork - At replication origins ORI: usually A-T rich; replication fork - helicase unwinds parental DNA strands - primase, a specialized RNA polymerase, forms a short RNA primer complementary to unwound template strands - DNA pol t ...
Oxidative nucleotide damage: consequences and prevention
... There are at least three steps required to prevent errors during DNA replication; (1) selection of a nucleotide complementary to the template by DNA polymerase, (2) removal of a misincorporated non-complementary nucleotide by an editing nuclease, associated with DNA polymerase, and (3) correction of ...
... There are at least three steps required to prevent errors during DNA replication; (1) selection of a nucleotide complementary to the template by DNA polymerase, (2) removal of a misincorporated non-complementary nucleotide by an editing nuclease, associated with DNA polymerase, and (3) correction of ...
An Approximate Approach to DNA Denaturation
... T h e dynamics of DNA transcription is among the most fascinating problems of modern biophysics because it is at the basis of life. However, it also is a very difficult problem due to the complex role played by RNA polymerases in the process. It is now well established (Freifelder 1987) t h a t loca ...
... T h e dynamics of DNA transcription is among the most fascinating problems of modern biophysics because it is at the basis of life. However, it also is a very difficult problem due to the complex role played by RNA polymerases in the process. It is now well established (Freifelder 1987) t h a t loca ...
Table II Transformation of various derived strains OSU Strain Outcrossed with
... as described earlier (Zsindely et al., 1977, Acta Biol. Acad. Sci. Hung. ...
... as described earlier (Zsindely et al., 1977, Acta Biol. Acad. Sci. Hung. ...
Structure of B-DNA with Cations Tethered in the Major Groove†
... Each of the four amino-propyl modifications is readily identifiable in sum and difference maps (Figure 3). Three amino-propyl groups (on residues 7, 8, and 19) extend radially out from the DNA and into intermolecular cavities in the crystal. These cationic amino groups do not appear to engage in sig ...
... Each of the four amino-propyl modifications is readily identifiable in sum and difference maps (Figure 3). Three amino-propyl groups (on residues 7, 8, and 19) extend radially out from the DNA and into intermolecular cavities in the crystal. These cationic amino groups do not appear to engage in sig ...
Chapter 20
... 300 base pairs • SNPs can be detected by PCR, and any SNP shared by people affected with a disorder but not among unaffected people may pinpoint the location of the disease-causing gene © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... 300 base pairs • SNPs can be detected by PCR, and any SNP shared by people affected with a disorder but not among unaffected people may pinpoint the location of the disease-causing gene © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 1
... explains why the molecules of living organism are mainly made of only a few elements. Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids, some of which are spontaneously formed in a pre-biotic world. The sugar molecules in a cell are also frequently interconnected into chains of carbohydrates, the second ...
... explains why the molecules of living organism are mainly made of only a few elements. Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids, some of which are spontaneously formed in a pre-biotic world. The sugar molecules in a cell are also frequently interconnected into chains of carbohydrates, the second ...
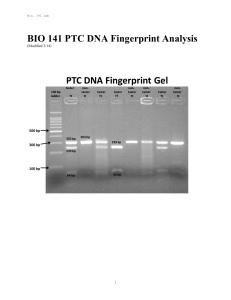
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... Visualizing your DNA fingerprint: Are you a taster or a non-taster? The next step is to cut your DNA with Fnu4HI to determine if you are a taster or non-taster. If you are a non-taster, you will be missing the Fnu4HI restriction enzyme site located at nucleotide position 785 and the fragment of DNA ...
... Visualizing your DNA fingerprint: Are you a taster or a non-taster? The next step is to cut your DNA with Fnu4HI to determine if you are a taster or non-taster. If you are a non-taster, you will be missing the Fnu4HI restriction enzyme site located at nucleotide position 785 and the fragment of DNA ...
Gel electrophoresis of restriction digest
... displaying different mobility are Bromphenol Blue and Xylene Cyanol. Xylene Cyanol migrates with DNA fragments around 5kb and Bromphenol Blue migrates with DNA fragments around 0.5kb. Bromphenol Blue provides visualization of the mobility of the fastest fragments and is valuable in determining the l ...
... displaying different mobility are Bromphenol Blue and Xylene Cyanol. Xylene Cyanol migrates with DNA fragments around 5kb and Bromphenol Blue migrates with DNA fragments around 0.5kb. Bromphenol Blue provides visualization of the mobility of the fastest fragments and is valuable in determining the l ...
Ch. 4 ppt
... Release of chemical energy in the cell often occurs through the oxidation of glucose. Burning glucose requires energy to begin the process. The end-products of these reactions are heat as well as stored energy. This stored energy is called ATP which has a chain of three ...
... Release of chemical energy in the cell often occurs through the oxidation of glucose. Burning glucose requires energy to begin the process. The end-products of these reactions are heat as well as stored energy. This stored energy is called ATP which has a chain of three ...
Chapter 17 Protein Synthesis
... called the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript • The template strand is always the same strand for a given gene • During translation, the mRNA base triplets, called codons, are read in the 5 to 3 direction ...
... called the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript • The template strand is always the same strand for a given gene • During translation, the mRNA base triplets, called codons, are read in the 5 to 3 direction ...
PPT presentation - Yavapai College
... which in turn changes protein sequence that codes for a specific protein in one of the many cell metabolic pathways ...
... which in turn changes protein sequence that codes for a specific protein in one of the many cell metabolic pathways ...
Genomic DNA Extraction from Buccal Cells
... aqueous environment without using ionic chaotropes, such as guanidinium isothiocyanate, or organic reagents, such as ethanol, phenol, chloroform or IPA. These reagents, used in most nucleic acid purification technologies are hazardous and can cause problems for liquid handling systems. Additionally, ...
... aqueous environment without using ionic chaotropes, such as guanidinium isothiocyanate, or organic reagents, such as ethanol, phenol, chloroform or IPA. These reagents, used in most nucleic acid purification technologies are hazardous and can cause problems for liquid handling systems. Additionally, ...
Biology Ch. 12
... The chromatin fibers supercoil to form chromosomes that are visible in the metaphase stage of mitosis. ...
... The chromatin fibers supercoil to form chromosomes that are visible in the metaphase stage of mitosis. ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.