MyTaq™ Blood PCR Kit
... room temperature set up because of the hot-start polymerase; (2) achieve the specificity and robustness required for selectively amplifying the CYP450 2D6 gene that is homologous to the CYP450 2D7 gene; (3) amplify 1.5 kb and 3 kb amplicons ...
... room temperature set up because of the hot-start polymerase; (2) achieve the specificity and robustness required for selectively amplifying the CYP450 2D6 gene that is homologous to the CYP450 2D7 gene; (3) amplify 1.5 kb and 3 kb amplicons ...
TRANSCRIPTION – TRANSLATION
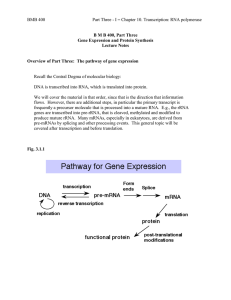
... RNA synthesis is transcription; protein synthesis is translation. RNA differs from DNA in that it is single stranded, contains Uracil instead of Thymine and ribose instead of deoxyribose, and has different functions. The central dogma depicts RNA as a messenger between gene and protein, but does not ...
... RNA synthesis is transcription; protein synthesis is translation. RNA differs from DNA in that it is single stranded, contains Uracil instead of Thymine and ribose instead of deoxyribose, and has different functions. The central dogma depicts RNA as a messenger between gene and protein, but does not ...
Aberrant replication timing induces defective chromosome
... Conclusions: The results not only reveal novel functions for ORC2 in chromosome architecture in metazoans, they also suggest that the correct timing of DNA replication may be essential for the assembly of chromatin that is fully competent to undergo mitotic condensation. ...
... Conclusions: The results not only reveal novel functions for ORC2 in chromosome architecture in metazoans, they also suggest that the correct timing of DNA replication may be essential for the assembly of chromatin that is fully competent to undergo mitotic condensation. ...
DNA barcoding: how it complements taxonomy, molecular
... soil nematodes and other small organisms in an approach known as ‘DNA taxonomy’ [17]. This approach differs from DNA barcoding in that it does not aim to link the genetic entities recognised through sequence analysis with Linnaean species. As such, it is most useful for groups of organisms that lack ...
... soil nematodes and other small organisms in an approach known as ‘DNA taxonomy’ [17]. This approach differs from DNA barcoding in that it does not aim to link the genetic entities recognised through sequence analysis with Linnaean species. As such, it is most useful for groups of organisms that lack ...
francis crick - American Philosophical Society
... composed of two intertwined polynucleotide chains, held together by hydrogen bonds formed between an adenine and a thymine, or between a guanine and a cytosine, on opposite sides of the double helix. The Central Dogma At first sight, Watson and Crick’s discovery of the double helical structure of th ...
... composed of two intertwined polynucleotide chains, held together by hydrogen bonds formed between an adenine and a thymine, or between a guanine and a cytosine, on opposite sides of the double helix. The Central Dogma At first sight, Watson and Crick’s discovery of the double helical structure of th ...
Recombinational Circularization of Salmonella Phage
... DNA in P22-infected cells destined for lysogeny. In the following experiment, we repeated their procedure and obtained similar results. A culture of strain 18 cells growing at 37” was infected with 32P-labeled c+ phage; the multiplicity of infection, 10 per cell, was sufficient to cause the lysogeni ...
... DNA in P22-infected cells destined for lysogeny. In the following experiment, we repeated their procedure and obtained similar results. A culture of strain 18 cells growing at 37” was infected with 32P-labeled c+ phage; the multiplicity of infection, 10 per cell, was sufficient to cause the lysogeni ...
Chpt10_TxnRNAPol.doc
... f. The reaction progresses (the enzyme moves) about 50 nts per sec. This is much slower than the rate of replication (about 1000 nts per sec). g. If the template is topologically constrained, the DNA ahead of the RNA polymerase becomes overwound (positive superhelical turns) and the DNA behind the R ...
... f. The reaction progresses (the enzyme moves) about 50 nts per sec. This is much slower than the rate of replication (about 1000 nts per sec). g. If the template is topologically constrained, the DNA ahead of the RNA polymerase becomes overwound (positive superhelical turns) and the DNA behind the R ...
Chapter 10 Review
... four possible bases. The nucleotides are connected to each other by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of the next nucleotide. The double helix arrangement is maintained by the formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 10-2.3 ...
... four possible bases. The nucleotides are connected to each other by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of the next nucleotide. The double helix arrangement is maintained by the formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 10-2.3 ...
Supplementary Text 1 (doc 52K)
... Sequencing of 16S rRNA genes and phylogenetic analysis PCR products were sequenced using the DYEnamic Direct cycle sequencing kit (Amersham Life Science) and a Model 4200 automated DNA sequencer (LI-COR) as described by Rink et al. (2007). Sequences were analysed by BLASTn search (http://www.ncbi.n ...
... Sequencing of 16S rRNA genes and phylogenetic analysis PCR products were sequenced using the DYEnamic Direct cycle sequencing kit (Amersham Life Science) and a Model 4200 automated DNA sequencer (LI-COR) as described by Rink et al. (2007). Sequences were analysed by BLASTn search (http://www.ncbi.n ...
Assay Quality Considerations
... Allele drop-out (ADO): the failure of a molecular test to amplify or detect one or more alleles Potential causes: DNA template concentration • Incomplete cell lysis • DNA degradation Non-optimized assay conditions Unknown polymorphisms in target sites Reagent component failure ...
... Allele drop-out (ADO): the failure of a molecular test to amplify or detect one or more alleles Potential causes: DNA template concentration • Incomplete cell lysis • DNA degradation Non-optimized assay conditions Unknown polymorphisms in target sites Reagent component failure ...
Chapter 4 powerpoint file
... They only perform one specific reaction While they change the reactants into new products enzymes themselves are not changed during a reaction They can be re-used multiple times They may be permanently or temporarily inhibited ...
... They only perform one specific reaction While they change the reactants into new products enzymes themselves are not changed during a reaction They can be re-used multiple times They may be permanently or temporarily inhibited ...
12_PPTLecture_LEC
... • Genomic libraries, sets of DNA fragments containing all of an organism’s genes ...
... • Genomic libraries, sets of DNA fragments containing all of an organism’s genes ...
3.2 Chromosomes - Peoria Public Schools
... that still allows for processes, such as replication and protein synthesis, to occur. Nucleosomes are formed by wrapping DNA around histone proteins ...
... that still allows for processes, such as replication and protein synthesis, to occur. Nucleosomes are formed by wrapping DNA around histone proteins ...
How to Use This Presentation
... Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is sometimes described as a zipper. Answer: DNA is often described as a zipper because the two strands of DNA look like each lengthwise half of a zipper and the bases and hydrogen bonds between the strands look like the “teeth” of a zipper. Chapter menu ...
... Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is sometimes described as a zipper. Answer: DNA is often described as a zipper because the two strands of DNA look like each lengthwise half of a zipper and the bases and hydrogen bonds between the strands look like the “teeth” of a zipper. Chapter menu ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.