Slide 1
... symbolic code, the genetic code. This code is used nearly universally by living organisms; it is one of the most ancient shared characteristics of living things. The “words” of the genetic code are nucleotide triplets called codons. Each codon codes for at most one amino acid. Codons that do not ...
... symbolic code, the genetic code. This code is used nearly universally by living organisms; it is one of the most ancient shared characteristics of living things. The “words” of the genetic code are nucleotide triplets called codons. Each codon codes for at most one amino acid. Codons that do not ...
CH7 DNAtoProtein
... operon to be turned “on”? • No glucose • Increasing levels of cAMP • cAMP binds to CAP, then complex binds next to lactose operon promoter at the activator region • RNA polymerase binds to promoter • Lactose present • Allolactose binds to repressor, keeping it from binding to the operator • RNA poly ...
... operon to be turned “on”? • No glucose • Increasing levels of cAMP • cAMP binds to CAP, then complex binds next to lactose operon promoter at the activator region • RNA polymerase binds to promoter • Lactose present • Allolactose binds to repressor, keeping it from binding to the operator • RNA poly ...
Genetics
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
BIO101 Objectives Unit3 Blinderman Mercer County Community
... 9. Describe in detail semiconservative replication of DNA. Include all enzymes and other proteins and the role of each (helicase, topoisomerase, SSB, DNA polymerase, primase, ligase) 10. Compare size of the human and E. coli genomes including number of bases and number of chromosomes 11. State the i ...
... 9. Describe in detail semiconservative replication of DNA. Include all enzymes and other proteins and the role of each (helicase, topoisomerase, SSB, DNA polymerase, primase, ligase) 10. Compare size of the human and E. coli genomes including number of bases and number of chromosomes 11. State the i ...
Genetic Technology
... DNA code of living organisms uses DNA technology to cure diseases, treat genetic disorders, improve food crops, etc. ...
... DNA code of living organisms uses DNA technology to cure diseases, treat genetic disorders, improve food crops, etc. ...
Tic Tac Toe Questions - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 15. THE MOVEMENT OF WATER ACROSS A PLASMA MEMBRANE IS CALLED? (Osmosis) 16. In DNA, Thymine binds with _____? (Adenine) 17. If 30% of your DNA is Guanine…..what percentage will be Adenine? (20%.....explanation: if Guanine is 30%, so should Cytosine since they bond together….that leaves 40% for Adeni ...
... 15. THE MOVEMENT OF WATER ACROSS A PLASMA MEMBRANE IS CALLED? (Osmosis) 16. In DNA, Thymine binds with _____? (Adenine) 17. If 30% of your DNA is Guanine…..what percentage will be Adenine? (20%.....explanation: if Guanine is 30%, so should Cytosine since they bond together….that leaves 40% for Adeni ...
DNA Structure and Function
... DNA Replication 8. Before a cell divides, it must replicate its _______________. This replication occurs during the _______________ stage of interphase. 9. During replication the two strands of the DNA are separated. It is a lot like unzipping a zipper. What are the bonds that are broken when the DN ...
... DNA Replication 8. Before a cell divides, it must replicate its _______________. This replication occurs during the _______________ stage of interphase. 9. During replication the two strands of the DNA are separated. It is a lot like unzipping a zipper. What are the bonds that are broken when the DN ...
Chap 3
... helix around which they wind; there is a major groove and a minor groove (Wilkins et al.). • The bases are in the core of the structure and the phosphates make up the “backbone” of the helices (Franklin and Gosling). • The bases form hydrogen bonds with complementary bases (“base pairing”) to connec ...
... helix around which they wind; there is a major groove and a minor groove (Wilkins et al.). • The bases are in the core of the structure and the phosphates make up the “backbone” of the helices (Franklin and Gosling). • The bases form hydrogen bonds with complementary bases (“base pairing”) to connec ...
FA15Lec8 Sequencing DNA and RNA
... Go over reading, HW, Class notes. Concepts—~ ½; write about them Calculations– about ~ ½ ...
... Go over reading, HW, Class notes. Concepts—~ ½; write about them Calculations– about ~ ½ ...
DNA Webquest - sciencewithskinner
... 1. Look at the cell model. Where is the DNA found that unzips when a protein is to be made? a) cytoplasm b) nucleolus c) nucleus d) ribosomes Follow the directions on the screen and answer the following questions. 2. List the RNA bases that pair up with the DNA nucleotides on the unzipped molecule d ...
... 1. Look at the cell model. Where is the DNA found that unzips when a protein is to be made? a) cytoplasm b) nucleolus c) nucleus d) ribosomes Follow the directions on the screen and answer the following questions. 2. List the RNA bases that pair up with the DNA nucleotides on the unzipped molecule d ...
Section J
... Deletion mutagenesis Progressively deleting DNA from one end is very useful for defining the important of particular sequences. Unidirectional deletion can be created using exonuclease III which removes one ztrand in a 3’ to 5’ direction from a recessed 3’-end. A single strand –specific nuclease the ...
... Deletion mutagenesis Progressively deleting DNA from one end is very useful for defining the important of particular sequences. Unidirectional deletion can be created using exonuclease III which removes one ztrand in a 3’ to 5’ direction from a recessed 3’-end. A single strand –specific nuclease the ...
DNA-RNA-Protein Synthesis
... recorder, and a demolisher (disassembly). The demolisher and builder may have two jobs. Decide as a group how to build a model of DNA. The artist should draw it for the group and label each base subunit (nitrogen base) according to the model. The recorder should write down the process (pair, unzip…) ...
... recorder, and a demolisher (disassembly). The demolisher and builder may have two jobs. Decide as a group how to build a model of DNA. The artist should draw it for the group and label each base subunit (nitrogen base) according to the model. The recorder should write down the process (pair, unzip…) ...
E1-3 NotesProtein Synth
... 5. Nitrogen base has 4 different kinds a. adenine (A) b. guanine (G) c. cytosine (C) d. thymine (T) 6. DNA – double helix (like a spiral staircase) a. discovered by Watson and Crick 7. Covalent bonds B/T sugar and phosphate 8. Nitrogen bases connect to sugar-phosphate backbone 9. 2 Nitrogen bases at ...
... 5. Nitrogen base has 4 different kinds a. adenine (A) b. guanine (G) c. cytosine (C) d. thymine (T) 6. DNA – double helix (like a spiral staircase) a. discovered by Watson and Crick 7. Covalent bonds B/T sugar and phosphate 8. Nitrogen bases connect to sugar-phosphate backbone 9. 2 Nitrogen bases at ...
4.1. Genetics as a Tool in Anthropology
... Statistical approach to link changes in gene structure to history of a population Gene structure can change randomly during replication or by chemical or radiation impact. The causes a change in base sequence ⇒ Mutation. Mutation can be a replacement of a base or base addition/deletion. Only a mutat ...
... Statistical approach to link changes in gene structure to history of a population Gene structure can change randomly during replication or by chemical or radiation impact. The causes a change in base sequence ⇒ Mutation. Mutation can be a replacement of a base or base addition/deletion. Only a mutat ...
DNA Slides - U3A in Kennet
... How come children get traits from grandmothers and mother? Young men make children, before later life traits develop? How can males produce females? ...
... How come children get traits from grandmothers and mother? Young men make children, before later life traits develop? How can males produce females? ...
Ch. 12 Notes
... These mutations are not passed down to offspring Sex cell: If the mutations occurs in the sex cells it will be passed down to the offspring and will be present in every cell of the offspring. The mutation may or may not affect the offspring. ...
... These mutations are not passed down to offspring Sex cell: If the mutations occurs in the sex cells it will be passed down to the offspring and will be present in every cell of the offspring. The mutation may or may not affect the offspring. ...
RNA - Burlington Township School District
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – Ribosomes are made of rRNA and protein. ...
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – Ribosomes are made of rRNA and protein. ...
DNA Transcription
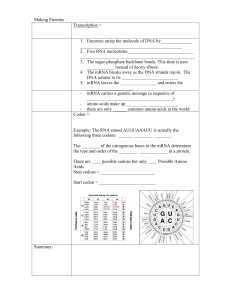
... More than one codon can code for the same amino acid BUT for any one codon, there can only by one amino acid!!! The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA at ...
... More than one codon can code for the same amino acid BUT for any one codon, there can only by one amino acid!!! The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA at ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.