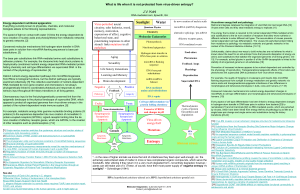
regulation of cell cycle
... to prepare the chromosomes for replication. Rising level of S-phase promoting factor (SPF) — which includes cyclin A bound to Cdk2 — enters the nucleus and prepares the cell to duplicate its DNA (and its centrosomes). As DNA replication continues, cyclin E is destroyed, and the level of mitotic cy ...
... to prepare the chromosomes for replication. Rising level of S-phase promoting factor (SPF) — which includes cyclin A bound to Cdk2 — enters the nucleus and prepares the cell to duplicate its DNA (and its centrosomes). As DNA replication continues, cyclin E is destroyed, and the level of mitotic cy ...
18 - cloudfront.net
... Reading the Sequence Researchers use a clever chemical trick to "read" DNA by determining the order of its bases. A single strand of DNA whose sequence of bases is not known is placed in a test tube. DNA polymerase, the enzyme that copies DNA, and the four nucleotide bases, A, T, G, and C, are added ...
... Reading the Sequence Researchers use a clever chemical trick to "read" DNA by determining the order of its bases. A single strand of DNA whose sequence of bases is not known is placed in a test tube. DNA polymerase, the enzyme that copies DNA, and the four nucleotide bases, A, T, G, and C, are added ...
13-2 Manipulating DNA
... Reading the Sequence Researchers use a clever chemical trick to "read" DNA by determining the order of its bases. A single strand of DNA whose sequence of bases is not known is placed in a test tube. DNA polymerase, the enzyme that copies DNA, and the four nucleotide bases, A, T, G, and C, are added ...
... Reading the Sequence Researchers use a clever chemical trick to "read" DNA by determining the order of its bases. A single strand of DNA whose sequence of bases is not known is placed in a test tube. DNA polymerase, the enzyme that copies DNA, and the four nucleotide bases, A, T, G, and C, are added ...
chapter 16 the molecule basis of inheritance
... Returning to the original problem at the replication fork, the leading strand requires the formation of only a single primer as the replication fork continues to separate. For synthesis of the lagging strand, each Okazaki fragment must be primed separately. Another DNA polymerase, DNA polymerase I ...
... Returning to the original problem at the replication fork, the leading strand requires the formation of only a single primer as the replication fork continues to separate. For synthesis of the lagging strand, each Okazaki fragment must be primed separately. Another DNA polymerase, DNA polymerase I ...
Protein Synthesis - TangHua2012-2013
... E. mRNA is released (Enzymes break the Hydrogen bonds). DNA ________________ back together. mRNA is first processed (_________________________________________________________) so it can leave the nucleus then passes through the _________________________ through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm. ...
... E. mRNA is released (Enzymes break the Hydrogen bonds). DNA ________________ back together. mRNA is first processed (_________________________________________________________) so it can leave the nucleus then passes through the _________________________ through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm. ...
Lesson Plan Construction Form
... 4. Fasten your molecule together using clear tape. Do not tape across base pairs. 5. As in step 1, copy the parts for A, G, and C RNA nucleotides. Use the same colors of construction paper as in step 1. Use the fifth color of construction paper to make copies of uracil nucleotides. 6. With scissors, ...
... 4. Fasten your molecule together using clear tape. Do not tape across base pairs. 5. As in step 1, copy the parts for A, G, and C RNA nucleotides. Use the same colors of construction paper as in step 1. Use the fifth color of construction paper to make copies of uracil nucleotides. 6. With scissors, ...
RNA Transcription
... strand for complementary base-pairing. In this way, the growing RNA chain is extended by one nucleotide at a time in the 5’-to-3’ direction, proceeding at a rate of about 50 nucleotides per second. The substrates are nucleoside triphosphates (ATP, CTP, UTP, and GTP), but unlike the situation in DNA ...
... strand for complementary base-pairing. In this way, the growing RNA chain is extended by one nucleotide at a time in the 5’-to-3’ direction, proceeding at a rate of about 50 nucleotides per second. The substrates are nucleoside triphosphates (ATP, CTP, UTP, and GTP), but unlike the situation in DNA ...
Practice using the RNA codon * amino acid Codon Chart*
... Name _____________________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: __________ INTRODUCTION: Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, ...
... Name _____________________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: __________ INTRODUCTION: Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, ...
1431236491.
... Heavy isotope was integrated into all the bacterial DNA (Grew E. coli in 15N for several generations so that all the DNA was labeled) They shifted cells to 14N media and allowed them to replicate their DNA 1 time Sample of DNA was taken. Cells were allowed to replicate their DNA again (total of 2 ti ...
... Heavy isotope was integrated into all the bacterial DNA (Grew E. coli in 15N for several generations so that all the DNA was labeled) They shifted cells to 14N media and allowed them to replicate their DNA 1 time Sample of DNA was taken. Cells were allowed to replicate their DNA again (total of 2 ti ...
Chapter 8: Microbial Genetics
... Each cell has a nucleus, each nucleus has chromosomes And DNA, baby, that spells DNA ...
... Each cell has a nucleus, each nucleus has chromosomes And DNA, baby, that spells DNA ...
Genetic Continuity
... 3. unpaired bases react with complimentary bases of nucleotides 4. New H bonds are formed ◦ DNA polymerase (an enzyme) catalyzes the process ...
... 3. unpaired bases react with complimentary bases of nucleotides 4. New H bonds are formed ◦ DNA polymerase (an enzyme) catalyzes the process ...
Nucleic Acids - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... Basically a chromosome is made up of DNA wrapped around proteins, coiled together to form nucleosomes that coil up into supercoils called a CHROMOSOME. ...
... Basically a chromosome is made up of DNA wrapped around proteins, coiled together to form nucleosomes that coil up into supercoils called a CHROMOSOME. ...
Genetic Engineering Notes
... Dolly, the first mammal to be cloned from adult DNA, was put down by lethal injection Feb. 14, 2003. Prior to her death, Dolly had been suffering from lung cancer and crippling arthritis. Although most Finn Dorset sheep live to be 11 to 12 years of age, postmortem examination of Dolly seemed to indi ...
... Dolly, the first mammal to be cloned from adult DNA, was put down by lethal injection Feb. 14, 2003. Prior to her death, Dolly had been suffering from lung cancer and crippling arthritis. Although most Finn Dorset sheep live to be 11 to 12 years of age, postmortem examination of Dolly seemed to indi ...
Assignment 2 with Key
... (b) Histones are rich in the electropositive (basic) amino acid residues lysine and arginine. These positive charges neutralize the negative charge of chromosomal DNA, which allows the strands to become condensed and packaged within the chromosome. ...
... (b) Histones are rich in the electropositive (basic) amino acid residues lysine and arginine. These positive charges neutralize the negative charge of chromosomal DNA, which allows the strands to become condensed and packaged within the chromosome. ...
Cross-Curricular Discussion
... 1. What are some of the important molecular and functional differences between DNA and RNA? [DNA and RNA have extremely similar molecular structures, but DNA is double-stranded while RNA is most often single-stranded. Instead of the base thymine, which is used in DNA, RNA has uracil which has a sli ...
... 1. What are some of the important molecular and functional differences between DNA and RNA? [DNA and RNA have extremely similar molecular structures, but DNA is double-stranded while RNA is most often single-stranded. Instead of the base thymine, which is used in DNA, RNA has uracil which has a sli ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.