chapt06b_lecture
... similar ligands. In this model, the first ligand is assumed to induce conformational changes that are transmitted sequentially to other protomers in the enzyme. Neither model above fully explains all allosteric enzyme activity. 6P2-29 ...
... similar ligands. In this model, the first ligand is assumed to induce conformational changes that are transmitted sequentially to other protomers in the enzyme. Neither model above fully explains all allosteric enzyme activity. 6P2-29 ...
Basic information on pathways
... Methyl group: A methyl group is simply a single carbon atom bonded to 3 hydrogen atoms (CH3). Methylation: Transfer of methyl groups from one chemical to another is called methylation. Essentially any chemical compound that has a methyl group as part of its chemical structure is capable of donating ...
... Methyl group: A methyl group is simply a single carbon atom bonded to 3 hydrogen atoms (CH3). Methylation: Transfer of methyl groups from one chemical to another is called methylation. Essentially any chemical compound that has a methyl group as part of its chemical structure is capable of donating ...
Scandium and Yttrium - Mercyhurst University
... resemble sunlight. As mentioned, scandium(III) triflate (Sc(CF3SO3)3) is a useful Lewis acid in organic synthesis as it is water-stable.1 Current Research Much like transition metals ions, scandium(III) and yttrium(III) will coordinate to a variety of ligands, including crown ethers, aza-crown ether ...
... resemble sunlight. As mentioned, scandium(III) triflate (Sc(CF3SO3)3) is a useful Lewis acid in organic synthesis as it is water-stable.1 Current Research Much like transition metals ions, scandium(III) and yttrium(III) will coordinate to a variety of ligands, including crown ethers, aza-crown ether ...
Word - Chemistry and More
... Fall Examination Study Questions 1. (Chapter 2) Identify the following properties as physical or chemical properties: a) Copper is shiny and orange. b) Potassium reacts explosively with fluorine gas to produce potassium fluoride. c) Oxygen is a gas at room temperature. d) Sodium oxide has a very hig ...
... Fall Examination Study Questions 1. (Chapter 2) Identify the following properties as physical or chemical properties: a) Copper is shiny and orange. b) Potassium reacts explosively with fluorine gas to produce potassium fluoride. c) Oxygen is a gas at room temperature. d) Sodium oxide has a very hig ...
Generation of Free Radical
... sense to collectively free radicals (O2.-, OH.) and non-free radicals (H2O2, 1O2, which are extremely reactive) of the biological system. ...
... sense to collectively free radicals (O2.-, OH.) and non-free radicals (H2O2, 1O2, which are extremely reactive) of the biological system. ...
growth regulators
... on herbicide absorption) that are primarily applied postemergence and translocate via the phloem to the growing points and other sink regions in the plant. At low doses, the growth regulator herbicides have a stimulatory effect on plant and cell growth similar to that of IAA. However, phytotoxic con ...
... on herbicide absorption) that are primarily applied postemergence and translocate via the phloem to the growing points and other sink regions in the plant. At low doses, the growth regulator herbicides have a stimulatory effect on plant and cell growth similar to that of IAA. However, phytotoxic con ...
File
... This results in the formation of • 6 molecules of NADH • 2 molecules of FADH2 • 2 molecules of ATP • 4 molecules of CO2 The NADH and FADH2 molecules then carry electrons to the electron transport system for production of ATPs by oxidative phosphorylation ...
... This results in the formation of • 6 molecules of NADH • 2 molecules of FADH2 • 2 molecules of ATP • 4 molecules of CO2 The NADH and FADH2 molecules then carry electrons to the electron transport system for production of ATPs by oxidative phosphorylation ...
welcome to ap chemistry - Garnet Valley School District
... I am delighted that you have chosen to take AP chemistry this fall. It is a challenging course and a strong foundation is necessary for your success. The material included in the summer work packet will enable you to cover the basics of chemistry, which are covered in chapters 1, 2, 3 and 4 of the t ...
... I am delighted that you have chosen to take AP chemistry this fall. It is a challenging course and a strong foundation is necessary for your success. The material included in the summer work packet will enable you to cover the basics of chemistry, which are covered in chapters 1, 2, 3 and 4 of the t ...
Effects of oxygen on the growth and metabolism of Actinomyces
... as an anaerobe, grew with a 2.4-times higher yield in aerated cultures than under anaerobic conditions (Fig. 2). The growth yield in aerated cultures (Yglucose= 149 g-mo1-1) cannot be accounted for by a fermentative metabolism and strongly suggested citric acid cycle activity coupled to electron tra ...
... as an anaerobe, grew with a 2.4-times higher yield in aerated cultures than under anaerobic conditions (Fig. 2). The growth yield in aerated cultures (Yglucose= 149 g-mo1-1) cannot be accounted for by a fermentative metabolism and strongly suggested citric acid cycle activity coupled to electron tra ...
Human Physiology/ The respiratory system
... result of the muscles relaxing). When the lungs are stretched and expanded, stretch receptors within the alveoli send inhibitory nerve impulses to the medulla oblongata, causing it to stop sending signals to the rib cage and diaphragm to contract. The muscles of respiration and the lungs themselves ...
... result of the muscles relaxing). When the lungs are stretched and expanded, stretch receptors within the alveoli send inhibitory nerve impulses to the medulla oblongata, causing it to stop sending signals to the rib cage and diaphragm to contract. The muscles of respiration and the lungs themselves ...
NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
... gene and is characterized by increased levels of adenosine and deoxyadenosine in blood and urine. Total or nearly total loss of enzyme activity results in a severe combined immunodeficiency affecting both B and T lymphocyte functions, and it has been found that deoxyadenosine at the high levels accu ...
... gene and is characterized by increased levels of adenosine and deoxyadenosine in blood and urine. Total or nearly total loss of enzyme activity results in a severe combined immunodeficiency affecting both B and T lymphocyte functions, and it has been found that deoxyadenosine at the high levels accu ...
summer fun - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
Dark Reactions
... by ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase. This enzyme has a 4Fe-4S cluster that couples the one electron transfers from reduced ferredoxin towards the two electron reduction of thioredoxin. Phosphoribulose kinase and glyceraldehydes 3phosphate dehydrogenase are also regulated by NADPH directly. In the da ...
... by ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase. This enzyme has a 4Fe-4S cluster that couples the one electron transfers from reduced ferredoxin towards the two electron reduction of thioredoxin. Phosphoribulose kinase and glyceraldehydes 3phosphate dehydrogenase are also regulated by NADPH directly. In the da ...
Questionsheet 1
... The gas produced can be identified using limewater. Name the gas and the result of this test. Name of gas ............................................................................................................................................... Result of test ................................... ...
... The gas produced can be identified using limewater. Name the gas and the result of this test. Name of gas ............................................................................................................................................... Result of test ................................... ...
ENZYMES - PROBLEMS - Chemistry@Elmhurst
... Normally folic acid is synthesized in two steps in bacteria by the top reaction on the left. If a sulfa drug is used, the first enzyme is not to specific and can use the sulfonamide in the first reaction. This reaction produces the product containing pteridine and the sulfa drug. The next and final ...
... Normally folic acid is synthesized in two steps in bacteria by the top reaction on the left. If a sulfa drug is used, the first enzyme is not to specific and can use the sulfonamide in the first reaction. This reaction produces the product containing pteridine and the sulfa drug. The next and final ...
Slides - WordPress.com
... since been identified in a variety of chemoautotrophs rTCA cycle specific enzymes are 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (Oor), fumarate reductase (Frd), and ATP citrate lyase (Acl) rTCA cycle pathway tends to be in organisms that live in low O2 ...
... since been identified in a variety of chemoautotrophs rTCA cycle specific enzymes are 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (Oor), fumarate reductase (Frd), and ATP citrate lyase (Acl) rTCA cycle pathway tends to be in organisms that live in low O2 ...
Shunt Pathway Significance of pentose phosphate pathway
... ● These patients cannot generate enough NADPH by the pentose phosphate pathway necessary for antioxidant system to defend erythrocytes against reactive oxygen species . ● Individuals with this genetic deficiency have attacks of severe hemolytic anemia and jaundice when taking certain drugs like anti ...
... ● These patients cannot generate enough NADPH by the pentose phosphate pathway necessary for antioxidant system to defend erythrocytes against reactive oxygen species . ● Individuals with this genetic deficiency have attacks of severe hemolytic anemia and jaundice when taking certain drugs like anti ...
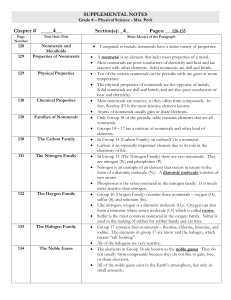
Name - TeacherWeb
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
Stoichiometry
... • How many molecules of water would be required to react with 3.64 g of Mg3N2? • What is the maximum number of grams of Mg(OH)2 that can be produced by the reaction of 10.0 g of Mg3N2 and 14.4 g of H2O? • What is the percent yield if 9.4 g of Mg(OH)2 are produced? • How many grams of the excess reag ...
... • How many molecules of water would be required to react with 3.64 g of Mg3N2? • What is the maximum number of grams of Mg(OH)2 that can be produced by the reaction of 10.0 g of Mg3N2 and 14.4 g of H2O? • What is the percent yield if 9.4 g of Mg(OH)2 are produced? • How many grams of the excess reag ...
Enzymes of the biosynthesis of octadecanoid
... Conconi et al., 1996a). The 13(S)-hydroperoxide serves as a substrate for several enzymes like divinylether synthase, peroxygenase, hydroperoxide lyase, and hydroperoxide reductase (Fig. 1) (BleÂe and Joyard, 1996; MareÂchal et al., 1997) or allene oxide synthase (AOS) (Vick and Zimmerman, 1981, 198 ...
... Conconi et al., 1996a). The 13(S)-hydroperoxide serves as a substrate for several enzymes like divinylether synthase, peroxygenase, hydroperoxide lyase, and hydroperoxide reductase (Fig. 1) (BleÂe and Joyard, 1996; MareÂchal et al., 1997) or allene oxide synthase (AOS) (Vick and Zimmerman, 1981, 198 ...
Hemoglobin - Mercer University
... elevation where the air is “thinner” and the partial pressure of oxygen gas is lower. At first you might experience shortness of breath at the higher elevation, but after a day or two you start feeling more “normal.” This is because your body acclimates to the higher elevation (in part) by increasin ...
... elevation where the air is “thinner” and the partial pressure of oxygen gas is lower. At first you might experience shortness of breath at the higher elevation, but after a day or two you start feeling more “normal.” This is because your body acclimates to the higher elevation (in part) by increasin ...
New Insights into the Metabolic and Molecular Mechanism of Plant
... plant specific, but are important parameters for most living organisms. Cytosolic-free calcium concentration is one of the most widespread signals among all living organisms. Calcium spikes are involved in the perception of many different stimuli or stresses; these spikes stimulate responses involve ...
... plant specific, but are important parameters for most living organisms. Cytosolic-free calcium concentration is one of the most widespread signals among all living organisms. Calcium spikes are involved in the perception of many different stimuli or stresses; these spikes stimulate responses involve ...
Step by Step Stoichiometry
... These problems will ask you to calculate the amount of one substance, in grams, that will be needed to react or be produced from a given mass for another substance. The plan for solving these kinds of problems: Mass of given amount of given in moles amount of unknown in moles mass of ...
... These problems will ask you to calculate the amount of one substance, in grams, that will be needed to react or be produced from a given mass for another substance. The plan for solving these kinds of problems: Mass of given amount of given in moles amount of unknown in moles mass of ...
Ch. 11-12 Supplements
... 3) a. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of aqueous sulfuric acid, H2SO4, and solid aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3 forming liquid water and aqueous aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3. If 30.0 grams of sulfuric acid and 25.0 grams of aluminum hydroxide react… b. How many grams of each product will b ...
... 3) a. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of aqueous sulfuric acid, H2SO4, and solid aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3 forming liquid water and aqueous aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3. If 30.0 grams of sulfuric acid and 25.0 grams of aluminum hydroxide react… b. How many grams of each product will b ...
WHY DO CARDIOMYOCYTES (HEART MUSCLE CELLS) STORE
... The "Krebs' Cycle", otherwise known as the "Citric Acid Cycle", is a well-‐known metabolic pathway. It occurs only in the mitochondrion, and is a circular metabolic route that starts and ends with oxal ...
... The "Krebs' Cycle", otherwise known as the "Citric Acid Cycle", is a well-‐known metabolic pathway. It occurs only in the mitochondrion, and is a circular metabolic route that starts and ends with oxal ...