Chapter-1-Intro - Mister Chemistry Welcomes You!
... A set of characteristics by which a substance can be recognized ...
... A set of characteristics by which a substance can be recognized ...
File
... remains the same. The substance may change form or state, however. All changes of state are physical changes. There are other physical changes that are not changes of state. Dissolving is a physical change. When sugar is dissolved it spreads out in the water but the sugar is still sugar. If the wate ...
... remains the same. The substance may change form or state, however. All changes of state are physical changes. There are other physical changes that are not changes of state. Dissolving is a physical change. When sugar is dissolved it spreads out in the water but the sugar is still sugar. If the wate ...
AFS Policy Statement #6
... recorded history. Increased urbanization, the Industrial Revolution, and an overall larger population base have accelerated the process considerably. While providing numerous societal benefits, modern chemical technology has also brought about a marked increase in the number and variety of chemicals ...
... recorded history. Increased urbanization, the Industrial Revolution, and an overall larger population base have accelerated the process considerably. While providing numerous societal benefits, modern chemical technology has also brought about a marked increase in the number and variety of chemicals ...
Characterization of Multi-constituent Substances for REACH
... points, phase transitions and decompositions. Many chemical analytical methods have been developed for measuring specific constituents and can distinguish between, for example, nitrate nitrogen and ammoniacal nitrogen. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION In addition to the actual analytical testing, it is import ...
... points, phase transitions and decompositions. Many chemical analytical methods have been developed for measuring specific constituents and can distinguish between, for example, nitrate nitrogen and ammoniacal nitrogen. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION In addition to the actual analytical testing, it is import ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) H2S(g) + FeCl2(aq) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) ...
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) H2S(g) + FeCl2(aq) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) ...
Name Objective 1: Matter and Energy C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
Nature of Life Study Guide
... o Know the location and proper usage of all lab safety equipment. o Know the egress plan for evacuation o Know the protocol for an emergency o Pass the written safety test. Introduction to Biology (section 1.1, 1.2) o Know the characteristics in common with all living organisms. Scientific Method (s ...
... o Know the location and proper usage of all lab safety equipment. o Know the egress plan for evacuation o Know the protocol for an emergency o Pass the written safety test. Introduction to Biology (section 1.1, 1.2) o Know the characteristics in common with all living organisms. Scientific Method (s ...
Lecture Notes
... A physical property that is closely related to density is Specific gravity. For liquids and solids, this property is the ratio of the mass of the substance to the mass of an equal volume of water at the same temperature. Specific Gravity = mass of the solid or liquid mass of an equal volume of water ...
... A physical property that is closely related to density is Specific gravity. For liquids and solids, this property is the ratio of the mass of the substance to the mass of an equal volume of water at the same temperature. Specific Gravity = mass of the solid or liquid mass of an equal volume of water ...
Topic2890 Thermodynamics and Kinetics A given system at
... reaction. In fact the link between the rate of chemical reaction (dξ / dt ) and the affinity for spontaneous change A is intuitively attractive. However while one may monitor the dependence of composition on time, dξ/dt, it is not immediately obvious ∂A how one might estimate the affinity A and ...
... reaction. In fact the link between the rate of chemical reaction (dξ / dt ) and the affinity for spontaneous change A is intuitively attractive. However while one may monitor the dependence of composition on time, dξ/dt, it is not immediately obvious ∂A how one might estimate the affinity A and ...
Chapter 1 Matter on the Atomic Scale
... • Constant collisions with neighbors. • Less confined, can move past each other. ...
... • Constant collisions with neighbors. • Less confined, can move past each other. ...
New Title
... a. H2 + O2 H2O b. Mg + O2 MgO c. Na + O2 Na2O d. 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 17. A number placed in front of a chemical formula in a chemical equation is called a(n) 18. What does a coefficient tell you? ...
... a. H2 + O2 H2O b. Mg + O2 MgO c. Na + O2 Na2O d. 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 17. A number placed in front of a chemical formula in a chemical equation is called a(n) 18. What does a coefficient tell you? ...
1 the four characteristics of a mineral (Section 1) 2 the two major
... the four characteristics of a mineral (Section 1) the two major classification groups of minerals (Section 1) the classification of minerals using common mineral identification techniques (Section 2) special properties of minerals (Section 2) the properties that make a mineral a gemstone (Section 3) ...
... the four characteristics of a mineral (Section 1) the two major classification groups of minerals (Section 1) the classification of minerals using common mineral identification techniques (Section 2) special properties of minerals (Section 2) the properties that make a mineral a gemstone (Section 3) ...
SAFETY AND CLEANROOM PRACTICE
... Additional material safety information is available as a set of Material Safety Data Sheets, available in the lab, or from your instructor. Semiconductor processing requires the use of hazardous chemicals and high temperatures, so certain safety guidelines must be followed. Keep in mind that althoug ...
... Additional material safety information is available as a set of Material Safety Data Sheets, available in the lab, or from your instructor. Semiconductor processing requires the use of hazardous chemicals and high temperatures, so certain safety guidelines must be followed. Keep in mind that althoug ...
Chapter 14, Section 1, pages 494-501
... Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactants to form products S8 + 8O2 ----------->8 SO2 Reversible Reactions are those in ...
... Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactants to form products S8 + 8O2 ----------->8 SO2 Reversible Reactions are those in ...
Chemistry 2011-2012
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matt ...
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matt ...
Chemistry Standard Outline
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical processes. SC6a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion ...
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical processes. SC6a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion ...
File Vocabulary PPT set #1
... FAMILIES / GROUPS • Elements that are grouped together based on their chemical properties and reactivity ...
... FAMILIES / GROUPS • Elements that are grouped together based on their chemical properties and reactivity ...
Discover Chemical Changes - gk-12
... with before and after chemical changes so that students can make the chemical changes happen themselves or at least make observations of chemical changes that have happened at each station. I have listed above 9 possible chemical changes that can be used. Students should move from station to station ...
... with before and after chemical changes so that students can make the chemical changes happen themselves or at least make observations of chemical changes that have happened at each station. I have listed above 9 possible chemical changes that can be used. Students should move from station to station ...
Properties of Matter PowerPoint
... between a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture. Based on the size of its largest particles, a mixture can be classified as a solution, a suspension, or a colloid. ...
... between a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture. Based on the size of its largest particles, a mixture can be classified as a solution, a suspension, or a colloid. ...
Chemical Reactions are…
... the quantity or amount of each element does not change. This means that each side of the equation must represent the same quantity of each element; in other words have the same number of each kind of atom ...
... the quantity or amount of each element does not change. This means that each side of the equation must represent the same quantity of each element; in other words have the same number of each kind of atom ...
Credit Recovery
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is an introduction to general biology. It will include the fundamental principles of living organisms including physical and chemical properties of life, cellular organization and function, the transfer of energy through metabolic systems, cellular reproduction, the c ...
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is an introduction to general biology. It will include the fundamental principles of living organisms including physical and chemical properties of life, cellular organization and function, the transfer of energy through metabolic systems, cellular reproduction, the c ...
Terminology 1
... Matter that has a definite or constant composition and distinct properties Matter that has a particular set of characteristics differs from the characteristics of another kind of matter ...
... Matter that has a definite or constant composition and distinct properties Matter that has a particular set of characteristics differs from the characteristics of another kind of matter ...
Balancing Chemical Equations Lab
... 1. Using your set of cards, replicate the chemical equation onto your desk. Record the following results into Table 1: 2. Identify the elements on the reactant side. 3. Count the number of atoms for each element. 4. Identify the elements on the product side. 5. Count the number of atoms on the produ ...
... 1. Using your set of cards, replicate the chemical equation onto your desk. Record the following results into Table 1: 2. Identify the elements on the reactant side. 3. Count the number of atoms for each element. 4. Identify the elements on the product side. 5. Count the number of atoms on the produ ...
Honors Chapter 2
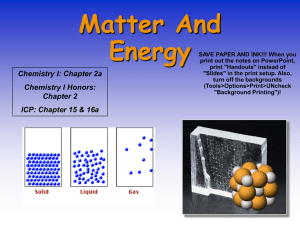
... Matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. Gases have no fixed shape or volume. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
... Matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. Gases have no fixed shape or volume. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
Safety data sheet
A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is an important component of product stewardship and occupational safety and health. It is intended to provide workers and emergency personnel with procedures for handling or working with that substance in a safe manner, and includes information such as physical data (melting point, boiling point, flash point, etc.), toxicity, health effects, first aid, reactivity, storage, disposal, protective equipment, and spill-handling procedures. SDS formats can vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements.SDSs are a widely used system for cataloging information on chemicals, chemical compounds, and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product. These data sheets can be found anywhere where chemicals are being used.There is also a duty to properly label substances on the basis of physico-chemical, health and/or environmental risk. Labels can include hazard symbols such as the European Union standard black diagonal cross on an orange background, used to denote a harmful substance.A SDS for a substance is not primarily intended for use by the general consumer, focusing instead on the hazards of working with the material in an occupational setting.In some jurisdictions, the SDS is required to state the chemical's risks, safety, and effect on the environment.It is important to use an SDS specific to both country and supplier, as the same product (e.g. paints sold under identical brand names by the same company) can have different formulations in different countries. The formulation and hazard of a product using a generic name (e.g. sugar soap) may vary between manufacturers in the same country.