![Amino Acids [PDF:247KB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002278939_1-1b03d0bc0e7fdaaa14234846bba6ef6c-300x300.png)
Amino Acids [PDF:247KB]
... crustaceans, and Meat): isoleucine, leucine, lysine, sulfur-containing amino acids (methionine, cystine), aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine), threonine, tryptophan, valine, and histidine as essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized in the body at all or sufficiently, and arginine, ...
... crustaceans, and Meat): isoleucine, leucine, lysine, sulfur-containing amino acids (methionine, cystine), aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine), threonine, tryptophan, valine, and histidine as essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized in the body at all or sufficiently, and arginine, ...
Glycolysis Lecture
... a. Electrostatic interactions occur between atoms have the same charge b. In water molecule, Oxygen is highly electrophilic. c. Water molecules are bound together through Ionic bonds. d. Buffers are made up of a mixture of a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate acid. e ...
... a. Electrostatic interactions occur between atoms have the same charge b. In water molecule, Oxygen is highly electrophilic. c. Water molecules are bound together through Ionic bonds. d. Buffers are made up of a mixture of a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate acid. e ...
Rhizobium
... These results agree with the previous results of Kato et al. (1997) where the seed exudates of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) had a higher potential for Rhizobium proliferation than root exudates. Also, Iizuka et al. (2002) reported that seed exudates of both cultivars Glycine max L. c.v. Enrei ...
... These results agree with the previous results of Kato et al. (1997) where the seed exudates of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) had a higher potential for Rhizobium proliferation than root exudates. Also, Iizuka et al. (2002) reported that seed exudates of both cultivars Glycine max L. c.v. Enrei ...
An Introduction to Enzyme Science
... reaction) is reasonably fast – as is the case for the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate anion or for the spontaneous hydrolysis of many lactones – an enzyme (in this case, carbonic anhydrase) is required to assure that the reaction’s pace is compatible with efficient metabol ...
... reaction) is reasonably fast – as is the case for the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate anion or for the spontaneous hydrolysis of many lactones – an enzyme (in this case, carbonic anhydrase) is required to assure that the reaction’s pace is compatible with efficient metabol ...
431 KB / 47 pages
... (a) We have seen (Investigate This 10.2) that electrolysis of a dilute aqueous solution of an ionic compound (magnesium sulfate) produces a gas at both electrodes and a basic solution at the cathode and acidic solution at the anode, just as the problem statement says is observed here for a dilute aq ...
... (a) We have seen (Investigate This 10.2) that electrolysis of a dilute aqueous solution of an ionic compound (magnesium sulfate) produces a gas at both electrodes and a basic solution at the cathode and acidic solution at the anode, just as the problem statement says is observed here for a dilute aq ...
Factors Controlling the Stable Nitrogen Isotopic Composition (δ15N
... vary substantially (-2 to + 2.1 ‰ [1]), but unlike the change in δ13C from lipid extraction (e.g. [16–18]), no clear relationship between Δδ15Nresidue-bulk and parameters such as lipid content or C:N ratio of the organisms has been found. The relatively large range in Δδ15Nresidue-bulk is problemati ...
... vary substantially (-2 to + 2.1 ‰ [1]), but unlike the change in δ13C from lipid extraction (e.g. [16–18]), no clear relationship between Δδ15Nresidue-bulk and parameters such as lipid content or C:N ratio of the organisms has been found. The relatively large range in Δδ15Nresidue-bulk is problemati ...
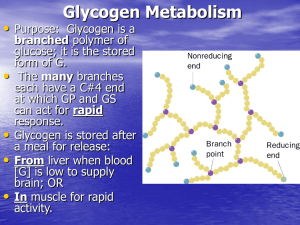
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... PEP pyr ACoA.) (These AAs are “ketogenic) So, these C’s of xs AA intake (in relation to need for protein synth) are used as fuel, just like dietary CH2O’s, fats. 2. Part (or all) of the C’s of 18 of the AAs can be converted to TCA intermediates, which can be converted to G (TCA int oxac PEP ...
... PEP pyr ACoA.) (These AAs are “ketogenic) So, these C’s of xs AA intake (in relation to need for protein synth) are used as fuel, just like dietary CH2O’s, fats. 2. Part (or all) of the C’s of 18 of the AAs can be converted to TCA intermediates, which can be converted to G (TCA int oxac PEP ...
Specific Activities of Enzymes of the Serine Pathway of Carbon
... lyase (Hersh & Bellion, 1972). The ratio of specific activities (methylamine-grown cells/ succinate-grown cells) was above 40 in each case. These enzymes can account for the net conversion of a reduced C1 unit and COz into acetyl-CoA via serine. The results also suggest that serine dehydratase is no ...
... lyase (Hersh & Bellion, 1972). The ratio of specific activities (methylamine-grown cells/ succinate-grown cells) was above 40 in each case. These enzymes can account for the net conversion of a reduced C1 unit and COz into acetyl-CoA via serine. The results also suggest that serine dehydratase is no ...
Lab 7 PPT - Dr Magrann
... into a Kreb machine, along with one of his Acetyl CoA molecules. • Three more NAD brothers, plus their cousin FAD have to come in to bear the burdens of the four H+ that will be generated. ...
... into a Kreb machine, along with one of his Acetyl CoA molecules. • Three more NAD brothers, plus their cousin FAD have to come in to bear the burdens of the four H+ that will be generated. ...
Biologically active octapeptides
... treating with a mild base, typically a tertiary amine such as triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine. The peptide resin is then ready for the coupling with the next amino acid which has a free carboxyl but which is protected at the alpha-amino group. Once the desired amino acid sequence is prepared, ...
... treating with a mild base, typically a tertiary amine such as triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine. The peptide resin is then ready for the coupling with the next amino acid which has a free carboxyl but which is protected at the alpha-amino group. Once the desired amino acid sequence is prepared, ...
4Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydr ...
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydr ...
Green Fluorescent Protein
... where the imidazolinone is formed by nucleophilic interaction between the amide of Gly67 and the carbonyl of residue Ser65, and the dehydration. Then, the molecular oxygen dehydrogenates the bonds of the aromatic group of residue 66 in conjunction with imidazolinone (Figure 3). At this stage the chr ...
... where the imidazolinone is formed by nucleophilic interaction between the amide of Gly67 and the carbonyl of residue Ser65, and the dehydration. Then, the molecular oxygen dehydrogenates the bonds of the aromatic group of residue 66 in conjunction with imidazolinone (Figure 3). At this stage the chr ...
Nitrogenous Wastes
... form a white paste or powder; it is excreted by birds, insects, and reptiles. Conversion of ammonia to uric acid requires more energy and is much more complex than conversion of ammonia to urea Figure 2. ...
... form a white paste or powder; it is excreted by birds, insects, and reptiles. Conversion of ammonia to uric acid requires more energy and is much more complex than conversion of ammonia to urea Figure 2. ...
respiration revision quiz
... Respiration is a series of ……………………….-‐catalyzed reactions that release ……………………. from ………………………. molecules in order to synthesize ……………………… . ………………………… respiration, which involves the participation of ...
... Respiration is a series of ……………………….-‐catalyzed reactions that release ……………………. from ………………………. molecules in order to synthesize ……………………… . ………………………… respiration, which involves the participation of ...
Creation/Evolution - Geoscience Research Institute
... representing a few amino acids or possibly one codon representing a “group” of amino acids More precise codon meaning evolves perhaps with only the first two bases having meaning with discrimination at the third position evolving later The code becomes “frozen” when the system becomes so complex tha ...
... representing a few amino acids or possibly one codon representing a “group” of amino acids More precise codon meaning evolves perhaps with only the first two bases having meaning with discrimination at the third position evolving later The code becomes “frozen” when the system becomes so complex tha ...
Authors` version - The Computable Plant
... for L-valine and L-isoleucine biosynthesis are catalyzed by a set of bi-functional enzymes that bind substrates from either pathway, L-valine inhibition of the first enzyme specific for its biosynthesis catalyzed by a single α-acetohydroxy acid synthase (AHAS) could compromise the cell for L-isoleuc ...
... for L-valine and L-isoleucine biosynthesis are catalyzed by a set of bi-functional enzymes that bind substrates from either pathway, L-valine inhibition of the first enzyme specific for its biosynthesis catalyzed by a single α-acetohydroxy acid synthase (AHAS) could compromise the cell for L-isoleuc ...
Rubidium
... This element is considered to be the 16th most abundant element in the earth's crust. It occurs naturally in the minerals leucite, pollucite, and zinnwaldite, which contains traces of up to 1% of its oxide. Lepidolite contains 1.5% rubidium and this is the commercial source of the element. Some pota ...
... This element is considered to be the 16th most abundant element in the earth's crust. It occurs naturally in the minerals leucite, pollucite, and zinnwaldite, which contains traces of up to 1% of its oxide. Lepidolite contains 1.5% rubidium and this is the commercial source of the element. Some pota ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.