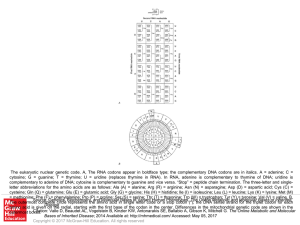
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... Ionic Bond - is a bond that results from the attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or molecules. Cation - is an ion that has a positive charge Anion - is an ion that has a negative charge. An ionic bond is form between two elements that have lost or gain electrons, creating charged particl ...
... Ionic Bond - is a bond that results from the attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or molecules. Cation - is an ion that has a positive charge Anion - is an ion that has a negative charge. An ionic bond is form between two elements that have lost or gain electrons, creating charged particl ...
chem notes unit 2 bk
... must collide with enough energy so that existing bonds will be broken and new bonds will be formed. If the reactants don’t have enough energy, they will be unchanged after the collision. Enzyme- substrate complex: Enzymes provide a site where reactants can be brought together to react. This site red ...
... must collide with enough energy so that existing bonds will be broken and new bonds will be formed. If the reactants don’t have enough energy, they will be unchanged after the collision. Enzyme- substrate complex: Enzymes provide a site where reactants can be brought together to react. This site red ...
Hein and Arena
... - Ex: palmitic acid, CH3(CH2)14COOH 2) Proteins (amino acids) - Source of reduced carbon atoms that can be catabolized to provide cellular energy. - Provide the major pool of usable nitrogen for cells. ...
... - Ex: palmitic acid, CH3(CH2)14COOH 2) Proteins (amino acids) - Source of reduced carbon atoms that can be catabolized to provide cellular energy. - Provide the major pool of usable nitrogen for cells. ...
BIOLOGY
... in the mitochondria. In this chain, electrons are transferred from one protein to another, RELEASING energy in the process. OXYGEN is the final electron acceptor in this process. Oxygen reacts with hydrogen and electrons to form water (H2O). Oxygen is important in the body since without it the prote ...
... in the mitochondria. In this chain, electrons are transferred from one protein to another, RELEASING energy in the process. OXYGEN is the final electron acceptor in this process. Oxygen reacts with hydrogen and electrons to form water (H2O). Oxygen is important in the body since without it the prote ...
Biochemistry Review Game
... • Each of the following slides will list a characteristic of one (or more) of the biomolecules. • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
... • Each of the following slides will list a characteristic of one (or more) of the biomolecules. • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
File
... The compound always burns in oxygen gas and always releases carbon dioxide and water. During incomplete combustion (a limited amt. of O2), carbon monoxide (CO) is also produced. Example: 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
... The compound always burns in oxygen gas and always releases carbon dioxide and water. During incomplete combustion (a limited amt. of O2), carbon monoxide (CO) is also produced. Example: 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
Preview Sample 2
... 2. Emphasize that the term "molecule" can mean: (1) the limit of physical subdivision of a molecular compound; (2) the smallest piece of a molecular compound; or (3) the basic building block of which a molecular compound is made. Do not try to differentiate at this time the differences between ionic ...
... 2. Emphasize that the term "molecule" can mean: (1) the limit of physical subdivision of a molecular compound; (2) the smallest piece of a molecular compound; or (3) the basic building block of which a molecular compound is made. Do not try to differentiate at this time the differences between ionic ...
CHAPTER 6 The Chemistry of Life
... 3. Other elements like iron are present in living things, but only in a very small amount a. these are referred to as trace elements E. How are elements identified? 1. By letter symbols on the periodic table Na=sodium, H=hydrogen 2. the periodic table contains the atomic number & the atomic mass a. ...
... 3. Other elements like iron are present in living things, but only in a very small amount a. these are referred to as trace elements E. How are elements identified? 1. By letter symbols on the periodic table Na=sodium, H=hydrogen 2. the periodic table contains the atomic number & the atomic mass a. ...
File - Garbally Chemistry
... Stable-does not react with the gases in the air and has good solubility. High relative molecular mass of Ammonium Iron (II) Sulphate(392) ensures a high degree of accuracy when weighing. When dissolving in water, sulphuric acid must be added to prevent it from reacting with the water (HYDROLYSIS) an ...
... Stable-does not react with the gases in the air and has good solubility. High relative molecular mass of Ammonium Iron (II) Sulphate(392) ensures a high degree of accuracy when weighing. When dissolving in water, sulphuric acid must be added to prevent it from reacting with the water (HYDROLYSIS) an ...
AP CHEMISTRY. We`re Bonding! page 1 of 4 1. A central atom
... 25. Explains why Xenon has a higher boiling point than Neon 26. Explains why alcohols, such as C2H5OH are liquids, while similarly sized hydrocarbons are gases at room temperature. 27. The bonding between the carbon atoms in C2H4 28. The bonding between the carbon and the oxygen in carbon dioxide. 2 ...
... 25. Explains why Xenon has a higher boiling point than Neon 26. Explains why alcohols, such as C2H5OH are liquids, while similarly sized hydrocarbons are gases at room temperature. 27. The bonding between the carbon atoms in C2H4 28. The bonding between the carbon and the oxygen in carbon dioxide. 2 ...
Slide ()
... cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to adenine of DNA; cytosine is complementary to guanine and vice versa. “Stop” = peptide chain termination. The three-letter and singleletter abbrev ...
... cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to adenine of DNA; cytosine is complementary to guanine and vice versa. “Stop” = peptide chain termination. The three-letter and singleletter abbrev ...
No Slide Title
... Protein Folding Protein folding is a “grand challenge” problem in biology the deciphering of the second half of the genetic code, of pressing practical significance Problem 1: given a protein’s amino acid sequence, predict its 3D structure, which is related to its function Problem 2: “… use the pro ...
... Protein Folding Protein folding is a “grand challenge” problem in biology the deciphering of the second half of the genetic code, of pressing practical significance Problem 1: given a protein’s amino acid sequence, predict its 3D structure, which is related to its function Problem 2: “… use the pro ...
Biol 178 Lecture 13
... Why is ATP not used as a long-term energy storage molecule? Too unstable - cells continually produce ATP for immediate use. ...
... Why is ATP not used as a long-term energy storage molecule? Too unstable - cells continually produce ATP for immediate use. ...
Handout
... distant portions of the molecule (see image – next slide) Quaternary Structure – shape due to interactions between different polypeptides making up a larger protein ...
... distant portions of the molecule (see image – next slide) Quaternary Structure – shape due to interactions between different polypeptides making up a larger protein ...
The Chemical Context of Life Chapter 2 Notes
... The different states of potential energy that electrons have in an atom are called energy levels or electron shells. - the first shell has the lowest energy. The second shell has more than the first, etc. Valence electrons: those in the outermost shell ...
... The different states of potential energy that electrons have in an atom are called energy levels or electron shells. - the first shell has the lowest energy. The second shell has more than the first, etc. Valence electrons: those in the outermost shell ...
Teacher practical Make your own protein Specification references
... A mutation is a change in the base sequence of DNA. a The mutation can change an amino acid in the protein chain. This can affect the bending and folding of the protein, changing its shape. b The function of the protein depends on its shape, for example, the active site shape in an enzyme. If you ch ...
... A mutation is a change in the base sequence of DNA. a The mutation can change an amino acid in the protein chain. This can affect the bending and folding of the protein, changing its shape. b The function of the protein depends on its shape, for example, the active site shape in an enzyme. If you ch ...
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
... The main uses of zinc are preventing steel from rusting and making alloys. (a) The main ore of zinc is zinc blende. Zinc blende consists mainly of zinc sulfide, ZnS. There are two major methods of extracting zinc from its ore. They are the direct reduction of zinc oxide to zinc and by electrolysis. ...
... The main uses of zinc are preventing steel from rusting and making alloys. (a) The main ore of zinc is zinc blende. Zinc blende consists mainly of zinc sulfide, ZnS. There are two major methods of extracting zinc from its ore. They are the direct reduction of zinc oxide to zinc and by electrolysis. ...
Complex Ion Equilibria - South Kingstown High School
... According to Le Chatelier’s principle, as C2O42ion is removed by the reaction with H3O+, more calcium oxalate dissolves. Therefore, you expect calcium oxalate to be more soluble in acidic solution (low pH) than in pure water. ...
... According to Le Chatelier’s principle, as C2O42ion is removed by the reaction with H3O+, more calcium oxalate dissolves. Therefore, you expect calcium oxalate to be more soluble in acidic solution (low pH) than in pure water. ...
Practice Exam II
... 13. What is the approximate percent efficiency of conversion of food energy to ATP energy in the body? a. 20 b. 50 c. 80 d. 99 14. What of the following lipoproteins is formed in the liver and is used to transport endogenous (made in the body) triglycerides to body cells? a. Chylomicrons b. VLDL c. ...
... 13. What is the approximate percent efficiency of conversion of food energy to ATP energy in the body? a. 20 b. 50 c. 80 d. 99 14. What of the following lipoproteins is formed in the liver and is used to transport endogenous (made in the body) triglycerides to body cells? a. Chylomicrons b. VLDL c. ...
Balance this equation:
... The diagram shows iron oxide, Fe2O3, and carbon monoxide, CO reacting to form iron and carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the correct full balanced chemical equation for the reaction depicted? ...
... The diagram shows iron oxide, Fe2O3, and carbon monoxide, CO reacting to form iron and carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the correct full balanced chemical equation for the reaction depicted? ...
Introduction
... The hydrogen-bond networks created among water molecules change constantly on a subpicosecond time scale At any moment the H-bonds look like those in crystalline ice Solutes disrupt the H-bond networks ...
... The hydrogen-bond networks created among water molecules change constantly on a subpicosecond time scale At any moment the H-bonds look like those in crystalline ice Solutes disrupt the H-bond networks ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.