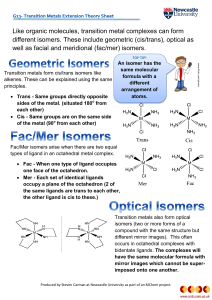
Like organic molecules, transition metal complexes can form
... Transition metals also form optical isomers (two or more forms of a compound with the same structure but different mirror images). This often occurs in octahedral complexes with bidentate ligands. The complexes will have the same molecular formula with mirror images which cannot be superimposed onto ...
... Transition metals also form optical isomers (two or more forms of a compound with the same structure but different mirror images). This often occurs in octahedral complexes with bidentate ligands. The complexes will have the same molecular formula with mirror images which cannot be superimposed onto ...
2 H
... • Aerobic respiration uses O2 • Anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic compound other than O2 (Ex. NO3-) ...
... • Aerobic respiration uses O2 • Anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic compound other than O2 (Ex. NO3-) ...
Week 7 - Acid-base, redox
... remember that oxidation results in an increase in oxidation number (or charge) across a reaction arrow, while reduction results in a decrease. Redox reactions are commercially important. Batteries, fuels, metals, and corrosion are redox reactions. Living systems are based on redox reactions. This se ...
... remember that oxidation results in an increase in oxidation number (or charge) across a reaction arrow, while reduction results in a decrease. Redox reactions are commercially important. Batteries, fuels, metals, and corrosion are redox reactions. Living systems are based on redox reactions. This se ...
proteins aminacids notesKelly
... Abnormal hemoglobin molecules crystallize; cause blood cells to become sickle shaped FACTORS AFFECTING CONFORMATION Folding occurs as protein is synthesized, but physical/chemical environment plays a role DENATURATION: = unraveling/ loss of native confirmation • makes proteins biologically inactive ...
... Abnormal hemoglobin molecules crystallize; cause blood cells to become sickle shaped FACTORS AFFECTING CONFORMATION Folding occurs as protein is synthesized, but physical/chemical environment plays a role DENATURATION: = unraveling/ loss of native confirmation • makes proteins biologically inactive ...
Slide 1
... In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as follows for O2 with glu ...
... In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as follows for O2 with glu ...
Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid
... The aldehyde forms a Schiff–base with an ε– amino group on the enzyme. This Schiff-bases can be exchanged for one with the α–amino group of an amino acid ...
... The aldehyde forms a Schiff–base with an ε– amino group on the enzyme. This Schiff-bases can be exchanged for one with the α–amino group of an amino acid ...
Representation of and Reasoning with signal networks
... • protein recruiting another protein – a process whereby certain molecules are attracted (recruited) by another molecule to a particular site within the cell, often to form a complex which is a component of a pathway. For example the T-cell receptor (TCR) is a membrane associated receptor with extra ...
... • protein recruiting another protein – a process whereby certain molecules are attracted (recruited) by another molecule to a particular site within the cell, often to form a complex which is a component of a pathway. For example the T-cell receptor (TCR) is a membrane associated receptor with extra ...
Organic Chemistry #2 Vocabulary Adhesion Cohesion Atom
... ______The graph shows that pepsin functions best in a low-pH (acidic) environment suggesting that the somach has a pH between 2 and 3. Trypsin functions best at ta pH of about 6 or 7 suggesting that the pH of the small intestine is about neutral Part B: The contents of the stomach are released into ...
... ______The graph shows that pepsin functions best in a low-pH (acidic) environment suggesting that the somach has a pH between 2 and 3. Trypsin functions best at ta pH of about 6 or 7 suggesting that the pH of the small intestine is about neutral Part B: The contents of the stomach are released into ...
Thursday, March 27, 2008
... The compound CO2(s) sublimes readily at 25°C. Which properties are usually associated with a compound that undergoes this kind of change? 1. high vapor pressure and high intermolecular ...
... The compound CO2(s) sublimes readily at 25°C. Which properties are usually associated with a compound that undergoes this kind of change? 1. high vapor pressure and high intermolecular ...
Three-Dimensional Structure of Adenosylcobinamide Kinase
... (11, 10). Interestingly, the kinase activity can utilize either ATP or GTP, whereas the transferase clearly shows a preference for GTP. During de noVo synthesis of the corrin ring it has been proposed that only the guanylyltransferase activity of CobU is needed for assembly of the nucleotide loop (1 ...
... (11, 10). Interestingly, the kinase activity can utilize either ATP or GTP, whereas the transferase clearly shows a preference for GTP. During de noVo synthesis of the corrin ring it has been proposed that only the guanylyltransferase activity of CobU is needed for assembly of the nucleotide loop (1 ...
makeup2
... 58. A solution of a non-electrolyte, x, contains 84 grams of x per kilogram of water and freezes at -1.46°C. What is the molecular weight of x? (Kf = 1.86) (A) 84 x 1.86 x 1.46 = 222 g/mol (B) 84 x (1.86 / 1.46) = 107 g/mol (C) 84 x (1.46 / 1.86) = 66 g/mol (D) 1.46 x (1.86 / 84) = 0.032 g/mol 59. ...
... 58. A solution of a non-electrolyte, x, contains 84 grams of x per kilogram of water and freezes at -1.46°C. What is the molecular weight of x? (Kf = 1.86) (A) 84 x 1.86 x 1.46 = 222 g/mol (B) 84 x (1.86 / 1.46) = 107 g/mol (C) 84 x (1.46 / 1.86) = 66 g/mol (D) 1.46 x (1.86 / 84) = 0.032 g/mol 59. ...
Chemistry of Life edit
... a. ionic bond = strong bond when one atom gives up an electron to another, forming two ions of opposite charge, holding the atoms together (think of a magnet) ...
... a. ionic bond = strong bond when one atom gives up an electron to another, forming two ions of opposite charge, holding the atoms together (think of a magnet) ...
THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... each atom is a. 11. b. 12. c. 23. d. 24. 2. The atom of an element has one proton and two neutrons. Its atomic number is a. 1. b. 2. c. 3. d. 6. 3. The atom of an element has six protons and eight neutrons. The number of electrons in this atom if neutral is a. 6. b. 8. c. 12. d. 14. 4. The relations ...
... each atom is a. 11. b. 12. c. 23. d. 24. 2. The atom of an element has one proton and two neutrons. Its atomic number is a. 1. b. 2. c. 3. d. 6. 3. The atom of an element has six protons and eight neutrons. The number of electrons in this atom if neutral is a. 6. b. 8. c. 12. d. 14. 4. The relations ...
Chapter 4 - Colby College Wiki
... concentration. If it takes 17.8 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition of one solution to another until one component ...
... concentration. If it takes 17.8 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition of one solution to another until one component ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... 3The hybridization of orbitals in the geometrical shape of an octahedron is: a- sp2 b- sp3 c- sp3 d1 d- sp3 d2 4The angle values of an octahedron are: a- 180º + 30º b- 180º + 60º c- 180º + 90º ...
... 3The hybridization of orbitals in the geometrical shape of an octahedron is: a- sp2 b- sp3 c- sp3 d1 d- sp3 d2 4The angle values of an octahedron are: a- 180º + 30º b- 180º + 60º c- 180º + 90º ...
Protein Nucleic Acids - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... • The most likely result of mixing both enzymes with their substrates in a single test tube is that: • A- only gastric protease would be active if the pH of the mixture was basic • B- gastric protease would be more active than intestinal protease at pH 6 • C-both enzymes would exhibit some activity ...
... • The most likely result of mixing both enzymes with their substrates in a single test tube is that: • A- only gastric protease would be active if the pH of the mixture was basic • B- gastric protease would be more active than intestinal protease at pH 6 • C-both enzymes would exhibit some activity ...
There are three parts in this exam (50% +20% +30%)
... 17. Which class of bond directly participates in the interaction of codons to anticodons between mRNAs and tRNAs? (A) Hydroxy bonds. (B) Ionic bonds. (C) Peptide bonds. (D) Covalent bonds. (E) Hydrogen bonds. 18. Isoelectric point is a point at which? (A) The net charge of protein is the highest; (B ...
... 17. Which class of bond directly participates in the interaction of codons to anticodons between mRNAs and tRNAs? (A) Hydroxy bonds. (B) Ionic bonds. (C) Peptide bonds. (D) Covalent bonds. (E) Hydrogen bonds. 18. Isoelectric point is a point at which? (A) The net charge of protein is the highest; (B ...
3.10 Neutralization
... ZnS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2S(g) ZnS(s) + 2H+ + 2Cl- → Zn2+ + 2Cl- + H2S(g) ⇒ZnS(s) + 2H+ → Zn2+ + H2S(g) – H+ is present in the form of H3O+ ...
... ZnS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2S(g) ZnS(s) + 2H+ + 2Cl- → Zn2+ + 2Cl- + H2S(g) ⇒ZnS(s) + 2H+ → Zn2+ + H2S(g) – H+ is present in the form of H3O+ ...
Exam 3 Stats
... Functions of Proteins: Examples Proteins have many diverse functions; they are the most functionally diverse type of macromolecules 1. Structural support (e.g. silk of spider webs) 2. Storage of energy & nitrogen (e.g. egg albumin) 3. Transport of substances within organisms (e.g. hemoglobin) or ac ...
... Functions of Proteins: Examples Proteins have many diverse functions; they are the most functionally diverse type of macromolecules 1. Structural support (e.g. silk of spider webs) 2. Storage of energy & nitrogen (e.g. egg albumin) 3. Transport of substances within organisms (e.g. hemoglobin) or ac ...
Proteins
... • Quaternary structure – Interaction between two or more polypeptide chains linked together to form one large protein. – Example: hemoglobin is a globular protein with quaternary structure composed of four chains – Single amino acid substitution causes sickle cell anemia ...
... • Quaternary structure – Interaction between two or more polypeptide chains linked together to form one large protein. – Example: hemoglobin is a globular protein with quaternary structure composed of four chains – Single amino acid substitution causes sickle cell anemia ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.