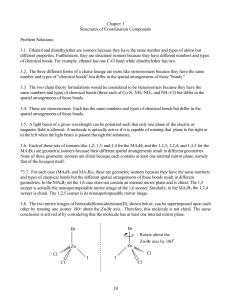
Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA gyrase ATPase domain structures
... [7,8] and ATPase activity [9,10]. The structure of the ATPase domain of the GyrB subunit of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase [7] showed that it contained two structural domains, an N-terminal GHKL domain [11] and a Cterminal transducer domain (Figure 1). A change in the relative positions of the GHKL and ...
... [7,8] and ATPase activity [9,10]. The structure of the ATPase domain of the GyrB subunit of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase [7] showed that it contained two structural domains, an N-terminal GHKL domain [11] and a Cterminal transducer domain (Figure 1). A change in the relative positions of the GHKL and ...
as a PDF
... where * refers to the reference experiment and all concentrations refer to dissolved Cd concentrations that can be measured directly (see Fig. 2). Note that this approach is only accurate if the ligand concentration exceeds the total Cd concentration by at least a factor of 5. This assumption is con ...
... where * refers to the reference experiment and all concentrations refer to dissolved Cd concentrations that can be measured directly (see Fig. 2). Note that this approach is only accurate if the ligand concentration exceeds the total Cd concentration by at least a factor of 5. This assumption is con ...
Design and Synthesis of RGD Mimetics as Potent Inhibitors of
... function of bioactive peptides. Known as peptidomimetics, these compounds have many advantages over their parent peptides.4 Peptides are characterized by their rapid digestion by proteolytic enzymes, low absorption through intestinal walls, and potential immunogenic reactions. 5 The proper design of ...
... function of bioactive peptides. Known as peptidomimetics, these compounds have many advantages over their parent peptides.4 Peptides are characterized by their rapid digestion by proteolytic enzymes, low absorption through intestinal walls, and potential immunogenic reactions. 5 The proper design of ...
carbon-11-labeled acetate
... ABSTRACT Although positron-emission tomography (PET) with labeled fatty acid delineates infarct size and permits qualitative assessment of fatty acid utilization, quantification of oxidative metabolism is limited by complex alterations in the pattern of utilization of fatty acid during ischemia and ...
... ABSTRACT Although positron-emission tomography (PET) with labeled fatty acid delineates infarct size and permits qualitative assessment of fatty acid utilization, quantification of oxidative metabolism is limited by complex alterations in the pattern of utilization of fatty acid during ischemia and ...
09_Lectures_PPT
... • Cellular respiration consumes oxygen and organic molecules and yields ATP • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, ...
... • Cellular respiration consumes oxygen and organic molecules and yields ATP • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, ...
mechanistic investigations of transition metal catalyzed reactions
... 7. References.................................................................................................................................. 92 ...
... 7. References.................................................................................................................................. 92 ...
The proofreading mechanism of isoleucyl
... Based on his results on isoleucyl‐tRNA synthetase’s rejection of valine Fersht proposed in 1978 a double‐sieve proofreading model for aminoacyl‐tRNA synthetases (Fersht and Dingwall, 1979d). According to this, substrates that are similar to the cognate one, and smaller, b ...
... Based on his results on isoleucyl‐tRNA synthetase’s rejection of valine Fersht proposed in 1978 a double‐sieve proofreading model for aminoacyl‐tRNA synthetases (Fersht and Dingwall, 1979d). According to this, substrates that are similar to the cognate one, and smaller, b ...
N-terminal portion acts as an initiator of the inactivation of pepsin at
... functionality, e.g. substrate specificities, do exist; thus the aspartic proteinases are ideal models to demonstrate structure– function relationships of enzymes. All proteins are synthesized in a neutral pH environment, thus their natural conformational state and functionality exists in this enviro ...
... functionality, e.g. substrate specificities, do exist; thus the aspartic proteinases are ideal models to demonstrate structure– function relationships of enzymes. All proteins are synthesized in a neutral pH environment, thus their natural conformational state and functionality exists in this enviro ...
A novel assay method for an amino acid racemase reaction based
... The new assay method established in the present study for the measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay met ...
... The new assay method established in the present study for the measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay met ...
L-Serine, D- and L-proline and alanine as respiratory substrates of
... 1995). These results suggested that glucose is not a preferred energy substrate of H. pylori. Candidates for the substrates of energy metabolism in this organism are thought to be organic acids such as pyruvate, D-lactate and succinate. Chang et al. (1995) reported that lower concentrations (25 mM) ...
... 1995). These results suggested that glucose is not a preferred energy substrate of H. pylori. Candidates for the substrates of energy metabolism in this organism are thought to be organic acids such as pyruvate, D-lactate and succinate. Chang et al. (1995) reported that lower concentrations (25 mM) ...
Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation alterations in heart failure
... O2 consumed is greater with when glucose is oxidized compared to fatty acids, fatty acids are a less efficient energy substrate than glucose. Six O2 are consumed and 31 ATP are produced from the full oxidation of one glucose molecule. Oxidation of one palmitate consumes 23 O2 while only producing 10 ...
... O2 consumed is greater with when glucose is oxidized compared to fatty acids, fatty acids are a less efficient energy substrate than glucose. Six O2 are consumed and 31 ATP are produced from the full oxidation of one glucose molecule. Oxidation of one palmitate consumes 23 O2 while only producing 10 ...
Studies on a Mutant Strain of Escherichia coli which
... of each determined. Ammonia, which interferes with this determination, was removed by the addition of borate buffer in methanol to each sample for assay, which was then dried over P200(Connell, Dixon & Hanes, 1955). Cell hydrolysates labelled with 8% and containing 1OOpg. amino-N, and the 1°C-labell ...
... of each determined. Ammonia, which interferes with this determination, was removed by the addition of borate buffer in methanol to each sample for assay, which was then dried over P200(Connell, Dixon & Hanes, 1955). Cell hydrolysates labelled with 8% and containing 1OOpg. amino-N, and the 1°C-labell ...
Chapter 5
... the normal substrate site, the other is an inhibitory site such that binding of ATP lowers the enzyme’s affinity for F6P. ATP is not the only regulator of PFK activity: AMP is also a positive regulator of PFK, and can increase it up to 5-fold. 4. There are two classes of aldolases: class I are found ...
... the normal substrate site, the other is an inhibitory site such that binding of ATP lowers the enzyme’s affinity for F6P. ATP is not the only regulator of PFK activity: AMP is also a positive regulator of PFK, and can increase it up to 5-fold. 4. There are two classes of aldolases: class I are found ...
Structural and Functional Studies on Proteinaceous Metallocarboxypeptidase Inhibitors Joan López Arolas
... cysteine enzymes and the aspartic protease cathepsin D via different domains (Lenarcic & Turk, 1999). For a few inhibitors, functions other than protease blockage have also been found such as growth factor activities, receptor clearance signaling or involvement in carcinogenesis (Clawson, 1996). The ...
... cysteine enzymes and the aspartic protease cathepsin D via different domains (Lenarcic & Turk, 1999). For a few inhibitors, functions other than protease blockage have also been found such as growth factor activities, receptor clearance signaling or involvement in carcinogenesis (Clawson, 1996). The ...
Structure and Antioxidant Catalytic Function of Plant Glutathione Trans
... antioxidant catalytic function of GSTs [9] is displayed through peroxidase (GPxs) [24], thioltransferase and dehydroascorbate reductase activity [21,25,26] (Fig. 2). Proteins able to participate in unrelated biological processes have been grouped under the generic name of moonlighting proteins [27,2 ...
... antioxidant catalytic function of GSTs [9] is displayed through peroxidase (GPxs) [24], thioltransferase and dehydroascorbate reductase activity [21,25,26] (Fig. 2). Proteins able to participate in unrelated biological processes have been grouped under the generic name of moonlighting proteins [27,2 ...
Solution Blowing of Soy Protein Fibers
... control, soy protein isolate was also subjected to the same treatment and it was found that it was never fully destroyed and left residual quite comparable in volume to the original soy protein. Therefore, it was established that after such treatment the PAN-based core−shell samples will not be holl ...
... control, soy protein isolate was also subjected to the same treatment and it was found that it was never fully destroyed and left residual quite comparable in volume to the original soy protein. Therefore, it was established that after such treatment the PAN-based core−shell samples will not be holl ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... Nutrient assimilation Assimilating N and S is very expensive! • Reducing NO3- to NH4+ costs 8 e- (1 NADPH + 6 Fd) • Assimilating NH4+ into amino acids also costs ATP + e• Nitrogen fixation costs 16 ATP + 8 e• SO42- reduction to S2- costs 8 e- + 2ATP • S2- assimilation into Cysteine costs 2 more e• ...
... Nutrient assimilation Assimilating N and S is very expensive! • Reducing NO3- to NH4+ costs 8 e- (1 NADPH + 6 Fd) • Assimilating NH4+ into amino acids also costs ATP + e• Nitrogen fixation costs 16 ATP + 8 e• SO42- reduction to S2- costs 8 e- + 2ATP • S2- assimilation into Cysteine costs 2 more e• ...
Fritz Lipmann - Nobel Lecture
... observation immediately suggested a rather sweeping biochemical significance, of transformations of electron transfer potential, respiratory or fermentative, to phosphate bond energy and therefrom to a wide range of biosynthetic reactions7. There was a further unusual feature in this pyruvate oxidat ...
... observation immediately suggested a rather sweeping biochemical significance, of transformations of electron transfer potential, respiratory or fermentative, to phosphate bond energy and therefrom to a wide range of biosynthetic reactions7. There was a further unusual feature in this pyruvate oxidat ...
Vitamins
... foods that contain fat. The body stores the fat soluble vitamins and because of this, people don’t usually need to make a special effort to include them in their diet. ...
... foods that contain fat. The body stores the fat soluble vitamins and because of this, people don’t usually need to make a special effort to include them in their diet. ...
Recombinant Brassinosteroid Insensitive 1 Receptor-Like
... phosphorylated peptides is increased relative to unphosphorylated peptides (Asara and Allison, 1999). Moreover, when the amino acid sequence of the protein is known, the mass of each potential tryptic peptide can be calculated and the phosphorylation state of a specific peptide can then be assigned ...
... phosphorylated peptides is increased relative to unphosphorylated peptides (Asara and Allison, 1999). Moreover, when the amino acid sequence of the protein is known, the mass of each potential tryptic peptide can be calculated and the phosphorylation state of a specific peptide can then be assigned ...
Case Study: BPTI
... formed by the internal packing of non-polar amino acid side chains. BPTI is no exception and due to its rather small overall size it also has a relatively small hydrophobic core. Thus, extra stability to support its three dimensional structure is provided by the three internal disulfide bonds that w ...
... formed by the internal packing of non-polar amino acid side chains. BPTI is no exception and due to its rather small overall size it also has a relatively small hydrophobic core. Thus, extra stability to support its three dimensional structure is provided by the three internal disulfide bonds that w ...
Enzymes at work
... Hydrolases catalyze hydrolysis, the cleavage of substrates by water. The reactions include the cleavage of peptide bonds in proteins by proteases, glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates by a variety of carbohydrases, and ester bonds in lipids by lipases. In general, larger molecules are broken down to sm ...
... Hydrolases catalyze hydrolysis, the cleavage of substrates by water. The reactions include the cleavage of peptide bonds in proteins by proteases, glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates by a variety of carbohydrases, and ester bonds in lipids by lipases. In general, larger molecules are broken down to sm ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.