AP BIOLOGY Ch. 2 Objectives “Chemistry”
... 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain what determines protein conformation and why it is impo ...
... 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain what determines protein conformation and why it is impo ...
1C - Edexcel
... (b) Compound X is made from ethene and is used in cars to prevent the engine coolant from freezing in cold weather. (i) Compound X contains 38.7% carbon, 9.7% hydrogen and 51.6% oxygen by mass. Calculate the empirical formula of X. ...
... (b) Compound X is made from ethene and is used in cars to prevent the engine coolant from freezing in cold weather. (i) Compound X contains 38.7% carbon, 9.7% hydrogen and 51.6% oxygen by mass. Calculate the empirical formula of X. ...
Dynamics of Plasmodium falciparum enoyl‐ACP reductase and
... sugars, into fatty acids that are subsequently esterified with glycerol to form lipids. There are two types of FAS pathways in nature.1 Humans, vertebrates, and some bacteria utilize type I FAS. In this associated pathway, all reactions are catalyzed by different domains of a single, multifunctional ...
... sugars, into fatty acids that are subsequently esterified with glycerol to form lipids. There are two types of FAS pathways in nature.1 Humans, vertebrates, and some bacteria utilize type I FAS. In this associated pathway, all reactions are catalyzed by different domains of a single, multifunctional ...
Respiration Respiration Respiration
... The goal of respiration is to produce ATP. -energy is released from oxidation reaction in the form of electrons -electrons are shuttled by electron carriers (e.g. NAD+) to an electron transport chain -electron energy is converted to ATP at the electron transport chain ...
... The goal of respiration is to produce ATP. -energy is released from oxidation reaction in the form of electrons -electrons are shuttled by electron carriers (e.g. NAD+) to an electron transport chain -electron energy is converted to ATP at the electron transport chain ...
Applied NanoWorks Announces New Water Soluble Titanate
... based molecule has only two alkoxy ligands, as opposed to four ligands common in traditional titanates. This feature facilitates water solubility, improves shrinkage, flexibility and the ability to engineer functional derivatives of the titanyl. This level of flexibility makes the titanyl molecule i ...
... based molecule has only two alkoxy ligands, as opposed to four ligands common in traditional titanates. This feature facilitates water solubility, improves shrinkage, flexibility and the ability to engineer functional derivatives of the titanyl. This level of flexibility makes the titanyl molecule i ...
How Cells Harvest Energy
... DG = -686kcal/mol of glucose DG can be even higher than this in a cell This large amount of energy must be released in small steps rather than all at once. ...
... DG = -686kcal/mol of glucose DG can be even higher than this in a cell This large amount of energy must be released in small steps rather than all at once. ...
BIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF LIFE
... II. Inorganic Do not contain the element, carbon, in a HC chain The transfer of electrons forms an ionic bond. Inorganic compounds form ionic bonds. Classes of inorganic compounds: ...
... II. Inorganic Do not contain the element, carbon, in a HC chain The transfer of electrons forms an ionic bond. Inorganic compounds form ionic bonds. Classes of inorganic compounds: ...
Chapter 25 LIPID METABOLISM
... B12 containing Direct conversion would involve an extremely unstable carbanion at C3 ...
... B12 containing Direct conversion would involve an extremely unstable carbanion at C3 ...
Characterizing the complexity of enzymes on the basis of their
... active site. Cofactors, both metal ions and small organic molecules, offer an extension of the catalytic power of enzymes. Recently, we have extended the MACiE database to include Metal-MACiE [7,31], in order to fully categorize and annotate the metal ions in MACiE, and their roles and functions. We ...
... active site. Cofactors, both metal ions and small organic molecules, offer an extension of the catalytic power of enzymes. Recently, we have extended the MACiE database to include Metal-MACiE [7,31], in order to fully categorize and annotate the metal ions in MACiE, and their roles and functions. We ...
Protein_hierarchy
... bonds which are formed by ........................... reactions. The linking bonds are formed between the ................ and ................. groups of the amino acids when ........................ is released from the reaction. The polypeptide chains may be folded into secondary structures, such ...
... bonds which are formed by ........................... reactions. The linking bonds are formed between the ................ and ................. groups of the amino acids when ........................ is released from the reaction. The polypeptide chains may be folded into secondary structures, such ...
Table S1.
... The enzymatic activity of all proteins was compared to the activity of wtSOD1 and a commercial recombinant SOD1 protein (hucSOD1). Of the mutant SOD1 purified, three have mutations located away from the metal binding/catalytic region, thus having properties similar to wtSOD1. These mutants are denot ...
... The enzymatic activity of all proteins was compared to the activity of wtSOD1 and a commercial recombinant SOD1 protein (hucSOD1). Of the mutant SOD1 purified, three have mutations located away from the metal binding/catalytic region, thus having properties similar to wtSOD1. These mutants are denot ...
Concept 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational
... to Speed up Biochemical Reactions • An exergonic reaction releases free energy (G), the amount of energy in a system that is available to do work. • Without a catalyst, the reaction will be very slow because there is an energy barrier between reactants and products. • An input of energy initiates th ...
... to Speed up Biochemical Reactions • An exergonic reaction releases free energy (G), the amount of energy in a system that is available to do work. • Without a catalyst, the reaction will be very slow because there is an energy barrier between reactants and products. • An input of energy initiates th ...
metabolism - anatomymodelimages
... 1. Vitamins – organic molecules; coenzyme or part; helps enzyme catalyze 2. Source – most we can’t make; bacteria K and pantothenic acid (B); vitamin D -a. Provitamin – like β carotene; used to make vitamin A (retinol) 3. Water soluble – C and B complex -a. Absorption – most with water in GI tract; ...
... 1. Vitamins – organic molecules; coenzyme or part; helps enzyme catalyze 2. Source – most we can’t make; bacteria K and pantothenic acid (B); vitamin D -a. Provitamin – like β carotene; used to make vitamin A (retinol) 3. Water soluble – C and B complex -a. Absorption – most with water in GI tract; ...
Effective Scoring Function for Protein Sequence Design
... Dunbrack is used in this study.22,24 Polar hydrogen atoms are added. 2 of Ser, Thr, and 3 of Tyr are assigned values of ⫺60°, 60°, and 180°. Three protonation states of His with the same expected frequencies are considered: N␦1 protonated, N⑀2 protonated, and both. 2 of Asn, His, and 3 of Gln ar ...
... Dunbrack is used in this study.22,24 Polar hydrogen atoms are added. 2 of Ser, Thr, and 3 of Tyr are assigned values of ⫺60°, 60°, and 180°. Three protonation states of His with the same expected frequencies are considered: N␦1 protonated, N⑀2 protonated, and both. 2 of Asn, His, and 3 of Gln ar ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 54. A sample of dolomitic limestone containing only CaCO3 and MgCO3 was analyzed. (a) When a 0.2800 gram sample of this limestone was decomposed by heating, 0.00308 moles of CO2 were evolved. How many grams of CO2 were produced? ...
... 54. A sample of dolomitic limestone containing only CaCO3 and MgCO3 was analyzed. (a) When a 0.2800 gram sample of this limestone was decomposed by heating, 0.00308 moles of CO2 were evolved. How many grams of CO2 were produced? ...
spectroscopic and antimicrobial studies of mixed ligand complexes
... availability of such structural information now allows a shift in the role of synthetic modeling from structural and spectroscopic endeavors to development of functional and catalytic models. Functional models can provide an opportunity to examine a biological reactivity at a small-molecule level of ...
... availability of such structural information now allows a shift in the role of synthetic modeling from structural and spectroscopic endeavors to development of functional and catalytic models. Functional models can provide an opportunity to examine a biological reactivity at a small-molecule level of ...
Various Career Options Available
... chemical compounds High-throughput screening can test 100,000 compounds a day for activity against a protein target Maybe tens of thousands of these compounds will show some activity for the protein The chemist needs to intelligently select the 2 - 3 classes of compounds that show the most promise f ...
... chemical compounds High-throughput screening can test 100,000 compounds a day for activity against a protein target Maybe tens of thousands of these compounds will show some activity for the protein The chemist needs to intelligently select the 2 - 3 classes of compounds that show the most promise f ...
Quiz 17
... 1. (a) (i) In both A and B, the living organisms take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide, while carbon dioxide is absorbed in the tube OR both use the intake of oxygen as the principle to measure the rate of respiration (1). In both A and B, the volume / pressure decrease / change is used to meas ...
... 1. (a) (i) In both A and B, the living organisms take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide, while carbon dioxide is absorbed in the tube OR both use the intake of oxygen as the principle to measure the rate of respiration (1). In both A and B, the volume / pressure decrease / change is used to meas ...
No Slide Title
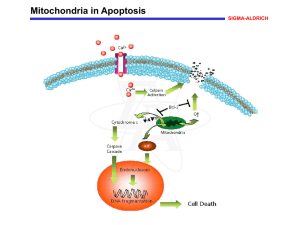
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
NAME_________________ 1 BIO 451 13th
... This question is presented in the form of a crossword puzzle. It is designed to test your familiarity with terms and concepts associated purine nucleotide metabolism. As with most crossword puzzles, following the clues is a parenthetical expression which indicates the number of letters/numbers requi ...
... This question is presented in the form of a crossword puzzle. It is designed to test your familiarity with terms and concepts associated purine nucleotide metabolism. As with most crossword puzzles, following the clues is a parenthetical expression which indicates the number of letters/numbers requi ...
Objective
... they give a yellow colored complex instead of a purple one. • Besides amino acids, other complex structures such as peptides, peptones and proteins also react positively when subjected to the ninhydrin ...
... they give a yellow colored complex instead of a purple one. • Besides amino acids, other complex structures such as peptides, peptones and proteins also react positively when subjected to the ninhydrin ...
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
... 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Atoms share pairs of electrons in covalent bonds. • A covalent bond forms when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. • A molecule is formed when atoms are bonded together by covalent bonds; it is not necessarily a compound..forms when atoms share one or more pai ...
... 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Atoms share pairs of electrons in covalent bonds. • A covalent bond forms when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. • A molecule is formed when atoms are bonded together by covalent bonds; it is not necessarily a compound..forms when atoms share one or more pai ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.