1 Organic Chemistry V : Enzyme Mechanisms and Natural Product
... How does an enzyme (or any catalyst) accelerate a chemical reaction? Our explanation is usually based on transition state theory, i.e. that the rate of a chemical reaction is determined by the energy difference between the ground state and the transition state of the reaction (Δ G#), in other words ...
... How does an enzyme (or any catalyst) accelerate a chemical reaction? Our explanation is usually based on transition state theory, i.e. that the rate of a chemical reaction is determined by the energy difference between the ground state and the transition state of the reaction (Δ G#), in other words ...
Control and Integration of Metabolism
... • Some enzymes possess properties that specifically endow them with regulatory roles in metabolism. Such more highly specialized forms are called Regulatory enzymes. Two types of regulatory enzymes: • (a) Allosteric enzymes: Whose catalytic activity is modulated through the non-covalent binding of a ...
... • Some enzymes possess properties that specifically endow them with regulatory roles in metabolism. Such more highly specialized forms are called Regulatory enzymes. Two types of regulatory enzymes: • (a) Allosteric enzymes: Whose catalytic activity is modulated through the non-covalent binding of a ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... the shortest bond, but big enough to run MetalionRNA calculations in a reasonable time. To avoid unnecessary calculations, the value of the potential in the target structure is calculated for cells of grid C around the previously defined RNA atom pairs only. For each RNA atom pair [a, b] (of which b ...
... the shortest bond, but big enough to run MetalionRNA calculations in a reasonable time. To avoid unnecessary calculations, the value of the potential in the target structure is calculated for cells of grid C around the previously defined RNA atom pairs only. For each RNA atom pair [a, b] (of which b ...
protein - Warren County Schools
... Pigment is produced in the petal cells of the plant as the result of a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell in which a colorless molecule is changed to a different molecule that now absorbs light and reflects red light without assistance. This reaction would ...
... Pigment is produced in the petal cells of the plant as the result of a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell in which a colorless molecule is changed to a different molecule that now absorbs light and reflects red light without assistance. This reaction would ...
Non-competitive inhibition
... and was mainly used to distinguish the whole microorganism, such as yeast (“organized ferments”), from that of extracts of the whole microorganisms (“unorganized ferments”). The implication was that enzymes were unorganized ferments in yeast. Although the vast majority of enzymes are proteins, certa ...
... and was mainly used to distinguish the whole microorganism, such as yeast (“organized ferments”), from that of extracts of the whole microorganisms (“unorganized ferments”). The implication was that enzymes were unorganized ferments in yeast. Although the vast majority of enzymes are proteins, certa ...
09_chapter 4
... shown. In a typical experiment, the powder catalyst sample (200 mg) was loaded into the catalytic reactor at room temperature and a flow of nitrogen (HP) at a rate of 40 ml min -1 was initiated. The catalyst zone furnace temperature was increased to initial reaction temperature of 650 °C over a time ...
... shown. In a typical experiment, the powder catalyst sample (200 mg) was loaded into the catalytic reactor at room temperature and a flow of nitrogen (HP) at a rate of 40 ml min -1 was initiated. The catalyst zone furnace temperature was increased to initial reaction temperature of 650 °C over a time ...
Empirical + Molecular Formula
... Q2.When boric acid (H3BO3) is applied as a coating on wood, it acts as a fire retardant by decreasing the rate of combustion. Thermal decomposition of boric acid takes place in two stages. In an experiment a sample of boric acid was heated in a crucible at 170 °C. The results of this experiment are ...
... Q2.When boric acid (H3BO3) is applied as a coating on wood, it acts as a fire retardant by decreasing the rate of combustion. Thermal decomposition of boric acid takes place in two stages. In an experiment a sample of boric acid was heated in a crucible at 170 °C. The results of this experiment are ...
Chapter 25: Metabolism
... – Because lipids, amino acids, and carbohydrates can be converted to acetyl-CoA ...
... – Because lipids, amino acids, and carbohydrates can be converted to acetyl-CoA ...
Lecture 2 - City University of New York
... D: H2O > F > RCO2 > OH > Cl > Br > I (also proton basicity) accepting ligands increase splitting and may be low spin ...
... D: H2O > F > RCO2 > OH > Cl > Br > I (also proton basicity) accepting ligands increase splitting and may be low spin ...
Xe– + Y → X + Ye–
... Concept 9.5 Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen 37. Fermentation allows for the production of ATP without using either oxygen or any electron transport chain. 38. For aerobic respiration to continue, the cell must be supplied with oxygen—the ultimate electron acc ...
... Concept 9.5 Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen 37. Fermentation allows for the production of ATP without using either oxygen or any electron transport chain. 38. For aerobic respiration to continue, the cell must be supplied with oxygen—the ultimate electron acc ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter5
... • Step 1: Write down the known or given quantity. Include both the numerical value and units of the quantity. • Step 2: Leave some working space and set the known quantity equal to the units of the unknown quantity. • Step 3: Multiply the known quantity by one or more factors, such that the units of ...
... • Step 1: Write down the known or given quantity. Include both the numerical value and units of the quantity. • Step 2: Leave some working space and set the known quantity equal to the units of the unknown quantity. • Step 3: Multiply the known quantity by one or more factors, such that the units of ...
How is DNA*s Genetic Code Used to Make Proteins?
... •tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome •The nucleotides on mRNA are divided into groups of 3 (“triplets”) •Each set of 3 nucleotides on mRNA is called a CODON •One codon is the “code” for one amino acid •Codons on mRNA match up with anticodons on tRNA for specific amino acids •Each tRNA delivers o ...
... •tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome •The nucleotides on mRNA are divided into groups of 3 (“triplets”) •Each set of 3 nucleotides on mRNA is called a CODON •One codon is the “code” for one amino acid •Codons on mRNA match up with anticodons on tRNA for specific amino acids •Each tRNA delivers o ...
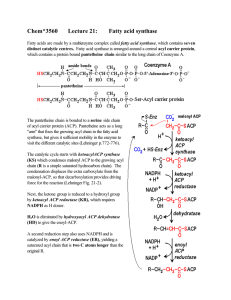
Chem*3560 Lecture 21: Fatty acid synthase
... The enzyme makes oxaloacetate as a bound intermediate, and then decarboxylates it to release pyruvate as a product. The decarboxylation provides the driving force needed to produce excess NADPH. Enz:[oxaloacetate] → pyruvate + CO2 Many organisms also contain an NADP + dependent isozyme of isocitrate ...
... The enzyme makes oxaloacetate as a bound intermediate, and then decarboxylates it to release pyruvate as a product. The decarboxylation provides the driving force needed to produce excess NADPH. Enz:[oxaloacetate] → pyruvate + CO2 Many organisms also contain an NADP + dependent isozyme of isocitrate ...
Steps for writing Lewis structures
... e) In most acids, such as H2SO4, and in many other compounds that contain both oxygen and hydrogen atoms, the hydrogen atoms are all bonded to oxygen atoms. 2. Find the total number of valence electrons. Add together the number of valence electrons contributed by each atom. If the species is an ion, ...
... e) In most acids, such as H2SO4, and in many other compounds that contain both oxygen and hydrogen atoms, the hydrogen atoms are all bonded to oxygen atoms. 2. Find the total number of valence electrons. Add together the number of valence electrons contributed by each atom. If the species is an ion, ...
Document
... (1) Oxidative decarboxilation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA (2) Aerobic oxidation of acetyl CoA by the citric acid cycle (3) Oxidation of fatty acids and amino acids ...
... (1) Oxidative decarboxilation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA (2) Aerobic oxidation of acetyl CoA by the citric acid cycle (3) Oxidation of fatty acids and amino acids ...
Chem 306 Ch 19 Enzymes Spring 2007
... typically 106 to 1012 times greater than those of the corresponding uncatalyzed reactions Turnover number: The number of molecules of substrate acted on by one molecule of enzyme per minute Ex: Carbonic anhydrase converts carbon dioxide to bicarbonate at a rate of 36 million molecules per minute. CO ...
... typically 106 to 1012 times greater than those of the corresponding uncatalyzed reactions Turnover number: The number of molecules of substrate acted on by one molecule of enzyme per minute Ex: Carbonic anhydrase converts carbon dioxide to bicarbonate at a rate of 36 million molecules per minute. CO ...
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis experiment pathway(II)
... had been covalently linked(共价结合) to the iron-containing protein ferritin(铁蛋白). • Because of the iron atoms, ferritin molecules are able to scatter a beam of electrons and thus can be visualized in electron microscope. • A temperature of 4℃ Ligands(配体) can bind to the cell surface but cannot be inter ...
... had been covalently linked(共价结合) to the iron-containing protein ferritin(铁蛋白). • Because of the iron atoms, ferritin molecules are able to scatter a beam of electrons and thus can be visualized in electron microscope. • A temperature of 4℃ Ligands(配体) can bind to the cell surface but cannot be inter ...
Protein - people.vcu.edu
... them. Such proteins are said to have quaternary structure. An example of this is the protein hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in blood. It consists of four separate polypeptide chains that interact with each other. Separately, each subunit can bind oxygen, due in part to the oxygen-binding mo ...
... them. Such proteins are said to have quaternary structure. An example of this is the protein hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in blood. It consists of four separate polypeptide chains that interact with each other. Separately, each subunit can bind oxygen, due in part to the oxygen-binding mo ...
SG 7,8,9,10
... Describe 3 important monosaccharides. Describe 4 important disaccharides, what are monosaccharides involved, details about. Describe polysaccharides (glycans) in terms of oligosaccharides, homoglycans, heteroglycans, starches, glycogen. Describe glycoconjugates; proteoglycans, glycoproteins and func ...
... Describe 3 important monosaccharides. Describe 4 important disaccharides, what are monosaccharides involved, details about. Describe polysaccharides (glycans) in terms of oligosaccharides, homoglycans, heteroglycans, starches, glycogen. Describe glycoconjugates; proteoglycans, glycoproteins and func ...
Lecture Sections 15.6 - Fulton County Schools
... Sulfide ion is often used to separate metal ions. See page 770. Let’s do: # 101 ...
... Sulfide ion is often used to separate metal ions. See page 770. Let’s do: # 101 ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.