METABOLIC DISEASES
... Most all have coarse facial features and dysostosis multiplex; hepatomegaly common. Can have obstructive hydrocephalus or cervical cord compression as a result of skeletal deformities at the base of the brain -Diagnosis: Glycosaminoglycan fragments are generated by alternative pathways and are excre ...
... Most all have coarse facial features and dysostosis multiplex; hepatomegaly common. Can have obstructive hydrocephalus or cervical cord compression as a result of skeletal deformities at the base of the brain -Diagnosis: Glycosaminoglycan fragments are generated by alternative pathways and are excre ...
Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature
... How can you differentiate between a trigonal planar molecule and a trigonal pyramidal molecule in terms of nonbonding electron pairs on the central atom? Trigonal planar molecules do not have nonbonding electrons on the central atom. Trigonal pyramidal molecules have a pair of nonbonding electrons ...
... How can you differentiate between a trigonal planar molecule and a trigonal pyramidal molecule in terms of nonbonding electron pairs on the central atom? Trigonal planar molecules do not have nonbonding electrons on the central atom. Trigonal pyramidal molecules have a pair of nonbonding electrons ...
Respiration in Plants
... Ans: During aerobic respiration, O2 is consumed and CO2 is released. The ratio of the volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed in respiration is called the respiratory quotient (RQ) or respiratory ratio. In living organisms respiratory substrates are often more than one. RQ values are used ...
... Ans: During aerobic respiration, O2 is consumed and CO2 is released. The ratio of the volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed in respiration is called the respiratory quotient (RQ) or respiratory ratio. In living organisms respiratory substrates are often more than one. RQ values are used ...
Lesson 4.Protein
... significant nonpolar characteristics due to its aromatic ring and could arguably be placed in the nonpolar group. 4.3.3 Acidic Amino Acids There are two acidic amino acids – aspartic acid and glutamic acid – whose R groups contain a carboxyl group. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid thus have a net neg ...
... significant nonpolar characteristics due to its aromatic ring and could arguably be placed in the nonpolar group. 4.3.3 Acidic Amino Acids There are two acidic amino acids – aspartic acid and glutamic acid – whose R groups contain a carboxyl group. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid thus have a net neg ...
Presentation
... • Disulfide bonds • Aggregation of hydrophobic side chains • van der Waals forces • Ionic bonds • Hydrogen bonds ...
... • Disulfide bonds • Aggregation of hydrophobic side chains • van der Waals forces • Ionic bonds • Hydrogen bonds ...
Oxidative ortho-C-N Fusion of Aniline by OsO4. Isolation
... characterize the presence of N-H and OsdO fragments, respectively. The NMR spectra (1H as well as 13C) of the representative complexes are submitted as Supporting Information, Figure S1 and S2). Notably, the two ligands in the complexes are magnetically equivalent because of the presence of a 2-fold ...
... characterize the presence of N-H and OsdO fragments, respectively. The NMR spectra (1H as well as 13C) of the representative complexes are submitted as Supporting Information, Figure S1 and S2). Notably, the two ligands in the complexes are magnetically equivalent because of the presence of a 2-fold ...
UNIT - I THE SOLID STATE KEY CONCEPTS
... solution are called components. Most of the solutions are binary i.e., consists of two components out of which one is solute and other is solvent. Solute - The component of solution which is present in smaller quantity. Solvent – The component of solution present in larger quantity or whose physical ...
... solution are called components. Most of the solutions are binary i.e., consists of two components out of which one is solute and other is solvent. Solute - The component of solution which is present in smaller quantity. Solvent – The component of solution present in larger quantity or whose physical ...
Marshall Nirenberg - Nobel Lecture
... reported that DNAase inhibited in vitro amino acid incorporation into protein. I had also observed this phenomenon and was greatly interested in it because the results strongly suggested that the cell-free synthesis of protein was dependent, ultimately, upon DNA templates. Heinrich Matthaei then joi ...
... reported that DNAase inhibited in vitro amino acid incorporation into protein. I had also observed this phenomenon and was greatly interested in it because the results strongly suggested that the cell-free synthesis of protein was dependent, ultimately, upon DNA templates. Heinrich Matthaei then joi ...
No Slide Title
... Chemical reactions of Alcohols 4.4 Alcohol oxidation (burning) * primary alcohols → aldehydes * secondary alcohols → ketones * tertiary alcohols → no reaction 4.5 Alcohol with caboxylic acid for Esterification reaction alcohol + acid → ester + H20 ...
... Chemical reactions of Alcohols 4.4 Alcohol oxidation (burning) * primary alcohols → aldehydes * secondary alcohols → ketones * tertiary alcohols → no reaction 4.5 Alcohol with caboxylic acid for Esterification reaction alcohol + acid → ester + H20 ...
Intro to Titrimetry
... 1. A Fajans titration of a 0.7908 g sample required 45.32 mL of 0.1046 M AgNO3. What is the %Cl of the sample? 2. The bismuth in 0.7405 g of an alloy was precipitated as BiOCl and separated from the solution by filtration. The washed precipitate was dissolved in nitric acid to convert all chlorine t ...
... 1. A Fajans titration of a 0.7908 g sample required 45.32 mL of 0.1046 M AgNO3. What is the %Cl of the sample? 2. The bismuth in 0.7405 g of an alloy was precipitated as BiOCl and separated from the solution by filtration. The washed precipitate was dissolved in nitric acid to convert all chlorine t ...
2H + CO3 H2CO3 H2O + CO2(g) H3N Co H3N NH3 OH2 Cl Cl H3N
... In the "octahedral" geometry there are 2 types of different Me groups (that is, they cannot be interconverted by a symmetry operation); these are cis and trans to a P, respectively. However in the "trigonal prism" structure all the Me groups are equivalent, so this is consistent with the NMR data. I ...
... In the "octahedral" geometry there are 2 types of different Me groups (that is, they cannot be interconverted by a symmetry operation); these are cis and trans to a P, respectively. However in the "trigonal prism" structure all the Me groups are equivalent, so this is consistent with the NMR data. I ...
Proteins with
... Genetic code scoring system – This assumes that changes in protein sequence arise from mutations. If only one point mutation is needed to change a given AA to another (at a specific position in alignment), the two amino-acids are more closely related than if two point mutations were required. Physic ...
... Genetic code scoring system – This assumes that changes in protein sequence arise from mutations. If only one point mutation is needed to change a given AA to another (at a specific position in alignment), the two amino-acids are more closely related than if two point mutations were required. Physic ...
Chemistry - Higher tier - Paper 4 - Sample assessment material
... A student heats 1.89 g of zinc nitrate until there is no further reaction. What is the total volume of gas, measured at room temperature and pressure, made in this reaction? Assume that one mole of gas occupies a volume of 24 dm3 at room temperature and ...
... A student heats 1.89 g of zinc nitrate until there is no further reaction. What is the total volume of gas, measured at room temperature and pressure, made in this reaction? Assume that one mole of gas occupies a volume of 24 dm3 at room temperature and ...
pharmaceutical biochemistry
... the aldehyde group is conserved by formation of the acid anhydride with phosphoric acid while NAD is reduced to NADH. The active site of the enzyme contains an –SH group (Cys residue) and it can be inhibited by monoiodoacetate. Arsenate toxicity is based on this reaction as well: arsenate is structu ...
... the aldehyde group is conserved by formation of the acid anhydride with phosphoric acid while NAD is reduced to NADH. The active site of the enzyme contains an –SH group (Cys residue) and it can be inhibited by monoiodoacetate. Arsenate toxicity is based on this reaction as well: arsenate is structu ...
OMB No. 0925-0001/0002 (Rev. 08/12), Biographical Sketch Format
... 1. Pioneering development of versatile, practical cell-free protein synthesis technology. Primarily started after I came to Stanford in 1998, the program focused on developing a complete technology package for the industrial production of pharmaceutical proteins. The major advance was gaining contro ...
... 1. Pioneering development of versatile, practical cell-free protein synthesis technology. Primarily started after I came to Stanford in 1998, the program focused on developing a complete technology package for the industrial production of pharmaceutical proteins. The major advance was gaining contro ...
nuclear receptors - SBI
... the expression of several genes. • Nuclear receptors are soluble proteins that can bind to specific DNA regulatory elements (response elements or REs) and act as cell typeand promoter-specific regulators of transcription. • In contrast to other transcription factors, the activity of nuclear receptor ...
... the expression of several genes. • Nuclear receptors are soluble proteins that can bind to specific DNA regulatory elements (response elements or REs) and act as cell typeand promoter-specific regulators of transcription. • In contrast to other transcription factors, the activity of nuclear receptor ...
SEPARATION OF MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANES OF
... matrix fraction was effected by digitonin treatment and discontinuous density gradient centrifugation . The solubilization of four isoleucine-valine biosynthetic enzymes was studied as a function of digitonin concentration and time of incubation in the detergent . The kinetics of the appearance of v ...
... matrix fraction was effected by digitonin treatment and discontinuous density gradient centrifugation . The solubilization of four isoleucine-valine biosynthetic enzymes was studied as a function of digitonin concentration and time of incubation in the detergent . The kinetics of the appearance of v ...
NMEICT PROJECT
... o A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is attached to a protein and is necessary for the protein's action. Cofactors can be considered as a "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical reactions. o Cofactors are divided in to two groups (organic and inorganic). o They can also be clas ...
... o A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is attached to a protein and is necessary for the protein's action. Cofactors can be considered as a "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical reactions. o Cofactors are divided in to two groups (organic and inorganic). o They can also be clas ...
Lecture 20
... Why do we need to eat d metals? Some critical enzymes in our cells are metalloproteins, giant biolmolecules which contain a metal atom These metalloproteins control key life processes such as respiration and protect cells against disease Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein which contains an iron atom an ...
... Why do we need to eat d metals? Some critical enzymes in our cells are metalloproteins, giant biolmolecules which contain a metal atom These metalloproteins control key life processes such as respiration and protect cells against disease Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein which contains an iron atom an ...
5 - University of San Diego Home Pages
... Aging is the process of allowing starter and finishing bacteria and their enzymes to alter composition of fresh cheese • The French term for ripening is affinage , which means ‘end’ or ‘ultimate point’. As such, at times this stage of cheese making is carried out by an affineur, a cheese tenderer o ...
... Aging is the process of allowing starter and finishing bacteria and their enzymes to alter composition of fresh cheese • The French term for ripening is affinage , which means ‘end’ or ‘ultimate point’. As such, at times this stage of cheese making is carried out by an affineur, a cheese tenderer o ...
Lecture 1 - "Hudel" Luecke
... ribosome the mRNA sequence (information) is read and the corresponding polypeptide (protein) is assembled. The rules for translating the linear nucleic acid sequence (mRNA) into the linear amino acid sequence (protein) are called the Genetic Code. ...
... ribosome the mRNA sequence (information) is read and the corresponding polypeptide (protein) is assembled. The rules for translating the linear nucleic acid sequence (mRNA) into the linear amino acid sequence (protein) are called the Genetic Code. ...
AVOGADRO EXAMS 1991 - 2002 PRACTICE BOOKLET
... 25. Assume that argon, at a constant temperature and pressure, behaves as an ideal gas. Which of the following is correct? (a) All argon atoms move with the same speed (b) All argon atoms collide with the container walls with the same force (c) Temperature is determined solely by the collision freq ...
... 25. Assume that argon, at a constant temperature and pressure, behaves as an ideal gas. Which of the following is correct? (a) All argon atoms move with the same speed (b) All argon atoms collide with the container walls with the same force (c) Temperature is determined solely by the collision freq ...
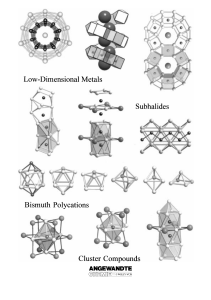
From the Metal to the Molecule
... Mostly, it is found to be more convenient to use intermetallic phases or metal halides as starting materials. In some cases, it is necessary to add auxiliary reagents, such as niobium halides, which modify the partial pressures in the gas phase through various equilibrium processes but are not incor ...
... Mostly, it is found to be more convenient to use intermetallic phases or metal halides as starting materials. In some cases, it is necessary to add auxiliary reagents, such as niobium halides, which modify the partial pressures in the gas phase through various equilibrium processes but are not incor ...
Chapter 25
... • Oxidation is the removal of electrons from a molecule and results in a decrease in the energy content of the molecule. Because most biological oxidations involve the loss of hydrogen atoms, they are called dehydrogenation reactions. • When a substance is oxidized, the liberated hydrogen atoms do n ...
... • Oxidation is the removal of electrons from a molecule and results in a decrease in the energy content of the molecule. Because most biological oxidations involve the loss of hydrogen atoms, they are called dehydrogenation reactions. • When a substance is oxidized, the liberated hydrogen atoms do n ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.