Structural and Biochemical Characterization of a Bifunctional
... Fuc3NAc, is an unusual dideoxysugar found in the O-antigens of various Gram-negative bacteria and in the S-layers glycans of some Gram-positive bacteria. The biosynthetic pathway for its production in Aneurinibacillus thermoaerophilus L420-91T was elucidated in 2003 and is shown in Scheme 1.1 The fir ...
... Fuc3NAc, is an unusual dideoxysugar found in the O-antigens of various Gram-negative bacteria and in the S-layers glycans of some Gram-positive bacteria. The biosynthetic pathway for its production in Aneurinibacillus thermoaerophilus L420-91T was elucidated in 2003 and is shown in Scheme 1.1 The fir ...
CBSE Living Science Chemistry Class X
... The above chemical equation is a skeletal chemical equation for the chemical reaction involved in the Activity 1 and is an unbalanced equation. By unbalanced equation, we mean that the number of atoms of each element on the left and right hand side of the arrow is not equal. There are two atoms of o ...
... The above chemical equation is a skeletal chemical equation for the chemical reaction involved in the Activity 1 and is an unbalanced equation. By unbalanced equation, we mean that the number of atoms of each element on the left and right hand side of the arrow is not equal. There are two atoms of o ...
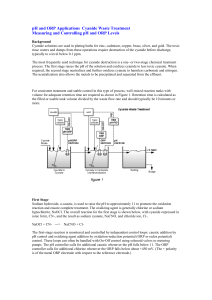
pH and ORP Applications Cyanide Waste Treatment
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
Chapter 6
... The energy from the electrons will be used to pump protons. The energy from the diffusion of protons will be used to make ATP. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... The energy from the electrons will be used to pump protons. The energy from the diffusion of protons will be used to make ATP. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Constitutive expression of Vitis vinifera thaumatin
... 1996). PR proteins are induced intra- and extracellularly by pathogens, chemical elicitors or, in some instances, environmental stresses. PR proteins are separated into several groups, based primarily upon sequence homology, but electrophoretic mobility and functional characteristics also are consid ...
... 1996). PR proteins are induced intra- and extracellularly by pathogens, chemical elicitors or, in some instances, environmental stresses. PR proteins are separated into several groups, based primarily upon sequence homology, but electrophoretic mobility and functional characteristics also are consid ...
Lecture #1 ~ Date_________
... BCCDDEE FF G G enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme ...
... BCCDDEE FF G G enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme ...
Valine Mydrogenase from Streptmzyces fiadipe
... K,HPO.,, 0.1;L-valine, 0.47; yeast extract, 0.05. Both media were adjusted to pH 7.3 with 1 M-HClbefore thermal sterilization. Cultivation was done in 500 ml flasks containing 70 ml medium on a reciprocal shaker (1.7 Hz, 29 "C). Enzyme and protein assay. The ammonium-assimilating activity of VDH was ...
... K,HPO.,, 0.1;L-valine, 0.47; yeast extract, 0.05. Both media were adjusted to pH 7.3 with 1 M-HClbefore thermal sterilization. Cultivation was done in 500 ml flasks containing 70 ml medium on a reciprocal shaker (1.7 Hz, 29 "C). Enzyme and protein assay. The ammonium-assimilating activity of VDH was ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12
... 97. What are the points necessary for an electric current to flow through an aqueous solution? In order for electricity to flow, the circuit should be (closed/ opened). Why CaCl2 solution conducts current but sugar in water does not 98. Why does aqueous CaCl2 solution conduct electricity but sugar i ...
... 97. What are the points necessary for an electric current to flow through an aqueous solution? In order for electricity to flow, the circuit should be (closed/ opened). Why CaCl2 solution conducts current but sugar in water does not 98. Why does aqueous CaCl2 solution conduct electricity but sugar i ...
Non-homologous Recombination of Deoxyribonucleoside Kinases
... Three of the four single-crossover chimeras have substrate-activity profiles that mirror the predominant parental enzyme (Table 1). The two chimeras with the majority of their sequence derived from DmdNK (DH-03 and HD-15) exhibited DmdNK-like substrate profiles, demonstrating activity towards pyrimi ...
... Three of the four single-crossover chimeras have substrate-activity profiles that mirror the predominant parental enzyme (Table 1). The two chimeras with the majority of their sequence derived from DmdNK (DH-03 and HD-15) exhibited DmdNK-like substrate profiles, demonstrating activity towards pyrimi ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... mitochondrial receptor for T3 was also described • Free thyroid hormone receptor (TR) without bound hormone is bound to hormone response element of DNA (HRE) and corepressor (CoR) • After binding T3 to receptor - CoR is liberated and coactivators (CoA) is bound and the transcription to mRNA begins ...
... mitochondrial receptor for T3 was also described • Free thyroid hormone receptor (TR) without bound hormone is bound to hormone response element of DNA (HRE) and corepressor (CoR) • After binding T3 to receptor - CoR is liberated and coactivators (CoA) is bound and the transcription to mRNA begins ...
GLYCOLYSIS
... molecular formula – so H must reattach somewhere h. Need to regenerate the catalyst ...
... molecular formula – so H must reattach somewhere h. Need to regenerate the catalyst ...
Lecture 11 – Reaction Types and Mechanisms for Inorganic
... [Cr(H2O)5(OH)]2+ + H2O [Cr(H2O)6]3+ + OHReactions of a ligand that take place without breaking the M-L bond. e.g. water ligand in the hexaaquochromium(III) reacting with a hydroxide ion to produce the corresponding hydroxo complex. Or replacement of the central hydrogen of acac with a Br atom. O ...
... [Cr(H2O)5(OH)]2+ + H2O [Cr(H2O)6]3+ + OHReactions of a ligand that take place without breaking the M-L bond. e.g. water ligand in the hexaaquochromium(III) reacting with a hydroxide ion to produce the corresponding hydroxo complex. Or replacement of the central hydrogen of acac with a Br atom. O ...
Chapter 18 Homework Assignment Chapter 18 Amino Acid
... In the liver, GLU is transported into the MT where it undergoes oxidative deamination ...
... In the liver, GLU is transported into the MT where it undergoes oxidative deamination ...
An archaebacterial homolog of pelota, a meiotic cell division protein
... factors [8], ribosomal proteins [9], and a VCP-like two-domain ATPase that in eukaryotes is involved in cell-cycle regulation [lo]. Thus, an appropriate archaebacterial genome could be a better ‘prokaryotic model of the eukaryotic genome’ than could any eubacterial genome. Sulfolobus solfataricus ha ...
... factors [8], ribosomal proteins [9], and a VCP-like two-domain ATPase that in eukaryotes is involved in cell-cycle regulation [lo]. Thus, an appropriate archaebacterial genome could be a better ‘prokaryotic model of the eukaryotic genome’ than could any eubacterial genome. Sulfolobus solfataricus ha ...
Chemical Equations Chemical Reaction: Interaction between
... Reducing agent: a compound that is oxidized while causing another compound to be reduced Oxidizing agent: a compound that is reduced while causing another compound to be oxidized •Zn acts as a reducing agent because it causes Cu2+ to gain electrons and become reduced. •Cu2+ acts as an oxidizing agen ...
... Reducing agent: a compound that is oxidized while causing another compound to be reduced Oxidizing agent: a compound that is reduced while causing another compound to be oxidized •Zn acts as a reducing agent because it causes Cu2+ to gain electrons and become reduced. •Cu2+ acts as an oxidizing agen ...
Amino acids used in Animal Nutrition
... Several Amino acids make a peptide chain A peptide chain can be up to 500 amino acids! Since there are only 20 amino acids, several will repeat! A protein is made up of one or more polypeptide chains ...
... Several Amino acids make a peptide chain A peptide chain can be up to 500 amino acids! Since there are only 20 amino acids, several will repeat! A protein is made up of one or more polypeptide chains ...
Chapter 5 ppt
... Reducing agent: a compound that is oxidized while causing another compound to be reduced Oxidizing agent: a compound that is reduced while causing another compound to be oxidized •Zn acts as a reducing agent because it causes Cu2+ to gain electrons and become reduced. •Cu2+ acts as an oxidizing agen ...
... Reducing agent: a compound that is oxidized while causing another compound to be reduced Oxidizing agent: a compound that is reduced while causing another compound to be oxidized •Zn acts as a reducing agent because it causes Cu2+ to gain electrons and become reduced. •Cu2+ acts as an oxidizing agen ...
Valence, Oxidation Number, and Formal Charge: Three Related but
... provided by hydrogen for which both H+ and H− have permissible closed-shell configurations (1s0 and 1s2, respectively). In this case, the charge assigned to hydrogen is determined by the relative electronegativity of the atom to which it is attached. As will be discussed in more detail below, it is ...
... provided by hydrogen for which both H+ and H− have permissible closed-shell configurations (1s0 and 1s2, respectively). In this case, the charge assigned to hydrogen is determined by the relative electronegativity of the atom to which it is attached. As will be discussed in more detail below, it is ...
Thin-Layer Chromatography of Amino Acids
... many different types of chromatography depending on the substances that need to be separated. The most commonly used methods include paper chromatography, gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, and thinlayer chromatography. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is used to separate solids from a liquid ...
... many different types of chromatography depending on the substances that need to be separated. The most commonly used methods include paper chromatography, gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, and thinlayer chromatography. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is used to separate solids from a liquid ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.