Proteomic analysis of the signaling pathway mediated by the
... other β-lactam antibiotic precursors [6]. The P. chrysogenum heterotrimeric Gα protein Pga1, belonging to the fungal subgroup I, has been characterized and shown to participate in the regulation of the global developmental program of the fungus, from spore germination to conidia formation [7–9]. In ...
... other β-lactam antibiotic precursors [6]. The P. chrysogenum heterotrimeric Gα protein Pga1, belonging to the fungal subgroup I, has been characterized and shown to participate in the regulation of the global developmental program of the fungus, from spore germination to conidia formation [7–9]. In ...
Chapter 8 THE ENERGY CONSUMING PROCESS OF RESPIRATION
... organisms can also produce ATP through chemical pathways that degrade (take apart) food molecules. The main degradative pathway requires free oxygen and is called (6) ______________. There are three stages of aerobic respiration. In the first stage, (7) ______________, glucose is partially degraded ...
... organisms can also produce ATP through chemical pathways that degrade (take apart) food molecules. The main degradative pathway requires free oxygen and is called (6) ______________. There are three stages of aerobic respiration. In the first stage, (7) ______________, glucose is partially degraded ...
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
... or the use of microsatellites (14). The use of proteins is limited. There are few publications connected with the taxonomy of plants from sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis (15, 16). There are two types of protein markers: the immunochemical, or serological ...
... or the use of microsatellites (14). The use of proteins is limited. There are few publications connected with the taxonomy of plants from sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis (15, 16). There are two types of protein markers: the immunochemical, or serological ...
03-232 Biochemistry Exam III - S2014 Name:________________________
... using ____NAD+______ as the electron acceptor. This reaction is catalyzed by a _dehydrogenase_ (general name). ii) In the _TCA/fatty acid oxidation_ pathway, an alkane is converted to a __alkene_____, using ___FAD_______ as the electron acceptor. This reaction is catalyzed by a _dehydrogenase_ (gene ...
... using ____NAD+______ as the electron acceptor. This reaction is catalyzed by a _dehydrogenase_ (general name). ii) In the _TCA/fatty acid oxidation_ pathway, an alkane is converted to a __alkene_____, using ___FAD_______ as the electron acceptor. This reaction is catalyzed by a _dehydrogenase_ (gene ...
Introducing densification mechanisms into the - LAAS-CNRS
... consists in trying to atomically control the growth by separating each of its steps. The film growth proceeds through self-terminating reactions on surfaces. The ALD process can be separated into two half-reactions; the first half-cycle reaction concerns the precursor gas exposure and the second half ...
... consists in trying to atomically control the growth by separating each of its steps. The film growth proceeds through self-terminating reactions on surfaces. The ALD process can be separated into two half-reactions; the first half-cycle reaction concerns the precursor gas exposure and the second half ...
chapter 14
... Respiration requires O2.. How did the first cells on the earth manage to survive in an atmosphere that lacked O2? ...
... Respiration requires O2.. How did the first cells on the earth manage to survive in an atmosphere that lacked O2? ...
Fall, 2002
... their amine groups (-NH2). The reaction is a dehydration between the amine and the carbonyl group with the formationof a C=N double bond. Write the equation for this reaction with this simple amine, CH3-NH2. ...
... their amine groups (-NH2). The reaction is a dehydration between the amine and the carbonyl group with the formationof a C=N double bond. Write the equation for this reaction with this simple amine, CH3-NH2. ...
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
... Inner membrane proteins reduced by NADH and FADH2 AcetylCoA broken down further, releasing two CO2 molecules; C electrons and H sequestered by NADH and FADH2 Oxygen reduced by electrons from inner membrane proteins; D binds with 2 protons and released as waste H2O E Glucose hydrolyzed into two pyruv ...
... Inner membrane proteins reduced by NADH and FADH2 AcetylCoA broken down further, releasing two CO2 molecules; C electrons and H sequestered by NADH and FADH2 Oxygen reduced by electrons from inner membrane proteins; D binds with 2 protons and released as waste H2O E Glucose hydrolyzed into two pyruv ...
Applications of Aqueous Equilibria II: Solubility and Ksp Reading
... Kf = 5.6 x 1018 Net: AgCl (s) + 2 CN-(aq) [Ag (CN)2]+(aq) + Cl-(aq) K=Ksp*Kf = 1 x109 Kf is the formation constant which gives quantitative information about the complexforming equilibrium step; note the net reaction is now favorable for dissolution of AgCl. ...
... Kf = 5.6 x 1018 Net: AgCl (s) + 2 CN-(aq) [Ag (CN)2]+(aq) + Cl-(aq) K=Ksp*Kf = 1 x109 Kf is the formation constant which gives quantitative information about the complexforming equilibrium step; note the net reaction is now favorable for dissolution of AgCl. ...
Relationship Between the Occurrence of Cysteine in Proteins and
... two other amino acids (C-(X)2-C motif; X may stand for any coded amino acid). Indeed, it is known that C-(X)2C motifs are well conserved parts of various iron-sulfur proteins and oxidoreductases (Shuber et al. 1986; Ammendola et al. 1992). However, we recognized that the occurrence of C-(X)2-C domai ...
... two other amino acids (C-(X)2-C motif; X may stand for any coded amino acid). Indeed, it is known that C-(X)2C motifs are well conserved parts of various iron-sulfur proteins and oxidoreductases (Shuber et al. 1986; Ammendola et al. 1992). However, we recognized that the occurrence of C-(X)2-C domai ...
Slide 1
... Cellular respiration is an exergonic process that transfers energy from the bonds in glucose to form ATP. Cellular respiration – produces up to 32 ATP molecules from each glucose molecule and – captures only about 34% of the energy originally stored in glucose. ...
... Cellular respiration is an exergonic process that transfers energy from the bonds in glucose to form ATP. Cellular respiration – produces up to 32 ATP molecules from each glucose molecule and – captures only about 34% of the energy originally stored in glucose. ...
respiration review
... are passed down the 9 components of the ETC, hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane, from the matrix side into the intermembrane space. As each component of the chain accepts and then donates an electron, it pumps hydrogen protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space. ...
... are passed down the 9 components of the ETC, hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane, from the matrix side into the intermembrane space. As each component of the chain accepts and then donates an electron, it pumps hydrogen protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space. ...
A New Type of a Multifunctional ß
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
Vitamins and Coenzymes - Rose
... non-specific for the alcohol, although it is quite specific for NAD compared to NADP. In the absence of substrate, the alcohol dehydrogenase active site is occupied by water molecules. Note the zinc ion, a metal ion cofactor that is required for catalytic activity (alcohol dehydrogenase actually bin ...
... non-specific for the alcohol, although it is quite specific for NAD compared to NADP. In the absence of substrate, the alcohol dehydrogenase active site is occupied by water molecules. Note the zinc ion, a metal ion cofactor that is required for catalytic activity (alcohol dehydrogenase actually bin ...
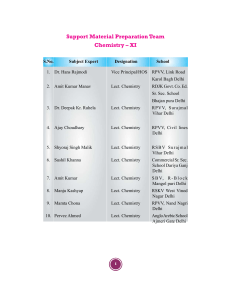
Support Material
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
1 - Max Planck Institut für Festkörperforschung
... networks at surfaces. This system has been investigated extensively by STM, providing excellent structural characterization of the several TPA + Fe phases which are observed at different Fe/TPA ratios.6 However, the STM is not able to directly characterize the charge state or local chemical environm ...
... networks at surfaces. This system has been investigated extensively by STM, providing excellent structural characterization of the several TPA + Fe phases which are observed at different Fe/TPA ratios.6 However, the STM is not able to directly characterize the charge state or local chemical environm ...
Sequence and evolutionary analysis of the human trypsin subfamily
... with other blood-clotting factors, but, due to mutation of the catalytic Asp and His, has no peptidase activity. With the near completion of the Human Genome Project, sequence information became available for almost all SP. In order to better understand the structural, functional and evolutionary as ...
... with other blood-clotting factors, but, due to mutation of the catalytic Asp and His, has no peptidase activity. With the near completion of the Human Genome Project, sequence information became available for almost all SP. In order to better understand the structural, functional and evolutionary as ...
Amino Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... In the digestion of fats (triacylglycerols), Bile salts break fat globules into smaller particles called micelles in the small intestine. Pancreatic lipases hydrolyze ester bonds to form monoacylglycerols and fatty acids, which recombine in the intestinal lining. Fatty acids bind with proteins ...
... In the digestion of fats (triacylglycerols), Bile salts break fat globules into smaller particles called micelles in the small intestine. Pancreatic lipases hydrolyze ester bonds to form monoacylglycerols and fatty acids, which recombine in the intestinal lining. Fatty acids bind with proteins ...
Enzyme Lecture PowerPoint
... Do not enter active site, but bind to another part of the enzyme, causing the enzyme & active site to change shape. Usually reversible, depending on concentration of inhibitor & substrate. EXAMPLE: You may know that compounds containing heavy metals such as lead, mercury, copper or silver are poison ...
... Do not enter active site, but bind to another part of the enzyme, causing the enzyme & active site to change shape. Usually reversible, depending on concentration of inhibitor & substrate. EXAMPLE: You may know that compounds containing heavy metals such as lead, mercury, copper or silver are poison ...
Enzyme
... • It is an inorganic ion which loosely bound to an enzyme or an substrate to increase the chance to an enzyme-substrate complex forming. Some times, the inorganic ions are free and does not bind to the enzyme or substrate, • e.g. copper, iron, calcium, Cl- etc. ...
... • It is an inorganic ion which loosely bound to an enzyme or an substrate to increase the chance to an enzyme-substrate complex forming. Some times, the inorganic ions are free and does not bind to the enzyme or substrate, • e.g. copper, iron, calcium, Cl- etc. ...
A New Type of a Multifunctional ß-Oxidation
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
Mitochondrial b
... (ETF) and ETF-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETFD), and the second dehydrogenation is linked to complex I of the respiratory chain via NADH. Hence, ATP production from b-oxidation comes both from direct production of reduced cofactors, and from subsequent oxidation of acetyl-CoA. There are multiple enzy ...
... (ETF) and ETF-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETFD), and the second dehydrogenation is linked to complex I of the respiratory chain via NADH. Hence, ATP production from b-oxidation comes both from direct production of reduced cofactors, and from subsequent oxidation of acetyl-CoA. There are multiple enzy ...
- DigitalCommons@Linfield
... stretches determine the secondary structure of the molecule. In the spectra of BSA, the amide stretches show a alpha-helical structure. The similar spectra between the colloidal solution and the nanoparticle film shows that BSA is orienting itself in the same manor such that the same amino acid resi ...
... stretches determine the secondary structure of the molecule. In the spectra of BSA, the amide stretches show a alpha-helical structure. The similar spectra between the colloidal solution and the nanoparticle film shows that BSA is orienting itself in the same manor such that the same amino acid resi ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.