Body Structures and Functions
... Standard 7: Circulatory System, the Heart, and Blood Vessels (0716.S.7) ...
... Standard 7: Circulatory System, the Heart, and Blood Vessels (0716.S.7) ...
Life Functions - duncanbiology
... • Nervous tissue consists of neurons and supporting cells. • A nerve is a bundle of axons. • The nervous system is divided into two ...
... • Nervous tissue consists of neurons and supporting cells. • A nerve is a bundle of axons. • The nervous system is divided into two ...
Robert S. Behnke, HSD
... muscles on the bones (crossing joints), and then observing how the joints move when the muscles contract. The book also discusses the nerves (including the central nervous system’s brain and ...
... muscles on the bones (crossing joints), and then observing how the joints move when the muscles contract. The book also discusses the nerves (including the central nervous system’s brain and ...
The Lobster Conservancy
... general diagram of the lobster’s nervous system. Shows the location of the brain from an exterior view as well as the cervical ...
... general diagram of the lobster’s nervous system. Shows the location of the brain from an exterior view as well as the cervical ...
Test 2
... 3. Intensity of impulse is always the same. When “on” it is fully turned on. This is called “all-or-none”. C. Parts of the Nervous System a. Brain i. Cerebrum 1. Structure a. Left and right hemispheres (Fig. 9.27) b. 5 lobes (Fig. 9.28) 2. Functions a. Motor – movements b. Sensory – all five senses ...
... 3. Intensity of impulse is always the same. When “on” it is fully turned on. This is called “all-or-none”. C. Parts of the Nervous System a. Brain i. Cerebrum 1. Structure a. Left and right hemispheres (Fig. 9.27) b. 5 lobes (Fig. 9.28) 2. Functions a. Motor – movements b. Sensory – all five senses ...
The Human Body
... of the body much like cables are attached to an elevator. When the muscles or the cables contract, the body or the elevator moves. But the skeletal muscles do not only cause large and obvious movements. They also enable us to accomplish much more subtle movements like smiling or frowning by contract ...
... of the body much like cables are attached to an elevator. When the muscles or the cables contract, the body or the elevator moves. But the skeletal muscles do not only cause large and obvious movements. They also enable us to accomplish much more subtle movements like smiling or frowning by contract ...
Anatomy and Physiology Benchmarks
... Identify the structural components of a sarcomere. Explain the key steps involved in the contraction of a skeletal muscle fiber. (HSLS2-3) Compare the different types of muscle contractions. (HSLS2-3) Describe the mechanisms by which muscles obtain and use energy to power contractions. (HSLS ...
... Identify the structural components of a sarcomere. Explain the key steps involved in the contraction of a skeletal muscle fiber. (HSLS2-3) Compare the different types of muscle contractions. (HSLS2-3) Describe the mechanisms by which muscles obtain and use energy to power contractions. (HSLS ...
Glossary - Zoology
... Gland: A group of cells organized into a descrete secretory organ. Gonad: An animal reproductive organ that generates gametes. Hermaphrodites: The presence in one individual of both ovarian and testicula tissue. Heterogenic: The production of offspring unlike the parents. Holotrich: typically with u ...
... Gland: A group of cells organized into a descrete secretory organ. Gonad: An animal reproductive organ that generates gametes. Hermaphrodites: The presence in one individual of both ovarian and testicula tissue. Heterogenic: The production of offspring unlike the parents. Holotrich: typically with u ...
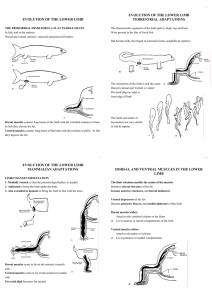
evolution of the lower limb terrestrial adaptations
... Upper limb has a whole set of muscles which can move and position the pectoral girdle with respect ot the trunk. Trapezius, rhomboids, levator scapulae, serratus anterior ...
... Upper limb has a whole set of muscles which can move and position the pectoral girdle with respect ot the trunk. Trapezius, rhomboids, levator scapulae, serratus anterior ...
Body Systems Quiz Part TWO
... 19. The __________________ system works with the immune system to protect the body from disease causing invaders. a. Endocrine b. Skeletal c. Integumentary d. Lymphatic 20. The ______________________ system carries white blood cells throughout the body, with the help of the circulatory system a. Imm ...
... 19. The __________________ system works with the immune system to protect the body from disease causing invaders. a. Endocrine b. Skeletal c. Integumentary d. Lymphatic 20. The ______________________ system carries white blood cells throughout the body, with the help of the circulatory system a. Imm ...
Plates 41 to 56
... Fig. 138. Transversal section through the ventral body wall just inside the foot margin, showing the pedal nerve cord with its superficial layer of nerve cells. Microphotograph. Spec. 111. Fig. 139. Transversal section through the statocyst. Note the high and dark epithelium forming the bottom and ...
... Fig. 138. Transversal section through the ventral body wall just inside the foot margin, showing the pedal nerve cord with its superficial layer of nerve cells. Microphotograph. Spec. 111. Fig. 139. Transversal section through the statocyst. Note the high and dark epithelium forming the bottom and ...
Take a Deep Breath: The Physiology of Slow Deep Breathing
... Baroreceptors are activated when they detect an increase in blood pressure. The signal from the aortic arch travels along the vagus nerve while the signal from the carotid sinus is relayed to the brainstem/“CPU” by the glossopharyngeal (9th) nerve. These signals arrive at the part of the brainstem/ ...
... Baroreceptors are activated when they detect an increase in blood pressure. The signal from the aortic arch travels along the vagus nerve while the signal from the carotid sinus is relayed to the brainstem/“CPU” by the glossopharyngeal (9th) nerve. These signals arrive at the part of the brainstem/ ...
Animal Systems
... contracts to pump blood. It is controlled by ____________________, and covered with a smooth layer of ____________________ that protects the heart and help blood flow smoothly. Blood is carried through the body in three types of ____________________. ________________ carry blood away from the heart. ...
... contracts to pump blood. It is controlled by ____________________, and covered with a smooth layer of ____________________ that protects the heart and help blood flow smoothly. Blood is carried through the body in three types of ____________________. ________________ carry blood away from the heart. ...
Human Body Systems DR. I MCSNEER
... things. It refers to the maintenance of the internal environment within tolerable limits. All sorts of factors affect the suitability of our body fluids to sustain life; these include properties like temperature, salinity, acidity, and the concentrations of nutrients and wastes. Because these proper ...
... things. It refers to the maintenance of the internal environment within tolerable limits. All sorts of factors affect the suitability of our body fluids to sustain life; these include properties like temperature, salinity, acidity, and the concentrations of nutrients and wastes. Because these proper ...
relationship-between tissues-of-the
... skeletal muscle tissue, which are under voluntary control and are responsible for movement and contraction of skeletal parts of the body; smooth muscle tissue is under involuntary control and is responsible ...
... skeletal muscle tissue, which are under voluntary control and are responsible for movement and contraction of skeletal parts of the body; smooth muscle tissue is under involuntary control and is responsible ...
Instructor*s Resource Guide with Test Bank, prepared by Josephine F
... 78. Evidence indicates that stress and illness are related because stress a) suppresses the respiratory system. b) suppresses the immune system. c) leads to increased damage to the hypothalamus. d) increases our basal metabolism rate which makes us age faster. Answer: b Section Reference: Less-Than- ...
... 78. Evidence indicates that stress and illness are related because stress a) suppresses the respiratory system. b) suppresses the immune system. c) leads to increased damage to the hypothalamus. d) increases our basal metabolism rate which makes us age faster. Answer: b Section Reference: Less-Than- ...
Earthworm Dissection
... 3. Use a hand lens as you observe all parts of the worm, externally and internally. Find the anterior end by locating the prostomium, which is a fleshy lobe that extends over the mouth. The other end of the worm’s body is the posterior end, where the anus is located. 4. Look for the worm’s setae, wh ...
... 3. Use a hand lens as you observe all parts of the worm, externally and internally. Find the anterior end by locating the prostomium, which is a fleshy lobe that extends over the mouth. The other end of the worm’s body is the posterior end, where the anus is located. 4. Look for the worm’s setae, wh ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 38.1 Overview of the central
... FIGURE 38.8 The hypothalamic-neurohypophysial control of vasopressin and oxytocin release is shown (top). Large cells (magnocellular) in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei synthesize vasopressin or oxytocin, which are transported by axonal transport into nerve terminals located in the posteri ...
... FIGURE 38.8 The hypothalamic-neurohypophysial control of vasopressin and oxytocin release is shown (top). Large cells (magnocellular) in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei synthesize vasopressin or oxytocin, which are transported by axonal transport into nerve terminals located in the posteri ...
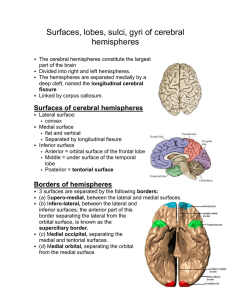
Surfaces, lobes, sulci, gyri of cerebral hemispheres
... the brain into lobes are often called fissures. Gyrus ridge Irregular eminences on the surface of brain formed by sulci The gyri and sulci are fairly constant in their arrangement ...
... the brain into lobes are often called fissures. Gyrus ridge Irregular eminences on the surface of brain formed by sulci The gyri and sulci are fairly constant in their arrangement ...
ch. 3: Biology and Behavior
... Answer: Earlier views did not show an understanding of the functioning of the brain and did not view thinking as a biological process. ...
... Answer: Earlier views did not show an understanding of the functioning of the brain and did not view thinking as a biological process. ...
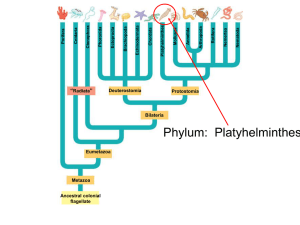
Platyhelminthes - The Bronx High School of Science
... •cross-fertilization •some mate by “penis-fencing” •sperm injected in body wall •fertilization and early ...
... •cross-fertilization •some mate by “penis-fencing” •sperm injected in body wall •fertilization and early ...
Cancer - Gadsby Wicks
... The largest blood vessel in the body which conveys oxygen rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body except the lungs. ...
... The largest blood vessel in the body which conveys oxygen rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body except the lungs. ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.