13 Renal Clearance overview
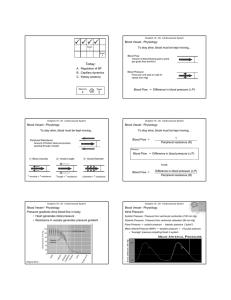
... If the blood is low in sodium, (after excessive sweating), aldosterone (from the adrenal cortex) will cause more sodium to be pumped out of the tubule and into the peritubular space. The sodium will then enter the capillaries. Since water follows where salt goes, whenever the body needs more wat ...
... If the blood is low in sodium, (after excessive sweating), aldosterone (from the adrenal cortex) will cause more sodium to be pumped out of the tubule and into the peritubular space. The sodium will then enter the capillaries. Since water follows where salt goes, whenever the body needs more wat ...
Cardiovascular Physiology 2016
... Purpose of the Cardiovascular System Purpose of CV system is to maintain adequate blood pressure (BP) to achieve perfusion of the ...
... Purpose of the Cardiovascular System Purpose of CV system is to maintain adequate blood pressure (BP) to achieve perfusion of the ...
Bodies Human Exhibit Guide
... the Thinker balance on the stool. The cerebellum coordinates body movements that are directed by other brain structures, like the cerebrum and helps maintain posture. Just recently, scientists discovered that the cerebellum also plays a role in language, problem solving and task planning. The other ...
... the Thinker balance on the stool. The cerebellum coordinates body movements that are directed by other brain structures, like the cerebrum and helps maintain posture. Just recently, scientists discovered that the cerebellum also plays a role in language, problem solving and task planning. The other ...
Chapter 1
... Absorption and Excretion Digestive System Receives food, converts molecules to forms that can pass through membranes, eliminates materials not absorbed Mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small and large intestines. ...
... Absorption and Excretion Digestive System Receives food, converts molecules to forms that can pass through membranes, eliminates materials not absorbed Mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small and large intestines. ...
Dear Notetaker:
... Not tested on reading assignments Remaining will be old Eliminate Lectures 1,2,3, 12 Dr. Donati will be around all week except Monday, all of next week and the Monday and Tuesday before final to answer any questions Pressure changes during ventilation Alveolar surface tension - Surfactant, breaks up ...
... Not tested on reading assignments Remaining will be old Eliminate Lectures 1,2,3, 12 Dr. Donati will be around all week except Monday, all of next week and the Monday and Tuesday before final to answer any questions Pressure changes during ventilation Alveolar surface tension - Surfactant, breaks up ...
Rat Anatomy Checklist
... 3. Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle via the tricuspid valve. Label each on the diagram. 4. Blood is then pumped through the pulmonary semilunar valve and into the pulmonary trunk where blood travels to the lungs. Label each. 5. Blood then flows through the pulmonary arteries ...
... 3. Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle via the tricuspid valve. Label each on the diagram. 4. Blood is then pumped through the pulmonary semilunar valve and into the pulmonary trunk where blood travels to the lungs. Label each. 5. Blood then flows through the pulmonary arteries ...
Chapter 1 Quiz 1
... c. the walls of the pericardial cavity. d. the walls of the thoracic cavity. e. the walls of the abdominopelvic cavity. 10. Gross anatomy includes all of the following except a. systemic anatomy. b. surface anatomy. c. cellular anatomy. d. regional anatomy. e. macroscopic anatomy. 11. Epithelium is ...
... c. the walls of the pericardial cavity. d. the walls of the thoracic cavity. e. the walls of the abdominopelvic cavity. 10. Gross anatomy includes all of the following except a. systemic anatomy. b. surface anatomy. c. cellular anatomy. d. regional anatomy. e. macroscopic anatomy. 11. Epithelium is ...
You can
... pressure was recorded in “mmHg.” Those units “mmHg” are still used for blood pressure today. These mercury filled Sphygmomanometers as still used in some places clinically today. In this lab, we will be using an aneroid (using air) Sphygmomanometer. A Sphygmomanometer functions by increasing the out ...
... pressure was recorded in “mmHg.” Those units “mmHg” are still used for blood pressure today. These mercury filled Sphygmomanometers as still used in some places clinically today. In this lab, we will be using an aneroid (using air) Sphygmomanometer. A Sphygmomanometer functions by increasing the out ...
chapt20_student2-1 - Human Anatomy and Physiology
... muscular and elastic tissue • collapse when empty, expand easily • have steady blood flow • merge to form larger veins • subjected to relatively low blood pressure – remains 10 mm Hg with little fluctuation ...
... muscular and elastic tissue • collapse when empty, expand easily • have steady blood flow • merge to form larger veins • subjected to relatively low blood pressure – remains 10 mm Hg with little fluctuation ...
Hypovolemic Shock
... blood flow by predictable adjustments in cardiovascular physiology. This is compensated shock. Signs of compensated hypovolemic shock are tachycardia and peripheral vasoconstriction. Vasoconstriction causes the signs of abnormal circulation to skin: delayed capillary refill time, and decreased pulse ...
... blood flow by predictable adjustments in cardiovascular physiology. This is compensated shock. Signs of compensated hypovolemic shock are tachycardia and peripheral vasoconstriction. Vasoconstriction causes the signs of abnormal circulation to skin: delayed capillary refill time, and decreased pulse ...
Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology (1st Diploma – option) Unit abstract
... The digestive system: parts of the digestive system and how they are involved in digestion, eg mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine; mechanical digestion (teeth, swallowing, peristalsis); chemical digestion (enzymatic breakdown of, eg carbohydrates, fats and proteins); absorption and ass ...
... The digestive system: parts of the digestive system and how they are involved in digestion, eg mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine; mechanical digestion (teeth, swallowing, peristalsis); chemical digestion (enzymatic breakdown of, eg carbohydrates, fats and proteins); absorption and ass ...
Midterm 2 - Creighton Biology
... a small number of slow oxidative fibers are each fully activated. a small number of fast glycolytic fibers are each fully activated. a large number of slow oxidative fibers are each partially activated. a large number of fast glycolytic fibers are each partially activated. all the fibers in the musc ...
... a small number of slow oxidative fibers are each fully activated. a small number of fast glycolytic fibers are each fully activated. a large number of slow oxidative fibers are each partially activated. a large number of fast glycolytic fibers are each partially activated. all the fibers in the musc ...
capillaries - Human Anatomy and Physiology
... muscular and elastic tissue • collapse when empty, expand easily • have steady blood flow • merge to form larger veins • subjected to relatively low blood pressure – remains 10 mm Hg with little fluctuation ...
... muscular and elastic tissue • collapse when empty, expand easily • have steady blood flow • merge to form larger veins • subjected to relatively low blood pressure – remains 10 mm Hg with little fluctuation ...
Anatomy 1
... Cephal- head. Cephalon is another term for the brain. (see capit-) Cerebro- brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is fluid circulating within the brain and spinal cord. Chole- bile, gall. Cholecestectomy is removal of the gallbladder. Chondro- cartilage. A chondrocyte is a cartilage cell. Chroma- color. ...
... Cephal- head. Cephalon is another term for the brain. (see capit-) Cerebro- brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is fluid circulating within the brain and spinal cord. Chole- bile, gall. Cholecestectomy is removal of the gallbladder. Chondro- cartilage. A chondrocyte is a cartilage cell. Chroma- color. ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... Cephal- head. Cephalon is another term for the brain. (see capit-) Cerebro- brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is fluid circulating within the brain and spinal cord. Chole- bile, gall. Cholecestectomy is removal of the gallbladder. Chondro- cartilage. A chondrocyte is a cartilage cell. Chroma- color. ...
... Cephal- head. Cephalon is another term for the brain. (see capit-) Cerebro- brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is fluid circulating within the brain and spinal cord. Chole- bile, gall. Cholecestectomy is removal of the gallbladder. Chondro- cartilage. A chondrocyte is a cartilage cell. Chroma- color. ...
Chapter 1 Chapter Overview Anatomy Physiology
... – groups of similar cells and the substances surrounding them that perform certain special functions. ...
... – groups of similar cells and the substances surrounding them that perform certain special functions. ...
The Human Body: Anatomical Regions, Directions, and Body Cavities
... Cardiovascular – operation of the heart and blood vessels ...
... Cardiovascular – operation of the heart and blood vessels ...
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Levels of Organization
... • Disorder = abnormality of function • Disease = homeostatic imbalance with distinct – symptoms---changes in body function felt by the patient such as nausea and – signs----changes in body function that can be observed by the doctor such as rash or fever ...
... • Disorder = abnormality of function • Disease = homeostatic imbalance with distinct – symptoms---changes in body function felt by the patient such as nausea and – signs----changes in body function that can be observed by the doctor such as rash or fever ...
Urinary System - Mohawk Medicinals
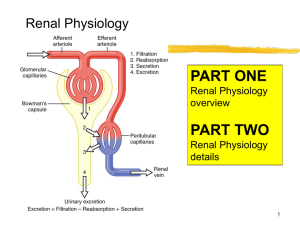
... Directly via nephron tubules Triggers release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex Contracts glomerular cells reducing the GFR Keeps blood in the capillaries (raises blood volume and BP) ...
... Directly via nephron tubules Triggers release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex Contracts glomerular cells reducing the GFR Keeps blood in the capillaries (raises blood volume and BP) ...
Blood Vessel - Oregon State University
... Methods of Autoregulation: 1) Metabolic Control: • Nutritional status of tissues regulate flow ...
... Methods of Autoregulation: 1) Metabolic Control: • Nutritional status of tissues regulate flow ...
CASE 14
... leg in such a way that flow is obstructed temporarily. However, reactive hyperemia also occurs along with active hyperemia during muscle contraction. For example, during contraction of ventricular muscle, vessels embedded in the myocardium are compressed to block flow. Metabolites continue to build ...
... leg in such a way that flow is obstructed temporarily. However, reactive hyperemia also occurs along with active hyperemia during muscle contraction. For example, during contraction of ventricular muscle, vessels embedded in the myocardium are compressed to block flow. Metabolites continue to build ...
Hypothalamic vascularization in the common tree
... communicating vein (ACoV) and the ACV by way of two main venous trunks. There are also some communicating venous channels situating near the anterior and lateral chiasmal borders that carry the venous blood into the venous networks in the interpeduncular fossa. Another venous arch called preinfundib ...
... communicating vein (ACoV) and the ACV by way of two main venous trunks. There are also some communicating venous channels situating near the anterior and lateral chiasmal borders that carry the venous blood into the venous networks in the interpeduncular fossa. Another venous arch called preinfundib ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology I BIO 201
... – x-rays discovered (William Roentgen) in 1885 – penetrate soft tissues & darken photographic film on other side of the body – dense tissue (bone, teeth and tumors) are not penetrated so photographic film remains white – radiopaque substances can be either injected (angiography) or swallowed for exa ...
... – x-rays discovered (William Roentgen) in 1885 – penetrate soft tissues & darken photographic film on other side of the body – dense tissue (bone, teeth and tumors) are not penetrated so photographic film remains white – radiopaque substances can be either injected (angiography) or swallowed for exa ...
Ministry of Health of Ukraine
... parietal layer, which lines the thoracic wall, covers the thoracic surface of the diaphragm and the lateral aspect of the mediastinum, and extends into the neck; visceral layer, which completely covers the outer surfaces of the lungs and extends into the depths of the interlobar fissures. The two la ...
... parietal layer, which lines the thoracic wall, covers the thoracic surface of the diaphragm and the lateral aspect of the mediastinum, and extends into the neck; visceral layer, which completely covers the outer surfaces of the lungs and extends into the depths of the interlobar fissures. The two la ...
Body Positioning
... * Breakdown of chemicals in the body so it can be absorbed * Mouth, tongue teeth, salivary gland, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small & large intestine, appendix, rectum ...
... * Breakdown of chemicals in the body so it can be absorbed * Mouth, tongue teeth, salivary gland, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small & large intestine, appendix, rectum ...
Circulatory system
The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, is an organ system that permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients (such as amino acids and electrolytes), oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilize temperature and pH, and maintain homeostasis. The study of the blood flow is called hemodynamics. The study of the properties of the blood flow is called hemorheology.The circulatory system is often seen to comprise both the cardiovascular system, which distributes blood, and the lymphatic system, which circulates lymph. These are two separate systems. The passage of lymph for example takes a lot longer than that of blood. Blood is a fluid consisting of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets that is circulated by the heart through the vertebrate vascular system, carrying oxygen and nutrients to and waste materials away from all body tissues. Lymph is essentially recycled excess blood plasma after it has been filtered from the interstitial fluid (between cells) and returned to the lymphatic system. The cardiovascular (from Latin words meaning 'heart' and 'vessel') system comprises the blood, heart, and blood vessels. The lymph, lymph nodes, and lymph vessels form the lymphatic system, which returns filtered blood plasma from the interstitial fluid (between cells) as lymph.While humans, as well as other vertebrates, have a closed cardiovascular system (meaning that the blood never leaves the network of arteries, veins and capillaries), some invertebrate groups have an open cardiovascular system. The lymphatic system, on the other hand, is an open system providing an accessory route for excess interstitial fluid to be returned to the blood. The more primitive, diploblastic animal phyla lack circulatory systems.