The Language of Anatomy
... Because the abdominopelvic cavity is quite large and contains many organs, it is helpful to divide it up into smaller areas for discussion or study. Most physicians and nurses use a scheme that divides the abdominal surface and the abdominopelvic cavity into four approximately equal regions called q ...
... Because the abdominopelvic cavity is quite large and contains many organs, it is helpful to divide it up into smaller areas for discussion or study. Most physicians and nurses use a scheme that divides the abdominal surface and the abdominopelvic cavity into four approximately equal regions called q ...
Ventral Body Cavity - Nutley Public Schools
... • Humans differ externally and internally – 90% of all structures present in body match description in textbook – Nerve or blood vessel may be out of place – Small muscle may be missing ...
... • Humans differ externally and internally – 90% of all structures present in body match description in textbook – Nerve or blood vessel may be out of place – Small muscle may be missing ...
Anatomical Terminology
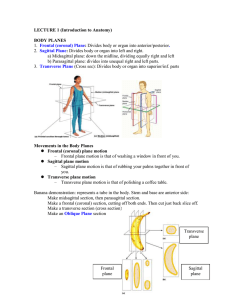
... • Describe the human body using directional and regional terms • Identify three planes most commonly used in the study of anatomy • Distinguish between the posterior (dorsal) and the anterior (ventral) body cavities, identifying their subdivisions and representative organs found in each • Describe s ...
... • Describe the human body using directional and regional terms • Identify three planes most commonly used in the study of anatomy • Distinguish between the posterior (dorsal) and the anterior (ventral) body cavities, identifying their subdivisions and representative organs found in each • Describe s ...
Study guide Exam #2 Sp 2012
... 3. Be familiar with the special characteristics and structure of each portion of the respiratory tract. 4. What is a deviated septum? What is cleft palate? 5. Know the regions of the pharynx 6. Know the structure of the larynx and the cartilage with which it is supported. 7. Be familiar with the voc ...
... 3. Be familiar with the special characteristics and structure of each portion of the respiratory tract. 4. What is a deviated septum? What is cleft palate? 5. Know the regions of the pharynx 6. Know the structure of the larynx and the cartilage with which it is supported. 7. Be familiar with the voc ...
The Language of Anatomy
... must learn to observe and identify the dissectible body structures formaJly. When beginning the study of any science, the student is often initially over come by jargon unique to the subject. The study of anatomy is no exception. But without this specialized terminology, confusion is inevitable. Fo ...
... must learn to observe and identify the dissectible body structures formaJly. When beginning the study of any science, the student is often initially over come by jargon unique to the subject. The study of anatomy is no exception. But without this specialized terminology, confusion is inevitable. Fo ...
Pelvis Muscle Table - Stritch School of Medicine
... Inferior rectal and transverse perineal Perineal artery ...
... Inferior rectal and transverse perineal Perineal artery ...
1-2 - Bloomsburg Area School District
... • Skeletal muscles and associated tendons Functions • Provides movement • Provides protection and support for other tissues • Generates heat that maintains body temperature ...
... • Skeletal muscles and associated tendons Functions • Provides movement • Provides protection and support for other tissues • Generates heat that maintains body temperature ...
Ch. 1 Outline
... 1. One-fifth of air 2. Used to release energy from nutrients D. Heat 1. Form of energy 2. Partly controls rate of metabolic reactions E. Pressure 1. Application of force on an object 2. Atmospheric pressure: important for breathing 3. Hydrostatic pressure: keeps blood flowing Homeostatic Control Mec ...
... 1. One-fifth of air 2. Used to release energy from nutrients D. Heat 1. Form of energy 2. Partly controls rate of metabolic reactions E. Pressure 1. Application of force on an object 2. Atmospheric pressure: important for breathing 3. Hydrostatic pressure: keeps blood flowing Homeostatic Control Mec ...
Introduction to Anatomy Module 6A and 6B
... By the end of this section, you will be able to: • Demonstrate the anatomical position • Describe the human body using directional and regional terms • Identify three planes most commonly used in the study of anatomy • Distinguish between the posterior (dorsal) and the anterior (ventral) body caviti ...
... By the end of this section, you will be able to: • Demonstrate the anatomical position • Describe the human body using directional and regional terms • Identify three planes most commonly used in the study of anatomy • Distinguish between the posterior (dorsal) and the anterior (ventral) body caviti ...
Body Organization
... These are terms used to describe the position of certain structures on the body. Note: These are “relative terms.” This means that these words are usually used in relating the position of one body structure to another. You can’t say, “He is shorter”. You have to say, “He is shorter than John”. Incor ...
... These are terms used to describe the position of certain structures on the body. Note: These are “relative terms.” This means that these words are usually used in relating the position of one body structure to another. You can’t say, “He is shorter”. You have to say, “He is shorter than John”. Incor ...
Chapter 2: Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
... In this chapter you will 4. Become acquainted with terms that ...
... In this chapter you will 4. Become acquainted with terms that ...
sheet #7 / Dr.Mohammad Al-Shayyab / A`amer
... muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle with motor fibers (posterior belly of digastric is innervated by the facial nerve). Also it contain some sensory fibers that supply the skin on the inferior and anterior surfaces of the mental protuberance. It also provides sensory innervation to ...
... muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle with motor fibers (posterior belly of digastric is innervated by the facial nerve). Also it contain some sensory fibers that supply the skin on the inferior and anterior surfaces of the mental protuberance. It also provides sensory innervation to ...
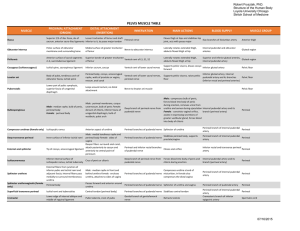
Slide 0
... A horizontal section through the thoracic cavity shows the relationship between the subdivisions of the ventral body cavity in this region. ...
... A horizontal section through the thoracic cavity shows the relationship between the subdivisions of the ventral body cavity in this region. ...
Hip Anatomy - Ronak Patel MD
... The hip joint is the junction where the hip joins the leg to the trunk of the body. It is comprised of two bones: the thigh bone or femur and the pelvis which is made up of three bones called ilium, ischium, and pubis. The ball of the hip joint is made by the femoral head while the socket is formed ...
... The hip joint is the junction where the hip joins the leg to the trunk of the body. It is comprised of two bones: the thigh bone or femur and the pelvis which is made up of three bones called ilium, ischium, and pubis. The ball of the hip joint is made by the femoral head while the socket is formed ...
The Language of Anatomy - E-Learning/An
... physiology. Let’s face it. You can’t just pick up an anatomy and physiology book and read it as though it were a novel. Unfortunately, confusion is inevitable without specialized terminology. For example, if you are looking at a ball, “above” always means the area over the top of the ball. Other dir ...
... physiology. Let’s face it. You can’t just pick up an anatomy and physiology book and read it as though it were a novel. Unfortunately, confusion is inevitable without specialized terminology. For example, if you are looking at a ball, “above” always means the area over the top of the ball. Other dir ...
Name: Investigation of a Chicken Wing Purpose The purpose of this
... 1. What material enables the skin to stretch instead of crack? 2. What function do you think is served by the bumps on the skin? They hold each feather. Muscles in them can contract to life the feathers, creating air pockets, so the bird can keep warm. 3. These bumps are similar to what structures i ...
... 1. What material enables the skin to stretch instead of crack? 2. What function do you think is served by the bumps on the skin? They hold each feather. Muscles in them can contract to life the feathers, creating air pockets, so the bird can keep warm. 3. These bumps are similar to what structures i ...
Untitled - Volvox Sport
... Joints are complex units which act as levers, hinges, and shock absorbers. Joints hold bones together, coordinate their movement so that bones slide across each other without friction; joints also allow us to perform every type of movement thanks to the functional unit formed by ligaments and tendon ...
... Joints are complex units which act as levers, hinges, and shock absorbers. Joints hold bones together, coordinate their movement so that bones slide across each other without friction; joints also allow us to perform every type of movement thanks to the functional unit formed by ligaments and tendon ...
Trace blood flow through body
... Physiology - Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations flashcards taken from the book Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual. 3 Objectives •Identify and discuss the factors involved in the generation of blood pressure and how they relate to each other •Define pulse and locate the major pulse. De ...
... Physiology - Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations flashcards taken from the book Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual. 3 Objectives •Identify and discuss the factors involved in the generation of blood pressure and how they relate to each other •Define pulse and locate the major pulse. De ...
Instructor`s Guide The Human Body: How It Works THE SKELETAL
... bony joint: The joint between bones that have fused together naturally (e.g., in the sacrum and coccyx). bony thorax: Also called the rib cage or thoracic cage, it consists of the sternum, ribs, and the twelve thoracic vertebrae. carpal bones: The eight bones of the wrist. cartilaginous joint: A joi ...
... bony joint: The joint between bones that have fused together naturally (e.g., in the sacrum and coccyx). bony thorax: Also called the rib cage or thoracic cage, it consists of the sternum, ribs, and the twelve thoracic vertebrae. carpal bones: The eight bones of the wrist. cartilaginous joint: A joi ...
PDF sample
... is favored in anatomy courses that include a dissecting laboratory component or a program that uses prosected specimens (specimens that were previously dissected). This textbook largely follows a regional approach, because most dental school anatomy programs include a laboratory component. Bones, jo ...
... is favored in anatomy courses that include a dissecting laboratory component or a program that uses prosected specimens (specimens that were previously dissected). This textbook largely follows a regional approach, because most dental school anatomy programs include a laboratory component. Bones, jo ...
Chapter 7_Time of Death
... exception of fetuses and newly born babies, the main source of these microorganisms in corpses is the right part of the large intestines. Microorganisms then invade the abdominal cavity, the chest, head, and limbs. The first visible signs of such activity are the greenish abdominal stains, accompani ...
... exception of fetuses and newly born babies, the main source of these microorganisms in corpses is the right part of the large intestines. Microorganisms then invade the abdominal cavity, the chest, head, and limbs. The first visible signs of such activity are the greenish abdominal stains, accompani ...
Sample Chapter
... Latin means “cutting,” because a fundamental way to learn about the human body is to cut it apart, or dissect (dis-sekt) it. Physiology (fiz-e-OL-o-je) is the term for the study of how the body functions, and is based on a Latin term meaning “nature.” Anatomy and physiology are closely related—that ...
... Latin means “cutting,” because a fundamental way to learn about the human body is to cut it apart, or dissect (dis-sekt) it. Physiology (fiz-e-OL-o-je) is the term for the study of how the body functions, and is based on a Latin term meaning “nature.” Anatomy and physiology are closely related—that ...
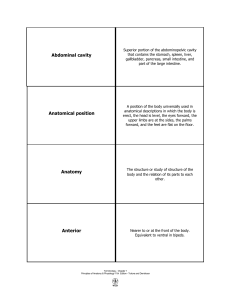
Abdominal cavity Anatomical position Anatomy Anterior
... Away from the head or toward the lower part of a structure. Also called caudad. ...
... Away from the head or toward the lower part of a structure. Also called caudad. ...
Head and neck anatomy

This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.