Gene Section BLM (Bloom) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... premature nonsense codons into the coding sequence have been described to date; one BLM mutation consisting in a 6 bp deletion accompanied by a 7 bp insertion at nucleic acid position 2281 is common in patients from Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry, leading to a truncated protein of 739 amino acids in leng ...
... premature nonsense codons into the coding sequence have been described to date; one BLM mutation consisting in a 6 bp deletion accompanied by a 7 bp insertion at nucleic acid position 2281 is common in patients from Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry, leading to a truncated protein of 739 amino acids in leng ...
Gibson Assembly™ – Building a Synthetic Biology Toolset
... involves the assembly of only eight to twelve 60-base oligonucleotides (with 30 bp overlaps) at one time. The resulting dsDNA molecules are sequence-verified and assembled into larger DNA fragments using the same approach. Because assembly itself does not generally introduce new errors, the final as ...
... involves the assembly of only eight to twelve 60-base oligonucleotides (with 30 bp overlaps) at one time. The resulting dsDNA molecules are sequence-verified and assembled into larger DNA fragments using the same approach. Because assembly itself does not generally introduce new errors, the final as ...
Primer Design Considerations for Adding a T7 Promoter
... Required: • T7 promoter sequence (5′-TAA TAC GAC TCA CTA TAG GG-3′). Required for transcription of the DNA template. • ATG start codon (5′-ATG-3′) if not present in the sequence being amplified. Needed for translation initiation. • Gene-specific sequence. Needed to allow priming of the ta ...
... Required: • T7 promoter sequence (5′-TAA TAC GAC TCA CTA TAG GG-3′). Required for transcription of the DNA template. • ATG start codon (5′-ATG-3′) if not present in the sequence being amplified. Needed for translation initiation. • Gene-specific sequence. Needed to allow priming of the ta ...
Topic 7.1
... • In which direction does DNA polymerase move along the template strand? What implication does this have for the addition of bases on the growing strand? A: DNA polymerase always moves in 5’ to 3’ direction. • Contrast replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. A: In prokaryotes there is one site of ...
... • In which direction does DNA polymerase move along the template strand? What implication does this have for the addition of bases on the growing strand? A: DNA polymerase always moves in 5’ to 3’ direction. • Contrast replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. A: In prokaryotes there is one site of ...
Appendix F - WordPress.com
... DNA is negatively charged and is repelled by the negative electrode (cathode) and attracted by the positive electrode (anode) when an electric current is applied across the gel. It separates because different lengths of DNA move through the gel matrix at different rates. Longer fragments move more s ...
... DNA is negatively charged and is repelled by the negative electrode (cathode) and attracted by the positive electrode (anode) when an electric current is applied across the gel. It separates because different lengths of DNA move through the gel matrix at different rates. Longer fragments move more s ...
Slide
... E-families diverge slowly, but persist for a long periods of time, thus diverging further than the paralogs in N-families N-families undergoes a more dynamic evolution: many duplicate get fixated, many other become pseudogenes. Level of sequence divergence is significantly lower. Duplicate in E-fami ...
... E-families diverge slowly, but persist for a long periods of time, thus diverging further than the paralogs in N-families N-families undergoes a more dynamic evolution: many duplicate get fixated, many other become pseudogenes. Level of sequence divergence is significantly lower. Duplicate in E-fami ...
Nerve activates contraction
... display many (but not all) characteristics of life…including the ability to EVOLVE! ...
... display many (but not all) characteristics of life…including the ability to EVOLVE! ...
DNA Structure and history10
... – purified DNA & proteins from Streptococcus bacteria – injected protein into bacteria ...
... – purified DNA & proteins from Streptococcus bacteria – injected protein into bacteria ...
fall break, take home exam
... Perform a BLASTN with this sequence against GenBank for an initial likely identification of the genome (mitochondrial or nuclear), and the organism. Perform A BLASTX with the correct genetic code to identify the name of the gene represented by this sequence: Genome (1 point): Organism (1 point): Gen ...
... Perform a BLASTN with this sequence against GenBank for an initial likely identification of the genome (mitochondrial or nuclear), and the organism. Perform A BLASTX with the correct genetic code to identify the name of the gene represented by this sequence: Genome (1 point): Organism (1 point): Gen ...
DNA Fingerprinting Lab
... One test used in forensic labs is DNA fingerprint. It is also called a DNA profile. Analysts use the DNA profile from potential suspects and compare it against DNA found at a crime scene. There’s DNA profiling for paternity tests. These days you can send a sample of DNA and find out your ancestry to ...
... One test used in forensic labs is DNA fingerprint. It is also called a DNA profile. Analysts use the DNA profile from potential suspects and compare it against DNA found at a crime scene. There’s DNA profiling for paternity tests. These days you can send a sample of DNA and find out your ancestry to ...
Chapter 10: Nucleic Acids And Protein Synthesis
... together to determine a specific amino acid 2. Several codons code for each amino acid 3. Start codon: AUG : tells the ribosome to start translating ...
... together to determine a specific amino acid 2. Several codons code for each amino acid 3. Start codon: AUG : tells the ribosome to start translating ...
Example: search for regulatory binding sites
... the so-called promoter region (TATA-box; or -10, -35) – Regulated by some (regulatory) proteins on DNA “near” the promoter region. – These binding sites on DNA are often “similar” in composition. Enhancers and repressors ...
... the so-called promoter region (TATA-box; or -10, -35) – Regulated by some (regulatory) proteins on DNA “near” the promoter region. – These binding sites on DNA are often “similar” in composition. Enhancers and repressors ...
ppt
... Use Fisher’s test to compare GO annotations of genes most and least differentially expressed (one test for each GO term) None significant with simple multiple testing adjustment, but there are many dependencies ...
... Use Fisher’s test to compare GO annotations of genes most and least differentially expressed (one test for each GO term) None significant with simple multiple testing adjustment, but there are many dependencies ...
Lecture 3 (BY 14)
... • Peptide bond – Type of covalent bond – Links amino group of one amino acid with carboxyl group of next – Forms through __________ _______ ...
... • Peptide bond – Type of covalent bond – Links amino group of one amino acid with carboxyl group of next – Forms through __________ _______ ...
Sequencing a genome and Basic Sequence Alignment
... The figure shows to sequences of nucleic acids. Some have the same base (nucleic acid ) and so there is a match at this position between the strands. This is represented by a vertical line and a blue highlight. Others do not match and have no vertical line and blue highlight: these are unmatched pai ...
... The figure shows to sequences of nucleic acids. Some have the same base (nucleic acid ) and so there is a match at this position between the strands. This is represented by a vertical line and a blue highlight. Others do not match and have no vertical line and blue highlight: these are unmatched pai ...
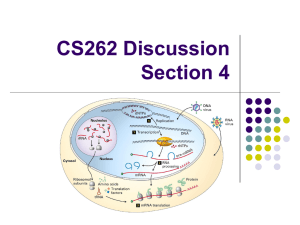
CS262 Discussion Section 4
... Deletions and insertions are collectively referred to as indels, because when two sequences are compared, it is impossible to tell whether a deletion has occurred in one, or an insertion has occurred in the other. In a coding region, an indel that is not a multiple of 3 nucleotides causes a frameshi ...
... Deletions and insertions are collectively referred to as indels, because when two sequences are compared, it is impossible to tell whether a deletion has occurred in one, or an insertion has occurred in the other. In a coding region, an indel that is not a multiple of 3 nucleotides causes a frameshi ...
HBS3 18. gene pool - Leeming-Biology-12
... • Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of allele frequencies in a population from one generation to the next. (e.g. the frequency of a particular trait could, for no obvious reason, drift from 2% in generation 1, to 11% in generation 2, to 5% in generation 3 etc.) ...
... • Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of allele frequencies in a population from one generation to the next. (e.g. the frequency of a particular trait could, for no obvious reason, drift from 2% in generation 1, to 11% in generation 2, to 5% in generation 3 etc.) ...
lesson viii - MisterSyracuse.com
... 7. These are the same as DNA, except Adenine pairs with Uracil, not Thymine. So the pairs are A with U, and C with G. Just to confuse you. 8. So there is a helicase that opens up the DNA, and then other proteins like gyrases and single-strand binding proteins to keep it open. 9. This time, though, ...
... 7. These are the same as DNA, except Adenine pairs with Uracil, not Thymine. So the pairs are A with U, and C with G. Just to confuse you. 8. So there is a helicase that opens up the DNA, and then other proteins like gyrases and single-strand binding proteins to keep it open. 9. This time, though, ...
Gene Interaction,sex linked inheritance
... another sex-linked trait. Hemophilia is treated by injecting the proper clotting proteins, isolated from the blood of normal people. In the early 1980’s, the blood supply was contaminated by HIV, the AIDS virus, and many hemophiliacs contracted AIDS at that time. Queen Victoria of England, who lived ...
... another sex-linked trait. Hemophilia is treated by injecting the proper clotting proteins, isolated from the blood of normal people. In the early 1980’s, the blood supply was contaminated by HIV, the AIDS virus, and many hemophiliacs contracted AIDS at that time. Queen Victoria of England, who lived ...
Biology~Chapter 12
... products leads to mental retardation. 1 in 15,000 infants has- treat with DIET! (no phenylalanine) Tay-Sachs Disease- degeneration of the nervous system. Children rarely survive past five years of ...
... products leads to mental retardation. 1 in 15,000 infants has- treat with DIET! (no phenylalanine) Tay-Sachs Disease- degeneration of the nervous system. Children rarely survive past five years of ...
Nature Nurture
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes – has two strands-forming a “double helix”- held together by bonds between pairs of nucleotides ...
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes – has two strands-forming a “double helix”- held together by bonds between pairs of nucleotides ...