M1 - Biochemistry Transcription III / mRNA Processing
... (2) removal of the intervening sequences “introns” with a splicing mechanism. (3) site-specific cleavage and polyA addition to the 3’ end, and Only ~1.5% of the human genome is translated into protein (“exons”, or coding segments of a gene). “Introns” are intervening nontranslated DNA sequences. ...
... (2) removal of the intervening sequences “introns” with a splicing mechanism. (3) site-specific cleavage and polyA addition to the 3’ end, and Only ~1.5% of the human genome is translated into protein (“exons”, or coding segments of a gene). “Introns” are intervening nontranslated DNA sequences. ...
Course Policies
... This is a literature-based seminar course, designed to introduce graduate students and advanced undergraduates to complex topics in genetics by close reading of primary literature. This course seeks to give students an in-depth appreciation of genetics by reading and evaluating the classic research ...
... This is a literature-based seminar course, designed to introduce graduate students and advanced undergraduates to complex topics in genetics by close reading of primary literature. This course seeks to give students an in-depth appreciation of genetics by reading and evaluating the classic research ...
Position Effect Variegation
... Advanced Molecular and Cellular Biology Bio4751 Spring 2003 Gary A. Bulla, PhD ...
... Advanced Molecular and Cellular Biology Bio4751 Spring 2003 Gary A. Bulla, PhD ...
Small, K, Wagener, M and Warren, ST: Isolation and characterization of the complete mouse emerin gene. Mammalian Genome 8:337-341 (1997).
... is, 1X) and female mouse DNAs (that is, 2X; data not shown). Mouse cDNA (of strain BALB/c) and exonic genomic sequences (of strain 129) were identical except for a single base (G or A) in the wobble position of codon 11 that did not change the amino acid sequence. All splice sites contained the cano ...
... is, 1X) and female mouse DNAs (that is, 2X; data not shown). Mouse cDNA (of strain BALB/c) and exonic genomic sequences (of strain 129) were identical except for a single base (G or A) in the wobble position of codon 11 that did not change the amino acid sequence. All splice sites contained the cano ...
PDF
... visual display methods using pedigrees, chronological tables, and Google Maps as well as delicate devices that have been adopted in these methods. Information about individual apes provided by the Primate Research Institute, Kyoto University, contains the results of the research projects and include ...
... visual display methods using pedigrees, chronological tables, and Google Maps as well as delicate devices that have been adopted in these methods. Information about individual apes provided by the Primate Research Institute, Kyoto University, contains the results of the research projects and include ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... a) is duplicated for some genes normally on six; b) is deficient for some genes normally on six; c) has picked up some genes from another chromosome; d) both a and b are correct; e) none of the above. 8. True or false: Due to the nature of the karyotypes shown here, there is no chance that this coup ...
... a) is duplicated for some genes normally on six; b) is deficient for some genes normally on six; c) has picked up some genes from another chromosome; d) both a and b are correct; e) none of the above. 8. True or false: Due to the nature of the karyotypes shown here, there is no chance that this coup ...
Exam 4 Review - Iowa State University
... 23.) Which of the following statements is true? A) The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability of a crossing over event will occur between them, B) The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are on the same chromosome has a maximum value of 100% C) All of the t ...
... 23.) Which of the following statements is true? A) The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability of a crossing over event will occur between them, B) The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are on the same chromosome has a maximum value of 100% C) All of the t ...
The Theoretical Course Of Directional Selection.
... case of semidominance, constant _T" The table brings out the extreme slowness with which favorable recessives rise from low frequencies if the selection coefficient is constant and corresponding extreme slowness with which favorable dominants approach complete fixation under this condition. ...
... case of semidominance, constant _T" The table brings out the extreme slowness with which favorable recessives rise from low frequencies if the selection coefficient is constant and corresponding extreme slowness with which favorable dominants approach complete fixation under this condition. ...
Small-Subunit Ribosomal RNA Sequence from
... after divergence of the ancestors of these two flagellate organisms. Extrachromosomal rRNA genes may therefore be the ancestral eukaryotic condition rather than a lineagespecific peculiarity. The positioning of the NaegZeria branch node so close to that of Euglena and Trypanosoma suggests a flagella ...
... after divergence of the ancestors of these two flagellate organisms. Extrachromosomal rRNA genes may therefore be the ancestral eukaryotic condition rather than a lineagespecific peculiarity. The positioning of the NaegZeria branch node so close to that of Euglena and Trypanosoma suggests a flagella ...
Document
... • Over long periods of time a sequence will acquire random mutations. – These mutations may result in a new amino acid at a given position, the deletion of an amino acid, or the introduction of a new one. – Over VERY long periods of time two sequences may diverge so much that their relationship can ...
... • Over long periods of time a sequence will acquire random mutations. – These mutations may result in a new amino acid at a given position, the deletion of an amino acid, or the introduction of a new one. – Over VERY long periods of time two sequences may diverge so much that their relationship can ...
Chapter 6.1 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
... units called genes A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. Genes determine how a body develops and functions. When genes are being used, the DNA is stretched out in the form of chromatin so that the information it contains ...
... units called genes A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. Genes determine how a body develops and functions. When genes are being used, the DNA is stretched out in the form of chromatin so that the information it contains ...
04BIO201 Exam 1 key
... 1. Albinism (lack of skin pigment) was thought to be caused solely by one recessive mutation in the gene encoding tyrosinase. However, a study from 1952 reported that two albino parents produced three normally pigmented children. How would you explain this phenomenon at a genetic level. In your answ ...
... 1. Albinism (lack of skin pigment) was thought to be caused solely by one recessive mutation in the gene encoding tyrosinase. However, a study from 1952 reported that two albino parents produced three normally pigmented children. How would you explain this phenomenon at a genetic level. In your answ ...
7 Genetics - Life Sciences
... enetics is the study of inheritance, the transmission of traits from parent to offspring and the expression of these traits. From earliest times, people have realized that certain traits in both plants and animals are passed on from parents to offspring. Artificial selection was practiced by farmers ...
... enetics is the study of inheritance, the transmission of traits from parent to offspring and the expression of these traits. From earliest times, people have realized that certain traits in both plants and animals are passed on from parents to offspring. Artificial selection was practiced by farmers ...
a. Define chromosome? Describe the structure, functions and their
... Ribosomes RNA, a molecular component of ribosomes, the cell's essential protein factory. Strictly speaking, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) does not make proteins. It makes polypeptides (assemblies of amino acids) that go to build up proteins.In the cytoplasm, ribsomal RNA (rRNA) and protein combine to form a ...
... Ribosomes RNA, a molecular component of ribosomes, the cell's essential protein factory. Strictly speaking, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) does not make proteins. It makes polypeptides (assemblies of amino acids) that go to build up proteins.In the cytoplasm, ribsomal RNA (rRNA) and protein combine to form a ...
The Genetic Basis for Evolution: Genetic Variation
... Mutations create new alleles of genes. Many (probably most) of these new alleles do not have any noticeable effect on the organism’s phenotype. Of those that do cause a change in the organism’s phenotype, most are likely to be harmful. But occasionally a mutation might be beneficial or useful! ...
... Mutations create new alleles of genes. Many (probably most) of these new alleles do not have any noticeable effect on the organism’s phenotype. Of those that do cause a change in the organism’s phenotype, most are likely to be harmful. But occasionally a mutation might be beneficial or useful! ...
Exemplar
... this portion of nucleic acid will code for a chain of eight amino acids. the sequence given will be complementary to the sequence C T C G T G C T T. the nucleic acid shown contains the sugar ribose. the nucleic acid shown is DNA. ...
... this portion of nucleic acid will code for a chain of eight amino acids. the sequence given will be complementary to the sequence C T C G T G C T T. the nucleic acid shown contains the sugar ribose. the nucleic acid shown is DNA. ...
life sciences p2
... this portion of nucleic acid will code for a chain of eight amino acids. the sequence given will be complementary to the sequence C T C G T G C T T. the nucleic acid shown contains the sugar ribose. the nucleic acid shown is DNA. ...
... this portion of nucleic acid will code for a chain of eight amino acids. the sequence given will be complementary to the sequence C T C G T G C T T. the nucleic acid shown contains the sugar ribose. the nucleic acid shown is DNA. ...
Lecture_12
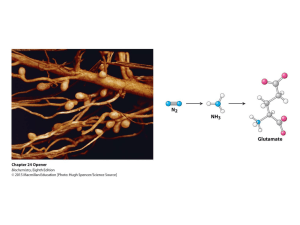
... Three key problems must be addressed to synthesize amino acids. 1. The inert N2 must be converted into an accessible from of nitrogen, usually NH3. 2. All the amino acids except glycine are chiral. Stereochemical control must yield only the L amino acids. 3. The amounts of the individual amino acid ...
... Three key problems must be addressed to synthesize amino acids. 1. The inert N2 must be converted into an accessible from of nitrogen, usually NH3. 2. All the amino acids except glycine are chiral. Stereochemical control must yield only the L amino acids. 3. The amounts of the individual amino acid ...
DNA transcription
... reached. For visualisation you can watch video at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gG7uCskUOrA. After a polypeptide chain is synthesized, it may undergo additional processes. For example, it may assume a folded shape due to interactions among its amino acids. It may also bind with other polypeptides ...
... reached. For visualisation you can watch video at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gG7uCskUOrA. After a polypeptide chain is synthesized, it may undergo additional processes. For example, it may assume a folded shape due to interactions among its amino acids. It may also bind with other polypeptides ...
How Relevant is the Escherichia coli UvrABC Model for Excision
... system responsible for the preferential repair of UVinduced CPDs from the transcribed strand of active genes (Venema et al. 1990a, for a review on preferential repair, see e.g. Smith and Mellon, 1990). The subpathway dealing with the slower and less-complete removal of lesions from the genome overal ...
... system responsible for the preferential repair of UVinduced CPDs from the transcribed strand of active genes (Venema et al. 1990a, for a review on preferential repair, see e.g. Smith and Mellon, 1990). The subpathway dealing with the slower and less-complete removal of lesions from the genome overal ...