CH2 Organic Chem notes only OrganicChem13
... Carbohydrates: C, H, and O ratio near 1:2:1 Main function ENERGY!!! Monosaccharides: simplest, glucose; most important metabolic fuel source C6 H12 O6 ...
... Carbohydrates: C, H, and O ratio near 1:2:1 Main function ENERGY!!! Monosaccharides: simplest, glucose; most important metabolic fuel source C6 H12 O6 ...
Enzyme - Northwest ISD Moodle
... chemical reactions in living organisms by decreasing the energy needed to start the Energy reaction (activation energy) ...
... chemical reactions in living organisms by decreasing the energy needed to start the Energy reaction (activation energy) ...
Arabidopsis Contains Nine Long-Chain Acyl
... chain fatty acids requires an active transport mechanism of some type, like the carnitine shuttle in mammalian mitochondrial -oxidation (Eaton et al., 1996) or receptor-mediated import as in yeast peroxisomes (Hettema and Tabak, 2000). In yeast, some evidence suggests that short- and medium-chain f ...
... chain fatty acids requires an active transport mechanism of some type, like the carnitine shuttle in mammalian mitochondrial -oxidation (Eaton et al., 1996) or receptor-mediated import as in yeast peroxisomes (Hettema and Tabak, 2000). In yeast, some evidence suggests that short- and medium-chain f ...
Amino acids and proteins
... One necklace may differ from another by the order of the beads and the frequency with which they occur Different amino acid content and sequence alters the properties of proteins ...
... One necklace may differ from another by the order of the beads and the frequency with which they occur Different amino acid content and sequence alters the properties of proteins ...
Structure, function and selective inhibition of bacterial acetyl
... for growth in vitro in a number of bacteria including Escherichia coli (Gerdes et al. 2003), Staphylococcus aureus (Forsyth et al. 2002; Payne et al. 2007) Streptococcus pneumoniae (Thanassi et al. 2002), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Sassetti et al. 2003), Helicobacter pylori (Salama et al. 2004) and ...
... for growth in vitro in a number of bacteria including Escherichia coli (Gerdes et al. 2003), Staphylococcus aureus (Forsyth et al. 2002; Payne et al. 2007) Streptococcus pneumoniae (Thanassi et al. 2002), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Sassetti et al. 2003), Helicobacter pylori (Salama et al. 2004) and ...
STRUCTURE OF ATP
... Under anaerobic conditions , pyruvate undergoes reductive decarboxylation to yield CO 2 and ethyl alcohol.Very less amount of energy is generated through this type of respiration in the cytoplasm of living cells. This occurs in lower organisms , such as many bacteria and some fungi. AEROBIC RESPIRAT ...
... Under anaerobic conditions , pyruvate undergoes reductive decarboxylation to yield CO 2 and ethyl alcohol.Very less amount of energy is generated through this type of respiration in the cytoplasm of living cells. This occurs in lower organisms , such as many bacteria and some fungi. AEROBIC RESPIRAT ...
Chapter 15 Cori and Alanine Cycles: Cori Cycle: Occurs between
... →Requires 2ATP/glucose molecule attached to a glycogen chain. →Pathway utilizes UDP-glucose as the activated glucose donor. UDP-glucose is activated because its hydroxyl group is esterified to the diphosphate moity of UDP. →UDP-glucose is added to the nonreducing ends of the glycogen molecule. ...
... →Requires 2ATP/glucose molecule attached to a glycogen chain. →Pathway utilizes UDP-glucose as the activated glucose donor. UDP-glucose is activated because its hydroxyl group is esterified to the diphosphate moity of UDP. →UDP-glucose is added to the nonreducing ends of the glycogen molecule. ...
Bil 255 – CMB
... 1. oxidation of COOH end of free fatty acid 2. transport of fatty acyl-coA into mitoplasm 3. oxidation of 2 carbon fragments as AcoA ...
... 1. oxidation of COOH end of free fatty acid 2. transport of fatty acyl-coA into mitoplasm 3. oxidation of 2 carbon fragments as AcoA ...
Amino Acid Synthesis in a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
... one of the essential materials for chemical evolution in early Earth. The prebiotic synthesis by electric discharge in reducing gasses (CH4, NH3, H2, and H2O) through Miller’s experiment has given experimental support to the chemical evolution [2]. After Miller’s report, many prebiotic syntheses in ...
... one of the essential materials for chemical evolution in early Earth. The prebiotic synthesis by electric discharge in reducing gasses (CH4, NH3, H2, and H2O) through Miller’s experiment has given experimental support to the chemical evolution [2]. After Miller’s report, many prebiotic syntheses in ...
Plant cuticles shine: advances in wax biosynthesis
... VLCFA precursors for cuticular wax production are synthesized in the epidermal cells by the multienzyme fatty acid elongase (FAE) complex found on the ER. Using plastid-generated C16 or C18 fatty acids and malonylcoenzyme A (CoA) as substrates, FAE performs a reiterative cycle of four reactions cata ...
... VLCFA precursors for cuticular wax production are synthesized in the epidermal cells by the multienzyme fatty acid elongase (FAE) complex found on the ER. Using plastid-generated C16 or C18 fatty acids and malonylcoenzyme A (CoA) as substrates, FAE performs a reiterative cycle of four reactions cata ...
File
... broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid • takes place in cytosol of cytoplasm • does not require oxygen • converts glucose, ADP, and NAD+ • to pyruvic acid, ATP, and NADH • net production of ATP: 2 ATP ...
... broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid • takes place in cytosol of cytoplasm • does not require oxygen • converts glucose, ADP, and NAD+ • to pyruvic acid, ATP, and NADH • net production of ATP: 2 ATP ...
C H
... This set of lectures on bioorganic chemistry intend for non-chemistry students, mainly those entering health sciences and related fields, such as medicine, dentistry. It also can be useful for students in environmental studies. Most students who take such courses consider bioorganic chemistry to be ...
... This set of lectures on bioorganic chemistry intend for non-chemistry students, mainly those entering health sciences and related fields, such as medicine, dentistry. It also can be useful for students in environmental studies. Most students who take such courses consider bioorganic chemistry to be ...
Bioenergetics and ioenergetics and Metabolism etabolism
... molecular oxygen is used to oxidize the coenzymes, which are reduced in the other 4 pathways, with the production of water and the conversion of ADP plus phosphate into ATP. One of the 5 energy-supplying processes, the glycolytic pathway, can be distinguished from the others because it is capable of ...
... molecular oxygen is used to oxidize the coenzymes, which are reduced in the other 4 pathways, with the production of water and the conversion of ADP plus phosphate into ATP. One of the 5 energy-supplying processes, the glycolytic pathway, can be distinguished from the others because it is capable of ...
Variability of Wax Ester Fermentation in Natural and Bleached
... it employs some enzymes shared with hydrogenosomes, but generates very different end products. Several Euglena species can grow at very low oxygen concentrations (Buetow 1989a): Euglena gracilis can survive up to 6 mo of hypoxia when grown in the dark with culturing on lactate (Carre, Bomsel, and Ca ...
... it employs some enzymes shared with hydrogenosomes, but generates very different end products. Several Euglena species can grow at very low oxygen concentrations (Buetow 1989a): Euglena gracilis can survive up to 6 mo of hypoxia when grown in the dark with culturing on lactate (Carre, Bomsel, and Ca ...
Glucose homeostasis in the blood (2) – un-storing energy
... Because the brain normally relies on glucose for energy, there must be a constant supply of glucose into the blood stream even when other tissues are using fatty acids or amino acids as their energy source. When glycogen stores are not enough, the liver will make new glucose to export into the blood ...
... Because the brain normally relies on glucose for energy, there must be a constant supply of glucose into the blood stream even when other tissues are using fatty acids or amino acids as their energy source. When glycogen stores are not enough, the liver will make new glucose to export into the blood ...
04 Purine_degradation-Gout
... final product of purine degradation is uric acid Uric acid is excreted in the urine Some animals convert uric acid to other products: ...
... final product of purine degradation is uric acid Uric acid is excreted in the urine Some animals convert uric acid to other products: ...
Microbiology - Chapter 7 & 8
... Several enzymes systematically oxidize the citric acid into a 5-C acid, then a 4-C acid and eventually back to the original oxaloacetic acid – thus a cycle. Each time the terminal carboxyl group is removed a CO2 molecule is produced. Thus, one glucose, causes the cycle to turn twice, each turn produ ...
... Several enzymes systematically oxidize the citric acid into a 5-C acid, then a 4-C acid and eventually back to the original oxaloacetic acid – thus a cycle. Each time the terminal carboxyl group is removed a CO2 molecule is produced. Thus, one glucose, causes the cycle to turn twice, each turn produ ...
a source of carbon , essential amino acids , essential fatty acids
... •Insects require basically the same nutrients as most other animals: a source of carbon , essential amino acids , essential fatty acids , inorganic salts , vitamins and a source of sterol. Water is also an essential nutrient. •Essential Nutrients are nutrients that require a diet source since they c ...
... •Insects require basically the same nutrients as most other animals: a source of carbon , essential amino acids , essential fatty acids , inorganic salts , vitamins and a source of sterol. Water is also an essential nutrient. •Essential Nutrients are nutrients that require a diet source since they c ...
Production of the Novel Lipopeptide Antibiotic Trifluorosurfactin via
... characteristics or improving their biological activity. ...
... characteristics or improving their biological activity. ...
HERE
... o α-Amino groups of most amino acids are ultimately transferred to αOxoglutarate by Transamination, forming Glutamate, the Amino group is then removed as Ammonia by Oxidation ...
... o α-Amino groups of most amino acids are ultimately transferred to αOxoglutarate by Transamination, forming Glutamate, the Amino group is then removed as Ammonia by Oxidation ...
Amino Acids
... • Tertiary structure is formed by packing structural elements into one or several compact globular units called domains. • The final protein may contain several polypeptide chains arranged in a quaternary structure. By formation of structures, amino acids far apart in the sequence can be brought clo ...
... • Tertiary structure is formed by packing structural elements into one or several compact globular units called domains. • The final protein may contain several polypeptide chains arranged in a quaternary structure. By formation of structures, amino acids far apart in the sequence can be brought clo ...
89. Carboxylic Acids as a Traceless Activation Group for Conjugate Additions: A Three-�Step Synthesis of (�)-�Lyrica
... conditions followed by treatment with acid promoted decarboxylation to afford racemic pregabalin in only three steps. In conclusion, we have demonstrated the utility of carboxylic acids as a traceless activation group for radical conjugate addition via visible light-mediated photoredox catalysis. The ...
... conditions followed by treatment with acid promoted decarboxylation to afford racemic pregabalin in only three steps. In conclusion, we have demonstrated the utility of carboxylic acids as a traceless activation group for radical conjugate addition via visible light-mediated photoredox catalysis. The ...
Midterm #2 - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... d) Assume that the PMF of the mitochondria (calculated above) is not coupled to the synthesis of ATP but is coupled to the uptake of pyruvate from the cytosol into the mitochondria (one proton and one molecule of pyruvate are co-transported into the mitochondria). Calculate the gradient of pyruvate ...
... d) Assume that the PMF of the mitochondria (calculated above) is not coupled to the synthesis of ATP but is coupled to the uptake of pyruvate from the cytosol into the mitochondria (one proton and one molecule of pyruvate are co-transported into the mitochondria). Calculate the gradient of pyruvate ...
Amines and amino acids
... Primary structure: sequence of amino acids in the protein chain Secondary structure: folding or twisting of the protein backbone Tertiary structure: 3-D structure of the entire protein chain Quarternary structure: In proteins composed of more than one chain, how these chains associate with e ...
... Primary structure: sequence of amino acids in the protein chain Secondary structure: folding or twisting of the protein backbone Tertiary structure: 3-D structure of the entire protein chain Quarternary structure: In proteins composed of more than one chain, how these chains associate with e ...
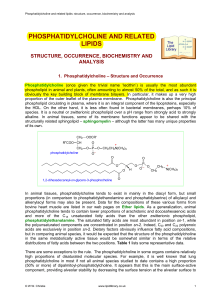
PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE AND RELATED LIPIDS
... sometimes termed the ‘Lands cycle’. The re-acylation step is catalysed by a specific lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase, which has been located within the endoplasmic reticulum in organs such as the liver, adipose tissue and pancreas. For example, the highly saturated molecular species of phosp ...
... sometimes termed the ‘Lands cycle’. The re-acylation step is catalysed by a specific lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase, which has been located within the endoplasmic reticulum in organs such as the liver, adipose tissue and pancreas. For example, the highly saturated molecular species of phosp ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.