Determination of Amino Acids in Wort and Beer by Reverse
... Several precolumn derivatization techniques have been applied to HPLC systems, using a reverse-phase column for separation. Two of the most widely used procedures are formation of derivates withdansyl (23), or o-phthaldialdehyde/2-mercaptoethanol (OPA/2-ME) (7,22). Nevertheless, dansyl derivates do ...
... Several precolumn derivatization techniques have been applied to HPLC systems, using a reverse-phase column for separation. Two of the most widely used procedures are formation of derivates withdansyl (23), or o-phthaldialdehyde/2-mercaptoethanol (OPA/2-ME) (7,22). Nevertheless, dansyl derivates do ...
2.277 December 2005 Final Exam
... An enzyme-catalyzed reaction was carried out with the substrate concentration initially 10 times greater than the Km for that substrate. After 15 minutes, 2% of the substrate had been converted to product, and the amount of product formed in the reaction mixture was 45 µmol. If, in a separate experi ...
... An enzyme-catalyzed reaction was carried out with the substrate concentration initially 10 times greater than the Km for that substrate. After 15 minutes, 2% of the substrate had been converted to product, and the amount of product formed in the reaction mixture was 45 µmol. If, in a separate experi ...
Anaerobic Respiration Gibb`s Free Energy PPT
... Fermentation compared to Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic ...
... Fermentation compared to Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic ...
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... H3N—CH2—COOH Positive ion at a pH lower than pI Total charge = 1+ ...
... H3N—CH2—COOH Positive ion at a pH lower than pI Total charge = 1+ ...
Amino acids used in Animal Nutrition
... Since there are only 20 amino acids, several will repeat! A protein is made up of one or more polypeptide chains ...
... Since there are only 20 amino acids, several will repeat! A protein is made up of one or more polypeptide chains ...
Formation of Benzoic Acid and
... synthase system as the chloroplasts of higher plants (Table V ). That can be seen if one compares the 3H /14C ratio in the product, benzoic acid, with the respective value in the possible intermediate, cin namic acid: 5.4 versus 0.12. In the column which outlines the amount of [3H] cinnamic acid pr ...
... synthase system as the chloroplasts of higher plants (Table V ). That can be seen if one compares the 3H /14C ratio in the product, benzoic acid, with the respective value in the possible intermediate, cin namic acid: 5.4 versus 0.12. In the column which outlines the amount of [3H] cinnamic acid pr ...
Chapter 9: Fermentation
... •Both use NAD+ as an electron acceptor. •In fermentation, the electrons of NADH are passed to an organic molecule, regenerating NAD+. • In respiration, the electrons of NADH are ultimately passed to O2, generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. •In addition, even more ATP is generated from the o ...
... •Both use NAD+ as an electron acceptor. •In fermentation, the electrons of NADH are passed to an organic molecule, regenerating NAD+. • In respiration, the electrons of NADH are ultimately passed to O2, generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. •In addition, even more ATP is generated from the o ...
Practical Methods for Biocatalysis and Biotransformations 2 Brochure
... are given and relevant references to the primary literature are cited. This second volume which can be used on its own or in combination with the first volume – concentrates on new techniques and new enzyme families that have been reported since the first volume. Up–to–date protocols and industry ex ...
... are given and relevant references to the primary literature are cited. This second volume which can be used on its own or in combination with the first volume – concentrates on new techniques and new enzyme families that have been reported since the first volume. Up–to–date protocols and industry ex ...
CHAPTER 6
... • SIRT1 binding to PPAR g represses transcription of these genes, leading to loss of fat stores. • Because adipose tissue functions as an endocrine organ, this loss of fat has significant hormonal consequences for energy metabolism ...
... • SIRT1 binding to PPAR g represses transcription of these genes, leading to loss of fat stores. • Because adipose tissue functions as an endocrine organ, this loss of fat has significant hormonal consequences for energy metabolism ...
Development of a novel analytical approach combining the quantification of
... plethora of metabolites in biological fluids such as cell or tissue extracts, urine, plasma, and seminal, amniotic23 or cerebrospinal fluids has consequently made metabolomics an encouraging science which can provide an integrated view of the whole system.24 Note that not only is metabolomics focuse ...
... plethora of metabolites in biological fluids such as cell or tissue extracts, urine, plasma, and seminal, amniotic23 or cerebrospinal fluids has consequently made metabolomics an encouraging science which can provide an integrated view of the whole system.24 Note that not only is metabolomics focuse ...
Chapter 17 Lipids
... Stearic acid is saturated and would have a higher melting point than the unsaturated fatty acids. Because linoleic has two double bonds, it would have a lower mp than oleic acid, which has one double ...
... Stearic acid is saturated and would have a higher melting point than the unsaturated fatty acids. Because linoleic has two double bonds, it would have a lower mp than oleic acid, which has one double ...
Arabidopsis 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase 9 is involved in the synthesis
... suberins, phospholipids, sphingolipids, and seed oils in the Brassicaceae. These lipids are involved in various functions, such as acting as protective barriers between plants and the environment, impermeable barriers to water and ions, energy-storage compounds in seeds, structural components of mem ...
... suberins, phospholipids, sphingolipids, and seed oils in the Brassicaceae. These lipids are involved in various functions, such as acting as protective barriers between plants and the environment, impermeable barriers to water and ions, energy-storage compounds in seeds, structural components of mem ...
Carbohydrate and sugar structure
... •Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): type M [skeletal muscle and liver] participates in the reduction of pyruvate to lactate (using NADH) while type H [heart muscle] catalyzes the reverse reaction. ...
... •Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): type M [skeletal muscle and liver] participates in the reduction of pyruvate to lactate (using NADH) while type H [heart muscle] catalyzes the reverse reaction. ...
Application Note
... using UHPLC, long equilibration and analysis times can be avoided. Furthermore a UV detection of amino acid concentrations in the range of 5 pmol to 500 pmol can be realized. The separation of hydrolyzed baby food demonstrates the potential of this analysis for several application areas. Investigati ...
... using UHPLC, long equilibration and analysis times can be avoided. Furthermore a UV detection of amino acid concentrations in the range of 5 pmol to 500 pmol can be realized. The separation of hydrolyzed baby food demonstrates the potential of this analysis for several application areas. Investigati ...
Protein mteabolism
... I- Removal of α-amino group: The removal of amino group takes place in two steps which are Transamination (that produce glutamate) followed by oxidative deamination of the produced glutamate to give ammonia. Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield ...
... I- Removal of α-amino group: The removal of amino group takes place in two steps which are Transamination (that produce glutamate) followed by oxidative deamination of the produced glutamate to give ammonia. Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield ...
Information Sheet - HJ Baker & Bro., Inc.
... Fishmeal contains many nutrients including: balanced source of essential amino acids, rich source of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids and cholesterol, vitamins and trace minerals, phosphorus, attractants such as free amino acids, nucleotides, and quaternary ammonium compounds, and ...
... Fishmeal contains many nutrients including: balanced source of essential amino acids, rich source of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids and cholesterol, vitamins and trace minerals, phosphorus, attractants such as free amino acids, nucleotides, and quaternary ammonium compounds, and ...
Metabolism
... two ATP from the cytoplasm. Substrate-level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation Each NADH produces net 2 ATP due to NADH transport over the mitrochondrial ...
... two ATP from the cytoplasm. Substrate-level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation Each NADH produces net 2 ATP due to NADH transport over the mitrochondrial ...
VITAMINS-6
... Vitamin B7 : What’s the role • Biotin is attached at the active site of five mammalian enzymes known as carboxylases • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase I and II catalyze the binding of bicarbonate to acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA • Malonyl-CoA is required for the synthesis of fatty acids • Pyruvate carboxyl ...
... Vitamin B7 : What’s the role • Biotin is attached at the active site of five mammalian enzymes known as carboxylases • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase I and II catalyze the binding of bicarbonate to acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA • Malonyl-CoA is required for the synthesis of fatty acids • Pyruvate carboxyl ...
Key - UCSB CLAS
... 1. What role do cofactors play? Give 2 examples of cofactors. Cofactors are molecules or metal ions that work with enzymes in biochemical reactions – examples include NAD+, FAD, TPP, biotin, PLP, lipoate, and CoASH 2. Niacin is required to make the coenzymes NAD+, NADP+, NADH and NADPH which are nec ...
... 1. What role do cofactors play? Give 2 examples of cofactors. Cofactors are molecules or metal ions that work with enzymes in biochemical reactions – examples include NAD+, FAD, TPP, biotin, PLP, lipoate, and CoASH 2. Niacin is required to make the coenzymes NAD+, NADP+, NADH and NADPH which are nec ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... acetate - is not possible with TCA • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-evolving steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is utilized • Isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are the short-circuiting enzymes ...
... acetate - is not possible with TCA • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-evolving steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is utilized • Isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are the short-circuiting enzymes ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... acetate - is not possible with TCA • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-evolving steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is utilized • Isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are the short-circuiting enzymes ...
... acetate - is not possible with TCA • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-evolving steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is utilized • Isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are the short-circuiting enzymes ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... 1. The preparatory (prep) reaction connects glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. 2. In this reaction, pyruvate is converted to a two-carbon acetyl group, and is attached to coenzyme A, resulting in the compound acetyl-CoA. 3. This reaction occurs twice for each glucose molecule. 4. CoA carries the ...
... 1. The preparatory (prep) reaction connects glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. 2. In this reaction, pyruvate is converted to a two-carbon acetyl group, and is attached to coenzyme A, resulting in the compound acetyl-CoA. 3. This reaction occurs twice for each glucose molecule. 4. CoA carries the ...
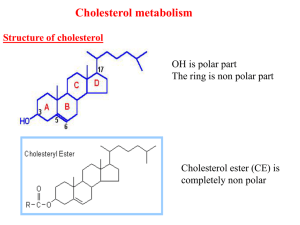
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... (high CHO diet) the excess acetyl CoA produced from glucose oxidation is used for biosynthesis of both FA and cholesterol ...
... (high CHO diet) the excess acetyl CoA produced from glucose oxidation is used for biosynthesis of both FA and cholesterol ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.