Next-generation protein drugs
... (such as phage3 or ribosome display4) to select a range of binders to a given therapeutic target; and fourth, use some form of screen to identify those leads that have the desired biological activity. If all goes according to plan, the outcome should be a protein that has all the desirable biophysic ...
... (such as phage3 or ribosome display4) to select a range of binders to a given therapeutic target; and fourth, use some form of screen to identify those leads that have the desired biological activity. If all goes according to plan, the outcome should be a protein that has all the desirable biophysic ...
Attomole Detection of Proteins in a Complex Mixture Using the
... Protein identification is often challenged by the sensitivity and specificity required. For example, the presence of contaminating peptides within the collision cell during the collision-induced dissociation process leading to mixed fragment ion spectra is often ignored. This is overcome by the use ...
... Protein identification is often challenged by the sensitivity and specificity required. For example, the presence of contaminating peptides within the collision cell during the collision-induced dissociation process leading to mixed fragment ion spectra is often ignored. This is overcome by the use ...
1.4.1: Draw a diagram of the fluid mosaic model:
... Gasses move easily… charged things or things that are large? Nope… ...
... Gasses move easily… charged things or things that are large? Nope… ...
Ligand Binding - Stroud
... • Thermodynamics of Protein Assembly • Structural Change on complexation • Empirical fitting of Atomic Interactions with Free Energy of Association • Estimate of free energy of H bonds and charge interactions in protein complexes and role of hydrophobic effect _______________________________________ ...
... • Thermodynamics of Protein Assembly • Structural Change on complexation • Empirical fitting of Atomic Interactions with Free Energy of Association • Estimate of free energy of H bonds and charge interactions in protein complexes and role of hydrophobic effect _______________________________________ ...
PowerPoint-presentatie
... Assessment of the pipeline's performance Coverage: up to 42%, 22% and 42%, respectively for the human, yeast and Arabidopsis subsets. ...
... Assessment of the pipeline's performance Coverage: up to 42%, 22% and 42%, respectively for the human, yeast and Arabidopsis subsets. ...
Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Human E. coli
... share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage of their precursor proteins, and each corresponds to approximately one half of the N-terminal portion of the precursor mole ...
... share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage of their precursor proteins, and each corresponds to approximately one half of the N-terminal portion of the precursor mole ...
L2 - Proteins
... The specific 3-D shape of a protein resulting from interactions between “R” groups of amino acid residues. ...
... The specific 3-D shape of a protein resulting from interactions between “R” groups of amino acid residues. ...
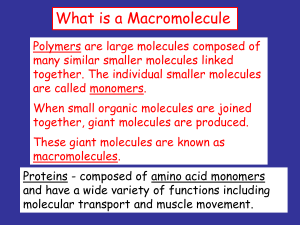
What is a Macromolecule
... • Hemoglobin is a protein found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) and this is what actually carries the oxygen found in blood • Four oxygen atoms can bond to each hemoglobin (one to each major subunit of hemoglobin) ...
... • Hemoglobin is a protein found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) and this is what actually carries the oxygen found in blood • Four oxygen atoms can bond to each hemoglobin (one to each major subunit of hemoglobin) ...
An Agriscience Lesson Plan: Protein Needs
... • No danger in over feeding protein, but it is usually the most expensive part of the feed • Once the animal has consumed all the protein needed for cell construction, muscle, fetal growth, etc., the rest is broken down for energy • Carbohydrates are a cheaper source of energy ...
... • No danger in over feeding protein, but it is usually the most expensive part of the feed • Once the animal has consumed all the protein needed for cell construction, muscle, fetal growth, etc., the rest is broken down for energy • Carbohydrates are a cheaper source of energy ...
Essential Amino Acids
... Protein requirements depend on the individual and daily activity. Tissue growth, whether due to growth, injury, weight training, or pregnancy effect protein requirements. During illness, protein is not only required for repair but is generally used as an energy source. According to RDA requirements, ...
... Protein requirements depend on the individual and daily activity. Tissue growth, whether due to growth, injury, weight training, or pregnancy effect protein requirements. During illness, protein is not only required for repair but is generally used as an energy source. According to RDA requirements, ...
Lab Activity 1
... • Passage of solutes through a semi-permeable membrane. • Pores in the dialysis membrane are of a certain size. • Protein stays in; water, salts, protein fragments, and other molecules smaller than the pore size pass through. ...
... • Passage of solutes through a semi-permeable membrane. • Pores in the dialysis membrane are of a certain size. • Protein stays in; water, salts, protein fragments, and other molecules smaller than the pore size pass through. ...
Self-assessment quiz for young scientist interested in autumn school
... 3. Why do Heparin-binding proteins often have many basic groups? 4. Why are ionic amino acid residues rarely found inside proteins, but frequently on the surface? 5. Flexible ligands often bind with lower affinity to proteins compared to similarly composed but more rigid ligands. What could be the r ...
... 3. Why do Heparin-binding proteins often have many basic groups? 4. Why are ionic amino acid residues rarely found inside proteins, but frequently on the surface? 5. Flexible ligands often bind with lower affinity to proteins compared to similarly composed but more rigid ligands. What could be the r ...
PPT (without movies)
... 1) A polar/charged core with mostly nonpolar residues on the surface. 2) A nonpolar core with mostly polar/charged residues on the surface. 3) An even mix of polar/charged and nonpolar residues in the core and on the surface. 4) Fatty acids on the inside, ribonucleotides on the outside. 5) Ralph Lau ...
... 1) A polar/charged core with mostly nonpolar residues on the surface. 2) A nonpolar core with mostly polar/charged residues on the surface. 3) An even mix of polar/charged and nonpolar residues in the core and on the surface. 4) Fatty acids on the inside, ribonucleotides on the outside. 5) Ralph Lau ...
Protein Feed - Article 43 of Regulation (EC) No 889/2008
... through for example, national actions plans in some Member states that promote local protein feed production. As these action plans are only in their infancy state or don’t even exist yet, any significant impact cannot be expected before 2018. In the meantime, other solutions should be explored, e.g ...
... through for example, national actions plans in some Member states that promote local protein feed production. As these action plans are only in their infancy state or don’t even exist yet, any significant impact cannot be expected before 2018. In the meantime, other solutions should be explored, e.g ...
Chapter 20 Amino acids and proteins
... Chapter 20 Amino acids and proteins 20.1: functions of proteins 1. Be able to list the 7 classes of proteins and their function in the cell or body. 20.2 amino acids 1. Draw the structure of amino acids 2. Given an amino acid, classify it as non-polar, polar, acidic, or basic. 3. Given an amino acid ...
... Chapter 20 Amino acids and proteins 20.1: functions of proteins 1. Be able to list the 7 classes of proteins and their function in the cell or body. 20.2 amino acids 1. Draw the structure of amino acids 2. Given an amino acid, classify it as non-polar, polar, acidic, or basic. 3. Given an amino acid ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... disulphide bonds and lack the tertiary structure. • The solubility of casein depends greatly on the PH of the medium. • The intermediate PH at which a protein molecule has a charge of zero is called, the isoelectric point of that protein. • At this point the solubility of protein is minimum, but inc ...
... disulphide bonds and lack the tertiary structure. • The solubility of casein depends greatly on the PH of the medium. • The intermediate PH at which a protein molecule has a charge of zero is called, the isoelectric point of that protein. • At this point the solubility of protein is minimum, but inc ...
Protein Synthesis in a Eukaryotic Cell.
... Protein synthesis – the generation of new proteins from amino acid subunits; in the cell, it includes transcription and translation Transcription – the process of deciphering a DNA nucleotide code and converting it into RNA nucleotide code; the RNA carries the genetic message to a ribosome for trans ...
... Protein synthesis – the generation of new proteins from amino acid subunits; in the cell, it includes transcription and translation Transcription – the process of deciphering a DNA nucleotide code and converting it into RNA nucleotide code; the RNA carries the genetic message to a ribosome for trans ...
Sander van Riet 13 June Reviewer Gene co
... Gene co-expression is widely used to find new associations between different genes. The paper of IvIiev et al. uses this concept together with Protein Atlas project in order to identify new genes associated with motile cilia. Data from 3 different regions known to harbour motile cilia obtained from ...
... Gene co-expression is widely used to find new associations between different genes. The paper of IvIiev et al. uses this concept together with Protein Atlas project in order to identify new genes associated with motile cilia. Data from 3 different regions known to harbour motile cilia obtained from ...
Protein purification
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells, tissues or whole organisms. Protein purification is vital for the characterization of the function, structure and interactions of the protein of interest. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture, and finally separate the desired protein from all other proteins. Separation of one protein from all others is typically the most laborious aspect of protein purification. Separation steps usually exploit differences in protein size, physico-chemical properties, binding affinity and biological activity. The pure result may be termed protein isolate.The methods used in protein purification can roughly be divided into analytical and preparative methods. The distinction is not exact, but the deciding factor is the amount of protein that can practically be purified with that method. Analytical methods aim to detect and identify a protein in a mixture, whereas preparative methods aim to produce large quantities of the protein for other purposes, such as structural biology or industrial use. In general, the preparative methods can be used in analytical applications, but not the other way around.