06_Metabolism of lipid
... • two lipoproteins — apo B-100 and apo E • the main transport form of TGs synthesized in the organism (liver) • deliver the TGs from liver to peripheral tissue (muscle for energy, adipose for storage) • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipases (triacylglycerols are again degraded into free fatty a ...
... • two lipoproteins — apo B-100 and apo E • the main transport form of TGs synthesized in the organism (liver) • deliver the TGs from liver to peripheral tissue (muscle for energy, adipose for storage) • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipases (triacylglycerols are again degraded into free fatty a ...
Investigation of asparagine deamidation in a SOD1
... mixture was then analyzed by MALDI-TOF with particular attention paid to peptides containing amino acid 26. The determined m/z value of the peptide 25–40 resulting from the digest revealed that the peptide mass is nearly 1 Da higher than expected (Fig. 3a). Atypical isotopic distribution of the pep ...
... mixture was then analyzed by MALDI-TOF with particular attention paid to peptides containing amino acid 26. The determined m/z value of the peptide 25–40 resulting from the digest revealed that the peptide mass is nearly 1 Da higher than expected (Fig. 3a). Atypical isotopic distribution of the pep ...
Antagonistic activities of lactic acid bacteria in food and feed
... solubility in water, acids with chain lengths greater than C1o or C n are not particularly efficient in this regard, and those with chain lengths greater than Cs are usually ineffective against Gramnegative bacteria [36]. Lipophilic acids such as acetic and lactic acid in their undissociated form ca ...
... solubility in water, acids with chain lengths greater than C1o or C n are not particularly efficient in this regard, and those with chain lengths greater than Cs are usually ineffective against Gramnegative bacteria [36]. Lipophilic acids such as acetic and lactic acid in their undissociated form ca ...
Sites of enzyme activity along the nephron
... within the proximal tubule as suggested previously by others [5]. Consideration of hexokinase and pyruvate kinase in the various structures of the distal tubule leads to the conclusion that these structures have a relatively high glycolytic capacity.3 Sodium reabsorption. Cohen and Barac-Nieto [5] h ...
... within the proximal tubule as suggested previously by others [5]. Consideration of hexokinase and pyruvate kinase in the various structures of the distal tubule leads to the conclusion that these structures have a relatively high glycolytic capacity.3 Sodium reabsorption. Cohen and Barac-Nieto [5] h ...
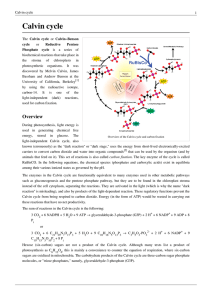
Calvin cycle
... known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds[2] that can be used by the organism (and by animals that feed on it). This set of reactions is also called carbon fi ...
... known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds[2] that can be used by the organism (and by animals that feed on it). This set of reactions is also called carbon fi ...
Chapter 9
... Regulation of Cellular Respiration via Feedback Mechanisms • Feedback inhibition is the most common mechanism for control • If ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down • Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activ ...
... Regulation of Cellular Respiration via Feedback Mechanisms • Feedback inhibition is the most common mechanism for control • If ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down • Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activ ...
Multiple Sclerosis and Epstein‐Barr Virus Infection An Epitope
... and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. Although the precise etiology of MS is unknown, data from epidemiological, genetic and twin studies suggest that MS develops in genetically susceptible individuals through the interaction with environmental ...
... and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. Although the precise etiology of MS is unknown, data from epidemiological, genetic and twin studies suggest that MS develops in genetically susceptible individuals through the interaction with environmental ...
Nucleotide Metabolism - Oregon State University
... Nucleotides Made from Very Simple Molecules - Amino Acids, One Carbon Donors, CO2 Synthesis Very Tightly Regulated - Imbalances Favor Mutation Purine Synthesis Begins on the Ribose Sugar Pyrimidine Rings Synthesized Separate from Sugar and Then Attached ...
... Nucleotides Made from Very Simple Molecules - Amino Acids, One Carbon Donors, CO2 Synthesis Very Tightly Regulated - Imbalances Favor Mutation Purine Synthesis Begins on the Ribose Sugar Pyrimidine Rings Synthesized Separate from Sugar and Then Attached ...
Mutational analysis of exoribonuclease I from Saccharomyces
... most in vivo and in vitro functions but confers a dominant negative growth inhibition when expressed at high levels. This growth inhibition is not due to the exonuclease function of the protein. To identify specific residues responsible for in vivo function, a screen was carried out for non-compleme ...
... most in vivo and in vitro functions but confers a dominant negative growth inhibition when expressed at high levels. This growth inhibition is not due to the exonuclease function of the protein. To identify specific residues responsible for in vivo function, a screen was carried out for non-compleme ...
Nucleotide Metabolism
... Nucleotides Made from Very Simple Molecules - Amino Acids, One Carbon Donors, CO2 Synthesis Very Tightly Regulated - Imbalances Favor Mutation Purine Synthesis Begins on the Ribose Sugar Pyrimidine Rings Synthesized Separate from Sugar and Then Attached ...
... Nucleotides Made from Very Simple Molecules - Amino Acids, One Carbon Donors, CO2 Synthesis Very Tightly Regulated - Imbalances Favor Mutation Purine Synthesis Begins on the Ribose Sugar Pyrimidine Rings Synthesized Separate from Sugar and Then Attached ...
Off-the-Vine Ripening of Tomato Fruit Causes Alteration
... -aminobutyrate (GABA), which is catabolized to succinic semialdehyde (SSA) by the GABA transaminase (GABA-T; EC 2.6.1.19) reaction in the mitochondria [15]. SSA can be further metabolized to succinate by SSA dehydrogenase (SSADH; EC 1.2.1.16). These three enzymes constitute the GABA shunt, a metabo ...
... -aminobutyrate (GABA), which is catabolized to succinic semialdehyde (SSA) by the GABA transaminase (GABA-T; EC 2.6.1.19) reaction in the mitochondria [15]. SSA can be further metabolized to succinate by SSA dehydrogenase (SSADH; EC 1.2.1.16). These three enzymes constitute the GABA shunt, a metabo ...
"Fermentation Pathways". In: Microbial Physiology (Fourth Edition)
... The fermentation products formed by yeast can also be altered drastically through metabolic engineering. For example, introduction of a lactate dehydrogenase gene from bovine muscle (LDH-A) into S. cerevisiae engenders the production of lactic acid at levels rivaling those achieved by lactic acid ba ...
... The fermentation products formed by yeast can also be altered drastically through metabolic engineering. For example, introduction of a lactate dehydrogenase gene from bovine muscle (LDH-A) into S. cerevisiae engenders the production of lactic acid at levels rivaling those achieved by lactic acid ba ...
Double muscling in cattle due to mutations in the myostatin gene
... sequences of nine other vertebrate species and the identification of mutations in the coding sequence of bovine myostatin in two breeds of double-muscled cattle, Belgian Blue and Piedmontese, which are known to have an increase in muscle mass relative to conventional cattle. The Belgian Blue myostat ...
... sequences of nine other vertebrate species and the identification of mutations in the coding sequence of bovine myostatin in two breeds of double-muscled cattle, Belgian Blue and Piedmontese, which are known to have an increase in muscle mass relative to conventional cattle. The Belgian Blue myostat ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... aminoacyl-tRNAs to bind to their codons on mRNA. small subunit of the ribosome is bound to mRNA large subunit carries the nascent polypeptide. A ribosome moves along mRNA from an initiation site in the 5′ region to a termination site in the 3′ region, and the appropriate aminoacyl-tRNAs respond to t ...
... aminoacyl-tRNAs to bind to their codons on mRNA. small subunit of the ribosome is bound to mRNA large subunit carries the nascent polypeptide. A ribosome moves along mRNA from an initiation site in the 5′ region to a termination site in the 3′ region, and the appropriate aminoacyl-tRNAs respond to t ...
"An Introduction to Sequence Similarity ("Homology") Searching". In
... requires j-1 gaps in sequence B, so S(1,j)=(j-1)δ + score(a1 ,bj ). Once the top row and first column are initialized, the entire matrix can be filled following the simple rule shown in Figure 3.1.1, and the score of the best possible alignment of the two sequences is the element in the lower right ...
... requires j-1 gaps in sequence B, so S(1,j)=(j-1)δ + score(a1 ,bj ). Once the top row and first column are initialized, the entire matrix can be filled following the simple rule shown in Figure 3.1.1, and the score of the best possible alignment of the two sequences is the element in the lower right ...
Analysis of TETRAKETIDE a-PYRONE
... showed that the oxidoreductases belong to a gene family conserved from mosses to flowering plants. Since similar gene conservation holds true for PKSA, PKSB, and ACOS5 genes, it appears that the whole biosynthetic pathway leading from medium or long-chain fatty acids to sporopollenin units is highly ...
... showed that the oxidoreductases belong to a gene family conserved from mosses to flowering plants. Since similar gene conservation holds true for PKSA, PKSB, and ACOS5 genes, it appears that the whole biosynthetic pathway leading from medium or long-chain fatty acids to sporopollenin units is highly ...
LITERATURE REVIEW: 1) Citric acid production by Aspergillusniger
... importantcommercial product with global production reaching 736,000 tons/yr. Furthermore, it isproduced almost through the submerged fermentation of the white rot fungus (Jianlong 2000). Citric acid is widely used in the food, beverage,pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries and it has other applicat ...
... importantcommercial product with global production reaching 736,000 tons/yr. Furthermore, it isproduced almost through the submerged fermentation of the white rot fungus (Jianlong 2000). Citric acid is widely used in the food, beverage,pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries and it has other applicat ...
Nonenzymatic, Self-Elimination Degradation
... three cases of pH (Fig. 4, d – f, and Fig. 5, b). To study the effect of the ionic strength on degradation, similar studies were performed using 20 mm sodium phosphate buffer. It was observed that different ionic strength at the same pH does not affect the degradation time (Fig. 4, g – i, and Fig. 5 ...
... three cases of pH (Fig. 4, d – f, and Fig. 5, b). To study the effect of the ionic strength on degradation, similar studies were performed using 20 mm sodium phosphate buffer. It was observed that different ionic strength at the same pH does not affect the degradation time (Fig. 4, g – i, and Fig. 5 ...
103 Lecture Ch23b
... • Glucose-1-phosphate can be converted to glucose-6phosphate, which can enter glycolysis • Phosphorylated glucose can’t be absorbed into cells - in the liver and kidneys, glucose-6-phosphate can be hydrolized to glucose • Glycogenolysis is activated by glucogon in the liver and epinephrine in muscle ...
... • Glucose-1-phosphate can be converted to glucose-6phosphate, which can enter glycolysis • Phosphorylated glucose can’t be absorbed into cells - in the liver and kidneys, glucose-6-phosphate can be hydrolized to glucose • Glycogenolysis is activated by glucogon in the liver and epinephrine in muscle ...
Methylation and Glutathione, Keys to Chronic
... Six have shown a methylation cycle partial block and depletion of reduced glutathione relative to oxidized glutathione. The seventh had a methylation cycle block but normal glutathione levels. Data from more patients are needed. ...
... Six have shown a methylation cycle partial block and depletion of reduced glutathione relative to oxidized glutathione. The seventh had a methylation cycle block but normal glutathione levels. Data from more patients are needed. ...
Methylation and Glutathione, Keys to Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
... Six have shown a methylation cycle partial block and depletion of reduced glutathione relative to oxidized glutathione. The seventh had a methylation cycle block but normal glutathione levels. Data from more patients are needed. ...
... Six have shown a methylation cycle partial block and depletion of reduced glutathione relative to oxidized glutathione. The seventh had a methylation cycle block but normal glutathione levels. Data from more patients are needed. ...