
A comparison of the amino acid sequence of the
... enzyme revealed from optimal alignment of conserved sequences are non-aligned 4, 6, 14 and 32 amino acid peptide sequences between Gln185-Arg186, Va1143Ala144, Ala179-Val180 and Lys213-Tyr214 of subtilisin BPN’, respectively. Such features are not uncommon among the serine proteases, in which they e ...
... enzyme revealed from optimal alignment of conserved sequences are non-aligned 4, 6, 14 and 32 amino acid peptide sequences between Gln185-Arg186, Va1143Ala144, Ala179-Val180 and Lys213-Tyr214 of subtilisin BPN’, respectively. Such features are not uncommon among the serine proteases, in which they e ...
Why study? Genetic disorders of nucleotide metabolsm cause
... First and second step are inhibited by IMP , AMP and GMP PRPP is not purely for Purine synthesis IMPwhatever step is regulated by its own end produce AMP shuts down AMP synthesis GMP shuts down GMP synthesis ...
... First and second step are inhibited by IMP , AMP and GMP PRPP is not purely for Purine synthesis IMPwhatever step is regulated by its own end produce AMP shuts down AMP synthesis GMP shuts down GMP synthesis ...
2054, Chap. 12, page 1 I. Genes: Expression and Regulation A
... 3. regulon = collection of genes or operons controlled by the same regulatory protein a. operons usually associated with a single pathway or function b. e.g., heat-shock proteins, glycerol catabolism 4. modulon = operons controlled by their own regulators that are also under the control of a common ...
... 3. regulon = collection of genes or operons controlled by the same regulatory protein a. operons usually associated with a single pathway or function b. e.g., heat-shock proteins, glycerol catabolism 4. modulon = operons controlled by their own regulators that are also under the control of a common ...
Handout: Fatty Acid Synthesis
... cytosolic face of the ER membrane. This is done by elongases that use malonyl-CoA to add the 2-carbon subunits. Oxidase ...
... cytosolic face of the ER membrane. This is done by elongases that use malonyl-CoA to add the 2-carbon subunits. Oxidase ...
Nucleic acids
... Cholesterol is vital for many bodily functions but in high amounts it can cause a serious condition known as atherosclerosis. Sex hormones such as testosterone and estrogen are responsible for development of sexual characteristics and regulating the menstrual cycle in females. ...
... Cholesterol is vital for many bodily functions but in high amounts it can cause a serious condition known as atherosclerosis. Sex hormones such as testosterone and estrogen are responsible for development of sexual characteristics and regulating the menstrual cycle in females. ...
Biochemistry PPT - Madison County Schools
... • These sugars give energy that lasts a little longer than monosaccharides because the glycosidic bond (a covalent bond between two monosaccharides) must be broken before the sugar can be used for energy ...
... • These sugars give energy that lasts a little longer than monosaccharides because the glycosidic bond (a covalent bond between two monosaccharides) must be broken before the sugar can be used for energy ...
STUDIES ON WHALE BLOOD. I.
... Two methods of synthesis have been worked out by Pymann.1m The most common material now being employed for hislidine manufacture is blood. There are two principal manufacturing methods, one by precipitating the silver salt in alkaline medium, 3)4)5) and the other using the mercuric salt.6>7 )3> The ...
... Two methods of synthesis have been worked out by Pymann.1m The most common material now being employed for hislidine manufacture is blood. There are two principal manufacturing methods, one by precipitating the silver salt in alkaline medium, 3)4)5) and the other using the mercuric salt.6>7 )3> The ...
Practice Exam 3
... Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium and are potential sites for major flux control. List the three enzymes and discuss why each enzyme is or is not the RDS of glycolysis. ...
... Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium and are potential sites for major flux control. List the three enzymes and discuss why each enzyme is or is not the RDS of glycolysis. ...
Practice Exam 3 Answers
... 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium and are potential sites for major flux control. List the three enzymes and discuss why each enzyme is or is not the RDS of glycolysis. ...
... 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium and are potential sites for major flux control. List the three enzymes and discuss why each enzyme is or is not the RDS of glycolysis. ...
Egri, Shawn March 23, 2015
... aminoacylation, or the attachment of an amino acid to its corresponding tRNA. Along with catalyzing this critical procedure many aaRSs have a secondary function as well. For ThreonyltRNA synthetase (ThrRS) this is promotion of angiogenesis, or blood vessel formation. Blood vessel formation is proble ...
... aminoacylation, or the attachment of an amino acid to its corresponding tRNA. Along with catalyzing this critical procedure many aaRSs have a secondary function as well. For ThreonyltRNA synthetase (ThrRS) this is promotion of angiogenesis, or blood vessel formation. Blood vessel formation is proble ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... Forming a Polypeptide To join two amino acids: Carboxyl group of one must meet the amino group of another An enzyme will join them via a dehydration reaction The resulting bond is called a peptide bond Repeating the process over and over creates a polypeptide ...
... Forming a Polypeptide To join two amino acids: Carboxyl group of one must meet the amino group of another An enzyme will join them via a dehydration reaction The resulting bond is called a peptide bond Repeating the process over and over creates a polypeptide ...
Macromolecules of Life
... Used for support such as connective tissue and keratin that forms hairs and fingernails Transport proteins move many substances through the body Ex. Hemoglobin which transports oxygen through the blood Hormone proteins. Ex, insulin which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood Help control moveme ...
... Used for support such as connective tissue and keratin that forms hairs and fingernails Transport proteins move many substances through the body Ex. Hemoglobin which transports oxygen through the blood Hormone proteins. Ex, insulin which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood Help control moveme ...
Lab Title
... DNA is a very long, thin molecule located in the nucleus. The DNA in one chromosome has 10s of millions of base pairs and hundreds or thousands of genes. Yet an individual cell will only use a small portion of those genes in its lifetime. Imagine a mechanic who spends a lifetime fixing nothing but c ...
... DNA is a very long, thin molecule located in the nucleus. The DNA in one chromosome has 10s of millions of base pairs and hundreds or thousands of genes. Yet an individual cell will only use a small portion of those genes in its lifetime. Imagine a mechanic who spends a lifetime fixing nothing but c ...
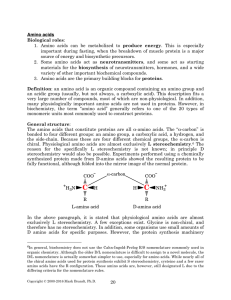
Amino Acids - Rose
... arithmetic mean of the pKa values for the α-carboxylate group and the α-amino group, because these are the only ionizable groups, and if both have charges of equal magnitudes, the molecule has zero net charge. This zero net charge state is known as the zwitterionic state (a zwitterion is capable of ...
... arithmetic mean of the pKa values for the α-carboxylate group and the α-amino group, because these are the only ionizable groups, and if both have charges of equal magnitudes, the molecule has zero net charge. This zero net charge state is known as the zwitterionic state (a zwitterion is capable of ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... Viruses: consist of a single DNA or RNA molecule wrapped in a protein package Not considered a life-form Deemed parasites – unable to carry out metabolism or reproduction without the assistance of host cell Are the caused of many plants and animals maladies and has resulted in much human suffering ...
... Viruses: consist of a single DNA or RNA molecule wrapped in a protein package Not considered a life-form Deemed parasites – unable to carry out metabolism or reproduction without the assistance of host cell Are the caused of many plants and animals maladies and has resulted in much human suffering ...
Four Types of Organic Molecules
... Peptide bonds Peptide bonds are covalent bonds formed by a condensation reaction that links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Has polarity with an amino group one end (Nterminus) and a carboxyl group on the other (C-terminus). Has a backbone of repeating N-C-C-N-C- ...
... Peptide bonds Peptide bonds are covalent bonds formed by a condensation reaction that links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Has polarity with an amino group one end (Nterminus) and a carboxyl group on the other (C-terminus). Has a backbone of repeating N-C-C-N-C- ...
gene expression - cloudfront.net
... strand of mRNA is synthesized according to the nitrogenous base code of DNA. Transcription can be summarized by the following steps: 1. The enzyme, RNA polymerase, binds to an area of one of the DNA molecules in the double helix. During transcription, only one DNA strand serves as a template (a guid ...
... strand of mRNA is synthesized according to the nitrogenous base code of DNA. Transcription can be summarized by the following steps: 1. The enzyme, RNA polymerase, binds to an area of one of the DNA molecules in the double helix. During transcription, only one DNA strand serves as a template (a guid ...
Chapter 14 Nutrition Nutrients A nutrient is a component of food that
... Eating red meat as a source of protein is high in saturated fats that can lead to CVD Food groups Food groups are not nutrient classes However, they are easier for most people to deal with Vitamins Organic compounds (other than proteins, fats, or carbohydrates) used for metabolism that are not ...
... Eating red meat as a source of protein is high in saturated fats that can lead to CVD Food groups Food groups are not nutrient classes However, they are easier for most people to deal with Vitamins Organic compounds (other than proteins, fats, or carbohydrates) used for metabolism that are not ...
BIOC*4520 - University of Guelph
... conflict should inform the instructor immediately. Alternative midterm exams will be arranged where appropriate and possible. Final Examination: The Registrar sets the time (Friday, Dec. 16, 11:30 - 1:30 pm) and location (to be determined.) The final exam is cumulative, but will stress material sinc ...
... conflict should inform the instructor immediately. Alternative midterm exams will be arranged where appropriate and possible. Final Examination: The Registrar sets the time (Friday, Dec. 16, 11:30 - 1:30 pm) and location (to be determined.) The final exam is cumulative, but will stress material sinc ...
Document
... acids are most common. Substitution of methyl group on the carbon atom separating the acid centre from the aromatic ring increase the anti-inflammatory activity. Group larger than methyl decrease activity. A second area of lipophilicity which is generally noncoplaner with aromatic or heteroaromatic ...
... acids are most common. Substitution of methyl group on the carbon atom separating the acid centre from the aromatic ring increase the anti-inflammatory activity. Group larger than methyl decrease activity. A second area of lipophilicity which is generally noncoplaner with aromatic or heteroaromatic ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
... If one base was equal to one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 4. If two bases was equal one amino acid, the maximum would be 16 codes. If three bases equal one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 64. ...
... If one base was equal to one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 4. If two bases was equal one amino acid, the maximum would be 16 codes. If three bases equal one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 64. ...
[edit] Amino acids and proteins [edit] Lipids
... through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy and will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. As enzymes act a ...
... through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy and will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. As enzymes act a ...






















![[edit] Amino acids and proteins [edit] Lipids](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017606867_1-0f8e8f7866b15e60475e6df20c71fc0c-300x300.png)