What are proteins?
... Secondary structure: areas of folding or coiling within a protein; examples include alpha helices and pleated sheets, which are stabilized by hydrogen bonding. Tertiary structure: Final three-dimensional structure of a protein, which results from a large number of noncovalent interactions between am ...
... Secondary structure: areas of folding or coiling within a protein; examples include alpha helices and pleated sheets, which are stabilized by hydrogen bonding. Tertiary structure: Final three-dimensional structure of a protein, which results from a large number of noncovalent interactions between am ...
Expt 9-Amino Acids and Proteins
... the mixture is heated, a yellow solution will result if the sample contains tyrosine or tryptophan. When this yellow solution is treated with a strong base (such as NaOH), it turns orange. Since most proteins contain one or both of these amino acids, most proteins will show a positive reaction in th ...
... the mixture is heated, a yellow solution will result if the sample contains tyrosine or tryptophan. When this yellow solution is treated with a strong base (such as NaOH), it turns orange. Since most proteins contain one or both of these amino acids, most proteins will show a positive reaction in th ...
lec4-5-biosynthesis_specificity
... – Dehydrogenases catalyst the transfer of hydrogen from the substrate to a particular side of nicotinamide ring in NAD+ or NADP+ – Phenylalanine hydroxylase uses L-Phe not D-Phe – NZ-catalysed rxns may yield stereospecific products even when substrate possesses no asymmetric carbon atom... ...
... – Dehydrogenases catalyst the transfer of hydrogen from the substrate to a particular side of nicotinamide ring in NAD+ or NADP+ – Phenylalanine hydroxylase uses L-Phe not D-Phe – NZ-catalysed rxns may yield stereospecific products even when substrate possesses no asymmetric carbon atom... ...
question bank acids, bases and salts
... 2. Name the source from which litmus solution is obtained. What is the use of this solution? 3. Explain why: An antacid tablet is taken when you suffer from acidity. 4. Explain why: Factory waste is neutralized before disposing it into the water bodies. 5. What are Indicators Give two examples? 6. W ...
... 2. Name the source from which litmus solution is obtained. What is the use of this solution? 3. Explain why: An antacid tablet is taken when you suffer from acidity. 4. Explain why: Factory waste is neutralized before disposing it into the water bodies. 5. What are Indicators Give two examples? 6. W ...
Proteins 101 - Virginia Tech
... – Catalysis: Almost all chemical reactions in a living cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. ...
... – Catalysis: Almost all chemical reactions in a living cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. ...
TRACE ELEMENTS
... Iodine is well absorbed from the stomach into the blood. About 30 percent goes to the thyroid gland, depending on the need. Iodine is eliminated rapidly. Most of the remaining 70 percent is filtered by the kidneys into the urine. Iodine's main role in animal biology is as constituents of the thyroid ...
... Iodine is well absorbed from the stomach into the blood. About 30 percent goes to the thyroid gland, depending on the need. Iodine is eliminated rapidly. Most of the remaining 70 percent is filtered by the kidneys into the urine. Iodine's main role in animal biology is as constituents of the thyroid ...
chapter 25 tortora
... • **Only transcribe a gene when it is needed • All cells have the same genes but have differential ...
... • **Only transcribe a gene when it is needed • All cells have the same genes but have differential ...
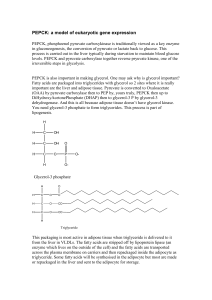
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... In the normal fed state PEPCK mRNA in the liver is rapidly turned over. This is typical for a sequence which is regulated at the level of gene expression. Why? In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK p ...
... In the normal fed state PEPCK mRNA in the liver is rapidly turned over. This is typical for a sequence which is regulated at the level of gene expression. Why? In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK p ...
Dehydration Synthesis
... Polymers are _______________ into monomers via hydrolysis reactions, in which a bond is broken, or lysed, by ___________ of a water molecule. hydro = __________, lysis = ____________ One molecule ______________ and the other takes an __________. requires the action of helping molecules calle ...
... Polymers are _______________ into monomers via hydrolysis reactions, in which a bond is broken, or lysed, by ___________ of a water molecule. hydro = __________, lysis = ____________ One molecule ______________ and the other takes an __________. requires the action of helping molecules calle ...
Final a
... 2. (10pts) Diagram the Q cycle of photosynthesis, showing where and how many quinone/quinol molecules are used and where and how protons are taken up and given off. Make sure you account for the stoichiometry of the cycle and show where electrons wind up. Make sure to show where the lumen and stroma ...
... 2. (10pts) Diagram the Q cycle of photosynthesis, showing where and how many quinone/quinol molecules are used and where and how protons are taken up and given off. Make sure you account for the stoichiometry of the cycle and show where electrons wind up. Make sure to show where the lumen and stroma ...
Enzymes - Land of Mayo
... fever makes us weak, but are more effective against bacteria ► Fevers do not allow bacterial cell division because their enzymes for cell division do not work correctly or at all at the higher temperature ► At elevated body temperatures, cell division do not work or makes “leaky” cell walls ...
... fever makes us weak, but are more effective against bacteria ► Fevers do not allow bacterial cell division because their enzymes for cell division do not work correctly or at all at the higher temperature ► At elevated body temperatures, cell division do not work or makes “leaky” cell walls ...
Enzyme LG 09
... e. Competitive inhibitors are inorganic c. Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. substances such as metal ions; d. Enzymes are the reactants in a chemical reaction. noncompetitive inhibitors are vitamins or e. All enzymes depend on protein cofactors to vitamin derivatives. function. 21. Bacterial pro ...
... e. Competitive inhibitors are inorganic c. Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. substances such as metal ions; d. Enzymes are the reactants in a chemical reaction. noncompetitive inhibitors are vitamins or e. All enzymes depend on protein cofactors to vitamin derivatives. function. 21. Bacterial pro ...
Enzymes
... • Cooperativity is a form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity • In cooperativity, binding by a substrate to one active site stabilizes favorable conformational changes at all ...
... • Cooperativity is a form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity • In cooperativity, binding by a substrate to one active site stabilizes favorable conformational changes at all ...
BCM 101 BIOCHEMISTRY BIOCHEMISTRY “Chemistry of proteins”
... The word “protein” is derived from the Greek word “proteios”, which means “of primary importance”. In fact, proteins plays an important role in all biochemical and physiological body processes; they act as enzymes, hormones, receptors, antibodies and are required for the structural integrity of cell ...
... The word “protein” is derived from the Greek word “proteios”, which means “of primary importance”. In fact, proteins plays an important role in all biochemical and physiological body processes; they act as enzymes, hormones, receptors, antibodies and are required for the structural integrity of cell ...
Chapter 7 - Coenzymes
... Coenzymes can be either cosubstrates (loosely bound to enzyme; is altered, then regenerated) or prosthetic groups (tightly bound to enzyme). Coenzymes can be classified by their source: 1) metabolite coenzymes synthesized by common metabolites include nucleoside triphosphates most abundant is ...
... Coenzymes can be either cosubstrates (loosely bound to enzyme; is altered, then regenerated) or prosthetic groups (tightly bound to enzyme). Coenzymes can be classified by their source: 1) metabolite coenzymes synthesized by common metabolites include nucleoside triphosphates most abundant is ...
amino acids M
... 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
... 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
the chemistry of organic molecules
... 3. Hormones-chemicals that regulate the growth and functioning of living organisms. 4. Steroids-there are several different types of steroids: a. Cholesterol-common steroid. 1) Humans do need a small amount of cholesterol for: a) The formation of Vitamin D b) The production of estrogen and testoster ...
... 3. Hormones-chemicals that regulate the growth and functioning of living organisms. 4. Steroids-there are several different types of steroids: a. Cholesterol-common steroid. 1) Humans do need a small amount of cholesterol for: a) The formation of Vitamin D b) The production of estrogen and testoster ...
Organic Chemistry and Biological Systems -Biochemistry
... cases, not only the nature of monomers but also the order in which they appear in the polymer, have functional significance. The two groups of macromolecules in which sequence carries genetically encoded specific information are nucleic acids and proteins. Both are linear polymers of covalently join ...
... cases, not only the nature of monomers but also the order in which they appear in the polymer, have functional significance. The two groups of macromolecules in which sequence carries genetically encoded specific information are nucleic acids and proteins. Both are linear polymers of covalently join ...
Carey_AminoAcids_Pep..
... —CO2H group, these groups are actually present as —NH3+ and —CO2– respectively. They are classified as a, b, g, etc. amino acids according the carbon that bears the nitrogen. ...
... —CO2H group, these groups are actually present as —NH3+ and —CO2– respectively. They are classified as a, b, g, etc. amino acids according the carbon that bears the nitrogen. ...
(L0668) - Datasheet - Sigma
... core polypeptide with O-linked and 17 asparaginelinked oligosaccharide side chains in mouse cells. This heavy glycosylation of LAMP2 may be important to protect the lysosomal membrane from proteolytic ...
... core polypeptide with O-linked and 17 asparaginelinked oligosaccharide side chains in mouse cells. This heavy glycosylation of LAMP2 may be important to protect the lysosomal membrane from proteolytic ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2001 - Third Exam:
... ii) You took your biochemistry final exam shortly after finishing this meal. The anxiety prompted the release of high levels of epinephrine (adrenaline) during the exam. Explain how the production of epinephrine may be beneficial to your final grade, given that your brain can only use glucose as its ...
... ii) You took your biochemistry final exam shortly after finishing this meal. The anxiety prompted the release of high levels of epinephrine (adrenaline) during the exam. Explain how the production of epinephrine may be beneficial to your final grade, given that your brain can only use glucose as its ...
Basic Minerals™ A Comprehensive Mineral/Trace Element Formula
... Minerals contains patented mineral amino acid chelates from Albion Laboratories and other welltolerated and highly absorbable mineral forms. Basic Minerals is iron-free, making it an appropriate choice for those concerned about getting too much iron but who want to supplement with a full-spectrum of ...
... Minerals contains patented mineral amino acid chelates from Albion Laboratories and other welltolerated and highly absorbable mineral forms. Basic Minerals is iron-free, making it an appropriate choice for those concerned about getting too much iron but who want to supplement with a full-spectrum of ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF LARGE
... 16. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 17. Name the two ends of a protein and explain the reason for their names. 18. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R ...
... 16. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 17. Name the two ends of a protein and explain the reason for their names. 18. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R ...