File - Georgetown ISD
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
Gene Regulation Prokaryoperon_RD_MP
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (d) Tertiary enzymes II. State whether the following statements are true or false, if false give reason (5 x 1= 5 marks) (6) Only the amino acids present at the active site of an enzyme are involved in product formation. (7) Replacement of the glutamate at the 35th position in lysozyme with serine w ...
... (d) Tertiary enzymes II. State whether the following statements are true or false, if false give reason (5 x 1= 5 marks) (6) Only the amino acids present at the active site of an enzyme are involved in product formation. (7) Replacement of the glutamate at the 35th position in lysozyme with serine w ...
Workshop: Protein Structure Introduction Learning Objectives
... In this workshop you will examine in detail the structures of proteins, from their amino acid building blocks to their fully folded, functional forms. In particular, you will be introduced to the chemical bonding interactions that stabilize the various levels of protein structure. As expressed in th ...
... In this workshop you will examine in detail the structures of proteins, from their amino acid building blocks to their fully folded, functional forms. In particular, you will be introduced to the chemical bonding interactions that stabilize the various levels of protein structure. As expressed in th ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... o Enzymes that speed up chemical reactions in our body o Antibodies o Hormones ...
... o Enzymes that speed up chemical reactions in our body o Antibodies o Hormones ...
Amino acids
... The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive and therefore not involved in any covalent chemistry in enzyme active centers. However, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. •The β carbon of isoleucine is optically ...
... The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive and therefore not involved in any covalent chemistry in enzyme active centers. However, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. •The β carbon of isoleucine is optically ...
Polymer Molecules
... All proteins contain the elements C,O,H, N. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body cannot make every type of amino acids that it needs. So our diet ...
... All proteins contain the elements C,O,H, N. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body cannot make every type of amino acids that it needs. So our diet ...
Amino acids
... The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive and therefore not involved in any covalent chemistry in enzyme active centers. However, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. •The β carbon of isoleucine is optically ...
... The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive and therefore not involved in any covalent chemistry in enzyme active centers. However, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. •The β carbon of isoleucine is optically ...
2-4_EnergyProd_FabinyiB
... contains proteins, enzymes and mitochondrial DNA. The citric acid cycle, the beta-oxidation and other processes are also placed here. Cells intakes multiple kind of possible fuels for energy, that has different routes to become ATP. The average human needs 160 g of glucose a day, of which 120 g used ...
... contains proteins, enzymes and mitochondrial DNA. The citric acid cycle, the beta-oxidation and other processes are also placed here. Cells intakes multiple kind of possible fuels for energy, that has different routes to become ATP. The average human needs 160 g of glucose a day, of which 120 g used ...
pages 46-50
... Proteins differ in the number and order of amino acids. The specific sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s structure and function. Two types of interactions between the side groups of some amino acids are especially important in protein structure. First, some side groups contain sulfur ato ...
... Proteins differ in the number and order of amino acids. The specific sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s structure and function. Two types of interactions between the side groups of some amino acids are especially important in protein structure. First, some side groups contain sulfur ato ...
Lecture 33
... opposite effects on two enzymes that control a shared step in two reaction pathways. For example, when energy charge in the cell is low, AMP levels are high leading to activation of PFK-1 (increased flux through glycolysis) and inhibition of FBPase-1 (decreased flux through gluconeogenesis). This ma ...
... opposite effects on two enzymes that control a shared step in two reaction pathways. For example, when energy charge in the cell is low, AMP levels are high leading to activation of PFK-1 (increased flux through glycolysis) and inhibition of FBPase-1 (decreased flux through gluconeogenesis). This ma ...
Fructose 6
... Figure 2. Using the non-oxidative branch of the pentose pathway to produce ribose-5-phosphate for the nucleic acid pathways (Mode 1). ...
... Figure 2. Using the non-oxidative branch of the pentose pathway to produce ribose-5-phosphate for the nucleic acid pathways (Mode 1). ...
Chapter 3 Overview - Greensburg.k12.in.us
... In living things, if it is not water, it probably is carbon ...
... In living things, if it is not water, it probably is carbon ...
Cheng BY 123 Raut – Mock Exam Unit I 09/21/14 1. Which of the
... 8. Phosphorus-31 is an isotope of phosphorus. Given that phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, what is proper number of protons, neutrons, and electrons on this atom? A) 15, 15, 16 B) 16, 15, 16 C) 15, 14, 17 D) 15, 16, 15 E) 14, 17, 15 9. What is not a fact about isotopes? A) they are different at ...
... 8. Phosphorus-31 is an isotope of phosphorus. Given that phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, what is proper number of protons, neutrons, and electrons on this atom? A) 15, 15, 16 B) 16, 15, 16 C) 15, 14, 17 D) 15, 16, 15 E) 14, 17, 15 9. What is not a fact about isotopes? A) they are different at ...
Exam Review 2 10/2/16
... D. The tail region of chlorophyll has no known function 43. Where does the Calvin cycle take place? A. Thylakoid membrane B. Cytoplasm C. Stroma D. Granum 44. The replication fork is: A. The Y-shaped region where the DNA is split into two separate strands for coding B. Growing as DNA replication pro ...
... D. The tail region of chlorophyll has no known function 43. Where does the Calvin cycle take place? A. Thylakoid membrane B. Cytoplasm C. Stroma D. Granum 44. The replication fork is: A. The Y-shaped region where the DNA is split into two separate strands for coding B. Growing as DNA replication pro ...
Lec. 25 - Translation 3
... Cells must have at least 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid ...
... Cells must have at least 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid ...
Biochemistry
... (6) Enzymes are classified by the reactions they catalyze (7) Isoenzyme are distinct forms of enzyme with the same catalytic activity : the conception of the isoenzyme 2. Mechanism of action of enzymes and coenzymes (1) Why a chemical reaction can take place (2) Enzymes speed up the rates by lowerin ...
... (6) Enzymes are classified by the reactions they catalyze (7) Isoenzyme are distinct forms of enzyme with the same catalytic activity : the conception of the isoenzyme 2. Mechanism of action of enzymes and coenzymes (1) Why a chemical reaction can take place (2) Enzymes speed up the rates by lowerin ...
Patterns of nucleotide and amino acid substitution
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
Building Blocks of Organic
... • Polymers (polypeptides) are formed from 20 different monomers (amino acids) • Structure of an amino acid ...
... • Polymers (polypeptides) are formed from 20 different monomers (amino acids) • Structure of an amino acid ...
syllabusbioch205 - OSU Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... physiology, the other basic medical sciences, and the clinical medical sciences. 21. To integrate biochemical knowledge into the larger biological system of the human body. 22. To recognize the limitations of biochemical science, its data, and to develop an enquiring mind that see each patient as a ...
... physiology, the other basic medical sciences, and the clinical medical sciences. 21. To integrate biochemical knowledge into the larger biological system of the human body. 22. To recognize the limitations of biochemical science, its data, and to develop an enquiring mind that see each patient as a ...
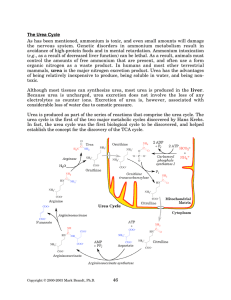
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... carbamoyl phosphate from inorganic ammonium and carbonate. This enzyme is thus another enzyme capable of fixing ammonium. The usual fate of the ammonium fixed by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is excretion in the form of urea, and therefore this enzyme is usually considered separately from glutami ...
... carbamoyl phosphate from inorganic ammonium and carbonate. This enzyme is thus another enzyme capable of fixing ammonium. The usual fate of the ammonium fixed by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is excretion in the form of urea, and therefore this enzyme is usually considered separately from glutami ...
Paper - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... 62. Mitochondrial DNA is advantageous for evolutionary studies because : (A) it is inherited only through the female parent and thus evolves in a way that allows trees of relationship to be easily constructed (B) it is inserted into X chromosome (C) it first appeared in humans and is not found in ot ...
... 62. Mitochondrial DNA is advantageous for evolutionary studies because : (A) it is inherited only through the female parent and thus evolves in a way that allows trees of relationship to be easily constructed (B) it is inserted into X chromosome (C) it first appeared in humans and is not found in ot ...