Chapter 13.1 and 13.2 RNA, Ribosomes, and Protein Synthesis
... cytoplasm. – On ribosome, translation begins at START codon. – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino acids bond and move along the mRNA – Continues until reaches STOP codon and forms polypeptide and mRNA is released. ...
... cytoplasm. – On ribosome, translation begins at START codon. – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino acids bond and move along the mRNA – Continues until reaches STOP codon and forms polypeptide and mRNA is released. ...
Chapter 5, part A
... • Oxidation is the removal of electrons. • Reduction is the gain of electrons. • Redox reaction is an oxidation reaction paired with a reduction reaction. ...
... • Oxidation is the removal of electrons. • Reduction is the gain of electrons. • Redox reaction is an oxidation reaction paired with a reduction reaction. ...
BIOL103 Review Questions for Midterm 2 SP16
... 7. Describe how proteins digest and absorb? Where does it start? Name all the enzymes. 8. What problems would someone with celiac disease or cystic fibrosis have when digesting certain proteins? 9. When syn ...
... 7. Describe how proteins digest and absorb? Where does it start? Name all the enzymes. 8. What problems would someone with celiac disease or cystic fibrosis have when digesting certain proteins? 9. When syn ...
Chapter 11 - Introduction to Metabolism
... each pathway may have branch points for metabolites to enter or leave Why have metabolic reactions with so many steps? 1) energy input and output can be controlled - energy transfer occurs in discrete steps as it it transferred to acceptors a little at a time 2) enzymes can catalyze only a single ...
... each pathway may have branch points for metabolites to enter or leave Why have metabolic reactions with so many steps? 1) energy input and output can be controlled - energy transfer occurs in discrete steps as it it transferred to acceptors a little at a time 2) enzymes can catalyze only a single ...
Energy Releasing Pathway
... to the amount of yeast present. 4. In 1897 the Buchner brothers outlined the steps of glycolysis key to fermentation. 5. In the early 1900’s Szent-Györgyi designed Citric Acid Cycle, failed to show relationship to fermentation. 6. Krebs in 1938 linked glycolysis to citric Acid Cycle via enzyme CoA. ...
... to the amount of yeast present. 4. In 1897 the Buchner brothers outlined the steps of glycolysis key to fermentation. 5. In the early 1900’s Szent-Györgyi designed Citric Acid Cycle, failed to show relationship to fermentation. 6. Krebs in 1938 linked glycolysis to citric Acid Cycle via enzyme CoA. ...
Effect of β-Alanine Supplementation on High
... diet. Direct oral β-alanine supplementation will compensate for low meat and fish intake, significantly increasing the muscle carnosine concentration by as much as 80% within 10 weeks, above that maintained by a mixed diet [2]. Supplementation is best achieved using a sustained release formulation o ...
... diet. Direct oral β-alanine supplementation will compensate for low meat and fish intake, significantly increasing the muscle carnosine concentration by as much as 80% within 10 weeks, above that maintained by a mixed diet [2]. Supplementation is best achieved using a sustained release formulation o ...
Resume - TILT - Colorado State University
... 1. Synthesis of Macromolecules by allylic oxidative cyclization Macromolecules are very important in common because it has significant characteristics of chemical nature. These Macromolecules can be synthesized by different methods of cyclization. Our group was successful in doing cyclization by all ...
... 1. Synthesis of Macromolecules by allylic oxidative cyclization Macromolecules are very important in common because it has significant characteristics of chemical nature. These Macromolecules can be synthesized by different methods of cyclization. Our group was successful in doing cyclization by all ...
ACID BASE - Union City High School
... ions, thereby increasing the concentration of H+ ions. Because hydrogen atom consists of a proton and an electron, H+ is simply a ...
... ions, thereby increasing the concentration of H+ ions. Because hydrogen atom consists of a proton and an electron, H+ is simply a ...
(18 pts) Pyruvate can be converted to a variety of othe
... The molecule could undergo any of a variety of different chemical reactions. Each would lead to a different product. Starting with pyruvate, for example, a carbon-carbon bond break would lead to ethanol and carbon dioxide. Reduction would lead to lactate. 2. (14 pts) Electron transport has some fund ...
... The molecule could undergo any of a variety of different chemical reactions. Each would lead to a different product. Starting with pyruvate, for example, a carbon-carbon bond break would lead to ethanol and carbon dioxide. Reduction would lead to lactate. 2. (14 pts) Electron transport has some fund ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... (1) Mix enzyme + substrate (2) Record rate of product formation as a function of time (the velocity of reaction) (3) Plot initial velocity versus substrate concentration. (4) Change substrate concentration and repeat ...
... (1) Mix enzyme + substrate (2) Record rate of product formation as a function of time (the velocity of reaction) (3) Plot initial velocity versus substrate concentration. (4) Change substrate concentration and repeat ...
October 15 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... allosteric inhibitor binds to allosteric site causes enzyme to change shape conformational change active site is no longer functional binding site keeps enzyme inactive ...
... allosteric inhibitor binds to allosteric site causes enzyme to change shape conformational change active site is no longer functional binding site keeps enzyme inactive ...
Improving orthogonal tRNA-synthetase recognition for
... Optimizing the anticodon recognition between orthogonal tRNA and synthetase significantly increased the incorporation efficiencies of various unnatural amino acids in mammalian cells, and the enhanced incorporation enabled efficient photocrosslinking of interacting proteins in mammalian cells. Unnat ...
... Optimizing the anticodon recognition between orthogonal tRNA and synthetase significantly increased the incorporation efficiencies of various unnatural amino acids in mammalian cells, and the enhanced incorporation enabled efficient photocrosslinking of interacting proteins in mammalian cells. Unnat ...
Open Reading Frames and Codon Bias in Streptomyces coelicolor
... Pro, Arg) while others are AT-rich (Phe, Tyr). A bias in amino acid composition of proteins has been noted in species with a very high or very low GC content [9]. We noted a severe bias in the amino acid composition of the putative protein products of the genes in S. coelicolor. Ten amino acids (GPA ...
... Pro, Arg) while others are AT-rich (Phe, Tyr). A bias in amino acid composition of proteins has been noted in species with a very high or very low GC content [9]. We noted a severe bias in the amino acid composition of the putative protein products of the genes in S. coelicolor. Ten amino acids (GPA ...
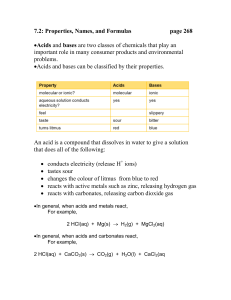
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
Request reprint ©
... as fuel during flight (Scaraffia and Wells, 2003). However, when proline serves as a source of energy, alanine and glutamine seem to be involved in the shuttling of the amino group between the flight muscle and the fat body to avoid ammonia’s toxic effects (Scaraffia and Wells, 2003). In correlation wit ...
... as fuel during flight (Scaraffia and Wells, 2003). However, when proline serves as a source of energy, alanine and glutamine seem to be involved in the shuttling of the amino group between the flight muscle and the fat body to avoid ammonia’s toxic effects (Scaraffia and Wells, 2003). In correlation wit ...
university of east anglia
... Answer ALL questions. Unless stated otherwise all multiple choice questions have ONE answer. ...
... Answer ALL questions. Unless stated otherwise all multiple choice questions have ONE answer. ...
AROMA COMPOUNDS IN FRENCH FRIES FROM THREE POTATO
... and Maris Piper (MP). Most of the remaining aroma compounds were clustered with King Edwards (KE) and the amino acids alanine, serine and glycine, which were separated from the other amino acids along PC 2. These amino acids have been shown to be important in the formation of low-molecular weight py ...
... and Maris Piper (MP). Most of the remaining aroma compounds were clustered with King Edwards (KE) and the amino acids alanine, serine and glycine, which were separated from the other amino acids along PC 2. These amino acids have been shown to be important in the formation of low-molecular weight py ...
Partial Class Notes Chapters 3 and 5 (4 slides/page)
... example of a mutation in humans, or in industryrelevant plants, animals or microbes. Present, on a single, one-sided, typed page, the amino acid mutated, the phenotype of the effect on the organism, the molecular reason that the mutation causes the effect(s), and the effect that this mutation has on ...
... example of a mutation in humans, or in industryrelevant plants, animals or microbes. Present, on a single, one-sided, typed page, the amino acid mutated, the phenotype of the effect on the organism, the molecular reason that the mutation causes the effect(s), and the effect that this mutation has on ...
The Chemistry of Life
... Enzyme- Biological Catalyst Catalyst a chemical agent that changes the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction Enzyme is a catalytic protein. Enzymes provide a way for reactions to occur by lowering the activation energy Activation Energy energy required to get a reaction ...
... Enzyme- Biological Catalyst Catalyst a chemical agent that changes the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction Enzyme is a catalytic protein. Enzymes provide a way for reactions to occur by lowering the activation energy Activation Energy energy required to get a reaction ...
Word Notes - Eric Hamber Secondary
... - some inhibitors are temporary, therefore, controlling the inhibitors controls the enzyme. ...
... - some inhibitors are temporary, therefore, controlling the inhibitors controls the enzyme. ...
BCMB 3100 – Chapter 3 (part 1)
... Most polypeptides contain between ____________ amino acids Average M.W. for an amino acid is ____________ so M.W. of most proteins is 5500 to 220,000 daltons. (One dalton equals one atomic mass unit; kilodalton = 1000 daltons). Most proteins have M.W. of 5.5-220 kd. Some proteins contain disulfide b ...
... Most polypeptides contain between ____________ amino acids Average M.W. for an amino acid is ____________ so M.W. of most proteins is 5500 to 220,000 daltons. (One dalton equals one atomic mass unit; kilodalton = 1000 daltons). Most proteins have M.W. of 5.5-220 kd. Some proteins contain disulfide b ...
Active site amino acid sequence of the bovine O6
... C containing 0.5M NaCl was used. This altered elution behaviour indicates possible aggregation of the methyltransferase or interaction with other proteins at the lower salt concentration. The active fractions were pooled and concentrated using an Amicon ultrafiltration cell equipped with a Diaflo YM ...
... C containing 0.5M NaCl was used. This altered elution behaviour indicates possible aggregation of the methyltransferase or interaction with other proteins at the lower salt concentration. The active fractions were pooled and concentrated using an Amicon ultrafiltration cell equipped with a Diaflo YM ...
practice midterm
... 76. For the DNA sequence GCCTAT in one polynucleotide chain, the sequence found in the other polynucleotide chain is A) CGGATA. B) GCCATA. C) CGGAUA. D) ATTCGC. E) GCCTAT. 77. The timing of DNA replication and cell division is regulated carefully for which of the following reasons? A) so that the DN ...
... 76. For the DNA sequence GCCTAT in one polynucleotide chain, the sequence found in the other polynucleotide chain is A) CGGATA. B) GCCATA. C) CGGAUA. D) ATTCGC. E) GCCTAT. 77. The timing of DNA replication and cell division is regulated carefully for which of the following reasons? A) so that the DN ...
File
... denaturing enzymes or occupying the enzyme's active site S9 that it does not function. In some cases, enzymes , will not function without cofactors, such as vitamins or trace elements. In the four graphs below, the rate of reaction or degree of enzyme activity is plotted against each of four factors ...
... denaturing enzymes or occupying the enzyme's active site S9 that it does not function. In some cases, enzymes , will not function without cofactors, such as vitamins or trace elements. In the four graphs below, the rate of reaction or degree of enzyme activity is plotted against each of four factors ...