Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life
... 1. Two plants live in a 35 degree environment. Which one is more likely to survive and reproduce: the one whose enzymes work best at 30 degrees, or the one whose enzymes work best at 20 degrees? Why? 2. Your body temperature is 98.6 degrees, and your body’s pH is close to 7. At what temperature and ...
... 1. Two plants live in a 35 degree environment. Which one is more likely to survive and reproduce: the one whose enzymes work best at 30 degrees, or the one whose enzymes work best at 20 degrees? Why? 2. Your body temperature is 98.6 degrees, and your body’s pH is close to 7. At what temperature and ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... lem even more by reducing it to a numerical exercise. There were four bases in DNA, he pointed out, and 20 amino acids in proteins. (The figure of 20 was a bold guess that turned out to be correct, though the actual 20 are not the same as those that Gamow listed.) How could a language with four lett ...
... lem even more by reducing it to a numerical exercise. There were four bases in DNA, he pointed out, and 20 amino acids in proteins. (The figure of 20 was a bold guess that turned out to be correct, though the actual 20 are not the same as those that Gamow listed.) How could a language with four lett ...
The Acid End-products of Glucose Metabolism of Oral
... (Hofstad, 1974; Tuyau & Sims, 1983). Table 1 shows that H.parainfluenza NCTC 4101 produced much less succinate than the other strains of H . parainfluenzae and was the only strain of Haemophilus to form significant amounts of oxalacetate and pyruvate, the former being its major product. Hollander (1 ...
... (Hofstad, 1974; Tuyau & Sims, 1983). Table 1 shows that H.parainfluenza NCTC 4101 produced much less succinate than the other strains of H . parainfluenzae and was the only strain of Haemophilus to form significant amounts of oxalacetate and pyruvate, the former being its major product. Hollander (1 ...
Chapter 7: Proteins
... The enzymes will break peptones into smaller peptides and amino acids Peptides and amino acids are ready for ...
... The enzymes will break peptones into smaller peptides and amino acids Peptides and amino acids are ready for ...
A gene fusion consisting of 960 base pairs of 5`
... NH^-terminal amino acid sequence was determined by the method of Edman degradation (27). The antino acid sequence analysis (Table 1) showed only one species of interferon molecule with the NH^-terminal sequence: NH^-Glu-Ala-Glu-Ala-Leu-Glu-Phe-Met-Cys-Asp... The sequence was determined by analyzing ...
... NH^-terminal amino acid sequence was determined by the method of Edman degradation (27). The antino acid sequence analysis (Table 1) showed only one species of interferon molecule with the NH^-terminal sequence: NH^-Glu-Ala-Glu-Ala-Leu-Glu-Phe-Met-Cys-Asp... The sequence was determined by analyzing ...
Notes
... C. Element – matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances via chemical reaction 1. there are 92 naturally-occurring elements 2. cannot be changed into a different element or destroyed via chemical reactions 3. about 25 elements are essential for life A) 4 of these make up 96% of living ...
... C. Element – matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances via chemical reaction 1. there are 92 naturally-occurring elements 2. cannot be changed into a different element or destroyed via chemical reactions 3. about 25 elements are essential for life A) 4 of these make up 96% of living ...
Chapter 20
... • An enzyme is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst. • Enzymes are incredibly selective for specific molecules. • An enzyme can speed up a biochemical reaction so that the rate is a million times faster than it would be in the absence of the enzyme. • Many reactions catalyzed by enzymes woul ...
... • An enzyme is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst. • Enzymes are incredibly selective for specific molecules. • An enzyme can speed up a biochemical reaction so that the rate is a million times faster than it would be in the absence of the enzyme. • Many reactions catalyzed by enzymes woul ...
Soil Biology and Biochemistry
... synthesis of A. brasilense UAP 14 strain) did not show any significant effect on the aminotransferase activity. To identify the aminotransferase enzymes that react with tryptophan, crude extracts and ammonium sulfate fractions were run on PAGE under non-denatured conditions. Our data clearly demonst ...
... synthesis of A. brasilense UAP 14 strain) did not show any significant effect on the aminotransferase activity. To identify the aminotransferase enzymes that react with tryptophan, crude extracts and ammonium sulfate fractions were run on PAGE under non-denatured conditions. Our data clearly demonst ...
Molecules of the Cell: The Building Blocks of Life
... In the primordial soup, the capture of organic molecules, the building blocks of life, into a concentrated area, within a membrane bound compartment, permitted the chemical reactions of life (metabolism) to take place at a reasonable rate, something that would not have happened with the molecules fl ...
... In the primordial soup, the capture of organic molecules, the building blocks of life, into a concentrated area, within a membrane bound compartment, permitted the chemical reactions of life (metabolism) to take place at a reasonable rate, something that would not have happened with the molecules fl ...
ap bio ch 5 study guide
... movement, and defense against foreign substances. ○ Most important, protein enzymes function as catalysts in cells, regulating metabolism by selectively accelerating certain chemical reactions without being consumed. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 8th Edition, © Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... movement, and defense against foreign substances. ○ Most important, protein enzymes function as catalysts in cells, regulating metabolism by selectively accelerating certain chemical reactions without being consumed. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 8th Edition, © Pearson Education, Inc. ...
CH 17_ From Gene to Protein
... – First: a correct match between a tRNA and an amino acid, done by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase – Second: a correct match between the tRNA anticodon and an mRNA codon ...
... – First: a correct match between a tRNA and an amino acid, done by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase – Second: a correct match between the tRNA anticodon and an mRNA codon ...
Stability, catalytic versatility and evolution of the
... between monomers and dimers; increasing the protein concentration, that is increasing the fraction of dimers, results in higher thermostability. Dimerisation, therefore, significantly stabilises the Phe55Gln variant and, by inference, the wild-type TrpF. The monomeric variants were catalytically as ...
... between monomers and dimers; increasing the protein concentration, that is increasing the fraction of dimers, results in higher thermostability. Dimerisation, therefore, significantly stabilises the Phe55Gln variant and, by inference, the wild-type TrpF. The monomeric variants were catalytically as ...
Slide 1
... from a limited set of small molecules The four classes of biological molecules contain very large molecules. – They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. – They are also called polymers because they are made from identical building blocks strung together. – The building bloc ...
... from a limited set of small molecules The four classes of biological molecules contain very large molecules. – They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. – They are also called polymers because they are made from identical building blocks strung together. – The building bloc ...
Test Results - Oregon State University
... • Fill in high points questions if you know the answers • Rapidly go through MC and fill ins and answer the ones you know • Use remaining time to use the process of elimination to better statistical chances on the remaining multiple choice • Revisit high point questions and try to garner some partia ...
... • Fill in high points questions if you know the answers • Rapidly go through MC and fill ins and answer the ones you know • Use remaining time to use the process of elimination to better statistical chances on the remaining multiple choice • Revisit high point questions and try to garner some partia ...
Practice Exam III
... What does this imply about the values of Vmax and KM for a “perfect” enzyme? a). The values of both Vmax and KM are very high. b). The values of both Vmax and KM are very low. c). The value of Vmax is very high and the value of KM is very low. d). The value of Vmax is very low and the value of KM is ...
... What does this imply about the values of Vmax and KM for a “perfect” enzyme? a). The values of both Vmax and KM are very high. b). The values of both Vmax and KM are very low. c). The value of Vmax is very high and the value of KM is very low. d). The value of Vmax is very low and the value of KM is ...
Teaching metabolic pathways
... dehydration; (5) aldol-type cleavage; and (6) the substrate-level phosphorylation. Living systems catalyse only a limited number of types of reactions. Often, a reaction type will be already familiar to students from their studies of other pathways. This should be pointed out by teachers. Memorizing ...
... dehydration; (5) aldol-type cleavage; and (6) the substrate-level phosphorylation. Living systems catalyse only a limited number of types of reactions. Often, a reaction type will be already familiar to students from their studies of other pathways. This should be pointed out by teachers. Memorizing ...
exam1_2007 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... Choice D (Enzyme activity & pH): An enzyme has an Aspartic acid residue that is important for function. The enzyme activity at pH=4.0 is ~10%, at pH=5.0 it is 50%, and at pH=6.0 it is ~90%. What is the pKa of this group? Which form is active (protonated or deprotonated)? Justify your answers to both ...
... Choice D (Enzyme activity & pH): An enzyme has an Aspartic acid residue that is important for function. The enzyme activity at pH=4.0 is ~10%, at pH=5.0 it is 50%, and at pH=6.0 it is ~90%. What is the pKa of this group? Which form is active (protonated or deprotonated)? Justify your answers to both ...
Biochemistry - Bonham Chemistry
... • Step 2: Oxidation of aldehyde to a carboxylic acid • Step 3: Formation of acetyl CoA • Step 4: Reoxidation of the lipoamide cofactor • Step 5: Regeneration of the oxidized FAD cofactor ...
... • Step 2: Oxidation of aldehyde to a carboxylic acid • Step 3: Formation of acetyl CoA • Step 4: Reoxidation of the lipoamide cofactor • Step 5: Regeneration of the oxidized FAD cofactor ...
H &
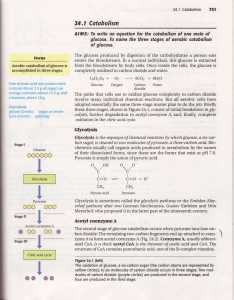
... The acetyl group of aceryl CoA enters the citric acid cycle. The citric acid, rycle ls the pathway used by most organisms to oxidize completely to carbon dioxide the acetyl carbons of acetyl CoAformed in the breakdown of sugars, fats, and amino acids. Prodrtction of two molecules of carbon dioxide a ...
... The acetyl group of aceryl CoA enters the citric acid cycle. The citric acid, rycle ls the pathway used by most organisms to oxidize completely to carbon dioxide the acetyl carbons of acetyl CoAformed in the breakdown of sugars, fats, and amino acids. Prodrtction of two molecules of carbon dioxide a ...
PASS MOCK EXAM
... d. glucose e. ATP 55. Phosphorylation does NOT play a regulatory role in the reaction catalyzed by: a. glycogen phosphorylase b. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase c. pyruvate dehydrogenase d. pyruvate kinase e. none of the above 56. When the liver converts excess glucose to fatty acids all o ...
... d. glucose e. ATP 55. Phosphorylation does NOT play a regulatory role in the reaction catalyzed by: a. glycogen phosphorylase b. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase c. pyruvate dehydrogenase d. pyruvate kinase e. none of the above 56. When the liver converts excess glucose to fatty acids all o ...
Unit I - E
... compounds in the blood, provides a medium for movement of molecules into and throughout cellular compartments, separates charged molecules, dissipates heat, and participates in chemical reactions. Most compounds in the body, including proteins, must interact with an aqueous medium function. In spite ...
... compounds in the blood, provides a medium for movement of molecules into and throughout cellular compartments, separates charged molecules, dissipates heat, and participates in chemical reactions. Most compounds in the body, including proteins, must interact with an aqueous medium function. In spite ...
Slide 1
... If the first T and the second –P were deleted, the relative position of T and –P would change. ...
... If the first T and the second –P were deleted, the relative position of T and –P would change. ...
ภาพนิ่ง 1
... enzyme will utilize (an example will be discussed). • It is also useful for comparing similar enzymes from different tissues or different organisms. • Also, it is the Km of the rate-limiting enzyme in many of the biochemical metabolic pathways that determines the amount of product and overall regula ...
... enzyme will utilize (an example will be discussed). • It is also useful for comparing similar enzymes from different tissues or different organisms. • Also, it is the Km of the rate-limiting enzyme in many of the biochemical metabolic pathways that determines the amount of product and overall regula ...