Document
... ROLE OF VIT C DEFICIENCY IN CHD: initiation of atherosclerotic plaque formation. Vitamin C and amino acid lysine (LP(a) binding inhibitors), prevent this molecule from binding to the walls of damaged arteries. These substances at high dosages are patented to prevent and to destroy existing athe ...
... ROLE OF VIT C DEFICIENCY IN CHD: initiation of atherosclerotic plaque formation. Vitamin C and amino acid lysine (LP(a) binding inhibitors), prevent this molecule from binding to the walls of damaged arteries. These substances at high dosages are patented to prevent and to destroy existing athe ...
Exam3 - Cornell College
... 3. A space probe, designed to land on a distant planet, is equipped to obtain samples of material, identify them according to molecular type and analyze their chemical makeup. Results obtained from samples from planet 205 indicate that the nucleic acid molecules contain just two types of nucleotides ...
... 3. A space probe, designed to land on a distant planet, is equipped to obtain samples of material, identify them according to molecular type and analyze their chemical makeup. Results obtained from samples from planet 205 indicate that the nucleic acid molecules contain just two types of nucleotides ...
Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning
... and animals synthesize sterols, the type that makes the most important contribution to human structure and function is cholesterol, which is synthesized by the liver in humans and animals and is also present in most animal-based foods. Like other lipids, cholesterol's hydrocarbons make it hydrophobi ...
... and animals synthesize sterols, the type that makes the most important contribution to human structure and function is cholesterol, which is synthesized by the liver in humans and animals and is also present in most animal-based foods. Like other lipids, cholesterol's hydrocarbons make it hydrophobi ...
bioinfo4
... Amino acids substitute easily for another due to similar physicochemical properties ...
... Amino acids substitute easily for another due to similar physicochemical properties ...
Trans-Tonoplast Transport of the Sulfur Containing
... Uptake of cysteine and methionine was measured by using the same uptake system. There was a significant capacity to transport methionine across the tonoplast (Table 2, cf. DIETZ & BUSCH 1990). Similar to the translocation of other amino acids, ATP stimulated the translocation even in the absence of ...
... Uptake of cysteine and methionine was measured by using the same uptake system. There was a significant capacity to transport methionine across the tonoplast (Table 2, cf. DIETZ & BUSCH 1990). Similar to the translocation of other amino acids, ATP stimulated the translocation even in the absence of ...
Protein Structure Analysis and Prediction
... Proteins are essential to biological processes. They are responsible for catalyzing and regulating biochemical reactions, transporting molecules, the chemistry of vision and of the photosynthetic conversion of light to growth, and they form the basis of structures such as skin, hair, and tendon. Pro ...
... Proteins are essential to biological processes. They are responsible for catalyzing and regulating biochemical reactions, transporting molecules, the chemistry of vision and of the photosynthetic conversion of light to growth, and they form the basis of structures such as skin, hair, and tendon. Pro ...
Biochemistry Final
... with the energy it needs, and some travels to the tissues as well to generate ATP necessary for function. Gluconeogenesis is also on in the liver to generate glucose from free intermediates. The liver can only store a day’s worth of glycogen, so when these stores get depleted, the brain is once agai ...
... with the energy it needs, and some travels to the tissues as well to generate ATP necessary for function. Gluconeogenesis is also on in the liver to generate glucose from free intermediates. The liver can only store a day’s worth of glycogen, so when these stores get depleted, the brain is once agai ...
Unit 2 Exam Biochem, Cell Bio, Metabolism
... fish. Explain why the nucleic acids of the fish do not change your appearance. In what ways is the structure of mRNA similar to DNA? How does mRNA differ from DNA? What is the function of mRNA? What is the function of tRNA? What is a codon? What is an anticodon? Explain the interrelationship of thes ...
... fish. Explain why the nucleic acids of the fish do not change your appearance. In what ways is the structure of mRNA similar to DNA? How does mRNA differ from DNA? What is the function of mRNA? What is the function of tRNA? What is a codon? What is an anticodon? Explain the interrelationship of thes ...
Buffering Capacity
... • Obtain 25mL of the next assigned buffer for each of the two beakers • Repeat the first protocol up to 30 drops of acid & base respectively, recording the pH values in table 1 • Calculate the ΔpH , ΔpH and ΔpH • Post your data on the board in the front of ...
... • Obtain 25mL of the next assigned buffer for each of the two beakers • Repeat the first protocol up to 30 drops of acid & base respectively, recording the pH values in table 1 • Calculate the ΔpH , ΔpH and ΔpH • Post your data on the board in the front of ...
PDF
... it had same retention time (5.80 min) with standard Leu, as shown in Fig. 4 A, which depicts chromatogram monitoring with the same mass. After analysis of the components with a retention time at 5.80 min, as shown in Fig. 4 A and B, with the LC-TOF MS, the resulting LC-TOF chromatography is shown in ...
... it had same retention time (5.80 min) with standard Leu, as shown in Fig. 4 A, which depicts chromatogram monitoring with the same mass. After analysis of the components with a retention time at 5.80 min, as shown in Fig. 4 A and B, with the LC-TOF MS, the resulting LC-TOF chromatography is shown in ...
Chemistry Of Lichens Complete
... • KC (K followed by C) - Turns yellow with usnic acid - Turns red with C- depsides and depsidones which undergo rapid hydrolysis to yield a mhydroxy phenolic moiety, e.g. alectoronic acid ...
... • KC (K followed by C) - Turns yellow with usnic acid - Turns red with C- depsides and depsidones which undergo rapid hydrolysis to yield a mhydroxy phenolic moiety, e.g. alectoronic acid ...
Chapter 19 Carbohydrate Biosynthesis
... • AMP inhibits fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase1), but activates phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1). • Citrate inhibits PFK-1 and activates FBPase-1. • Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (a regulator, not an intermediate) in liver cells, signaling a high blood glucose/glucagon level, activates PFK-1 and inhibi ...
... • AMP inhibits fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase1), but activates phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1). • Citrate inhibits PFK-1 and activates FBPase-1. • Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (a regulator, not an intermediate) in liver cells, signaling a high blood glucose/glucagon level, activates PFK-1 and inhibi ...
Introduction to Metabolism
... _______ Accepts the acetyl group from reduced lipoic acid. _______ Oxidizes the reduced form of lipoic acid. _______ Initial electron acceptor in oxidation of pyruvate. ...
... _______ Accepts the acetyl group from reduced lipoic acid. _______ Oxidizes the reduced form of lipoic acid. _______ Initial electron acceptor in oxidation of pyruvate. ...
Amino Acids 2 Questions
... identified by HPLC. When the native peptide was exposed to cyanogen bromide (BrCN), a heptapeptide and free glycine were recovered. Incubation of the native protein with trypsin gave a tetrapeptide, a tripeptide, and free lysine. The peptides were separated and each run through one cycle of the E ...
... identified by HPLC. When the native peptide was exposed to cyanogen bromide (BrCN), a heptapeptide and free glycine were recovered. Incubation of the native protein with trypsin gave a tetrapeptide, a tripeptide, and free lysine. The peptides were separated and each run through one cycle of the E ...
`Chargaff`s Rules` for Protein Folding: Stoichiometric Leitmotif Made
... Protein folding! The first thing that almost always comes to mind when someone hears this term is Anfinsen’s hypothesis. So much so that protein folding and Anfinsen’s hypothesis have long since been considered synonyms of each other. Anfinsen’s hypothesis laid the ground rule for protein folding. T ...
... Protein folding! The first thing that almost always comes to mind when someone hears this term is Anfinsen’s hypothesis. So much so that protein folding and Anfinsen’s hypothesis have long since been considered synonyms of each other. Anfinsen’s hypothesis laid the ground rule for protein folding. T ...
Plasma Amino Acid Response to Graded Levels of Escape Protein
... &Least squares mean concentrations (micromolar). bOnly coefficients with P c .lo reported. Values represent change in concentration/kilogram of test protein consumed (linear) or (concentration/kiloga& (quadratic). CSEM for 20, 35, 50, 65, and 80% levels based on n = 8 at each level (n = 30 for 0 lev ...
... &Least squares mean concentrations (micromolar). bOnly coefficients with P c .lo reported. Values represent change in concentration/kilogram of test protein consumed (linear) or (concentration/kiloga& (quadratic). CSEM for 20, 35, 50, 65, and 80% levels based on n = 8 at each level (n = 30 for 0 lev ...
Protein Module Student Handout Name__________________ 1
... Protein Module Student Handout 17. You will now use qwikMD to make these mutations in your protein. In the Structure Manipulation window, click the circle next to “Mutate.” You may choose whether you want to try all of the mutations at once or run them one at a time. Click on the name of the amino ...
... Protein Module Student Handout 17. You will now use qwikMD to make these mutations in your protein. In the Structure Manipulation window, click the circle next to “Mutate.” You may choose whether you want to try all of the mutations at once or run them one at a time. Click on the name of the amino ...
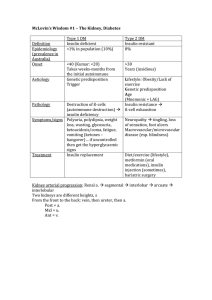
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
Final Examination
... amino acids and other carbohydrates Fatty acids cannot be made into glucose and glycerol is minor fatty acids (from lipids) and glycerol (from triacylglycerols) fatty acids (from lipids) and amino acids amino acids and glycerol (from triacylglycerols) ...
... amino acids and other carbohydrates Fatty acids cannot be made into glucose and glycerol is minor fatty acids (from lipids) and glycerol (from triacylglycerols) fatty acids (from lipids) and amino acids amino acids and glycerol (from triacylglycerols) ...
Lecture 15: Translation and Transcription
... Nucleotide triplets are known as codons (ii) Basic unit of the genetic code (iii) Specify either individual amino acids or termination ...
... Nucleotide triplets are known as codons (ii) Basic unit of the genetic code (iii) Specify either individual amino acids or termination ...
lec27_2013 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... Citric acid (TCA, Krebs) cycle Electron transport Oxidative phosphorylation (ATP synthesis) ...
... Citric acid (TCA, Krebs) cycle Electron transport Oxidative phosphorylation (ATP synthesis) ...