A2 2, Analytical, Transition Metals, Electrochemistry and
... (iii) Explain how the purified product formed between putrescine and excess ethanoyl chloride could be used to identify putrescine. ...
... (iii) Explain how the purified product formed between putrescine and excess ethanoyl chloride could be used to identify putrescine. ...
Reassembled Biosynthetic Pathway for Large
... achieves the same goal with the use of only one plasmid and a single strain. All the enzymes essential for oligosaccharide synthesis, including the glycosyltransferases, and the sugar ± nucleotide regeneration are in one E. coli strain. Thus, this approach avoids unnecessary transport of the interme ...
... achieves the same goal with the use of only one plasmid and a single strain. All the enzymes essential for oligosaccharide synthesis, including the glycosyltransferases, and the sugar ± nucleotide regeneration are in one E. coli strain. Thus, this approach avoids unnecessary transport of the interme ...
Antimicrobial Agents..........................................................
... A. Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis B. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis C. Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis D. Effects on cell membrane sterols (antifungal agents) E. Inhibition of unique metabolic steps ...
... A. Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis B. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis C. Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis D. Effects on cell membrane sterols (antifungal agents) E. Inhibition of unique metabolic steps ...
Lecture 8 - People Server at UNCW
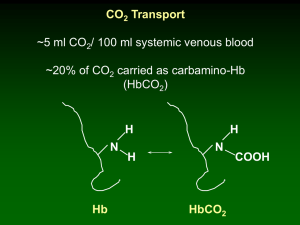
... Reverse chloride shift HCO3- / Cl- exchanger moves Cl- out of RBC and HCO3- in. ...
... Reverse chloride shift HCO3- / Cl- exchanger moves Cl- out of RBC and HCO3- in. ...
mcb101_exam2_F07a
... desulfhydrase, which catalyzes the breakdown of cysteine. What product of this reaction reacts with the iron that is in the agar, to produce the black precipitate that is the sign of a positive test? A. ammonia D. various acids ...
... desulfhydrase, which catalyzes the breakdown of cysteine. What product of this reaction reacts with the iron that is in the agar, to produce the black precipitate that is the sign of a positive test? A. ammonia D. various acids ...
Effect of Glycine on Phospholipids of Mycobacterium
... Small molecules may act as regulatory signals for enzymes involved in different metabolic pathways, e.g. one amino acid may influence enzymes on the biosynthetic pathway of one or more other amino acids (Jensen, 1969). Hence it is possible that high concentrations of glycine influence either directl ...
... Small molecules may act as regulatory signals for enzymes involved in different metabolic pathways, e.g. one amino acid may influence enzymes on the biosynthetic pathway of one or more other amino acids (Jensen, 1969). Hence it is possible that high concentrations of glycine influence either directl ...
BIOCHEMISTRY I (CHMI 2227 E) PROBLEMS and
... This problem set has been prepared for students taking the course Biochemistry I (CHMI 2227E), as offered at Laurentian University. It contains several problems taken from textbooks and from the author’s imagination. While the vast majority of the problems found in this book can be relatively easily ...
... This problem set has been prepared for students taking the course Biochemistry I (CHMI 2227E), as offered at Laurentian University. It contains several problems taken from textbooks and from the author’s imagination. While the vast majority of the problems found in this book can be relatively easily ...
Lecture 21
... Inhibitors were used. Reagents are found that inhibit the production of pathway products, thereby causing the buildup of metabolites that can be identified as pathway intermediates. Fluoride- leads to the buildup of 3-phosphoglycerate and 2-phosphoglycerate ...
... Inhibitors were used. Reagents are found that inhibit the production of pathway products, thereby causing the buildup of metabolites that can be identified as pathway intermediates. Fluoride- leads to the buildup of 3-phosphoglycerate and 2-phosphoglycerate ...
Gene7-07
... anticodons that read new codons Missense mutations change a single codon and so may cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either i ...
... anticodons that read new codons Missense mutations change a single codon and so may cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either i ...
Unit 1: The Nature of Life
... v. Enzymes are very specific, generally catalyzing only one chemical reaction. vi. For this reason, part of an enzyme’s name is usually derived from the reaction it catalyzes. j. Enzyme Action i. For a chemical reaction to take place, the reactants must collide with enough energy so that existing bo ...
... v. Enzymes are very specific, generally catalyzing only one chemical reaction. vi. For this reason, part of an enzyme’s name is usually derived from the reaction it catalyzes. j. Enzyme Action i. For a chemical reaction to take place, the reactants must collide with enough energy so that existing bo ...
Serine Proteases
... A general base (His) that can accept a proton from the hydroxyl group of the reactive serine ¾ Tight binding and stabilization of the tetrahedral transition state ¾ Oxyanion hole-provision of groups that can form hydrogen bonds to the negatively charged oxygen ...
... A general base (His) that can accept a proton from the hydroxyl group of the reactive serine ¾ Tight binding and stabilization of the tetrahedral transition state ¾ Oxyanion hole-provision of groups that can form hydrogen bonds to the negatively charged oxygen ...
Assessment of the mathematical issues involved
... represents a potentially important new advance in methodology. Concomitant with the advantages of the flooding dose technique, there are potential problems stemming from the requisite assumptions. The most crucial assumption is that the bolus injection of an amount of amino acid well in excess of th ...
... represents a potentially important new advance in methodology. Concomitant with the advantages of the flooding dose technique, there are potential problems stemming from the requisite assumptions. The most crucial assumption is that the bolus injection of an amount of amino acid well in excess of th ...
Amino Acids - Building Blocks of Proteins
... recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food it ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship is also true at all levels below the Potassium macro level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular Ion level. For two examples of proteins and their func ...
... recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food it ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship is also true at all levels below the Potassium macro level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular Ion level. For two examples of proteins and their func ...
Enzymes Recap
... • The chemical structure is such that its successive oxida5on yields high energy electrons that can be harnessed to drive ATP synthesis in an energy efficient manner ...
... • The chemical structure is such that its successive oxida5on yields high energy electrons that can be harnessed to drive ATP synthesis in an energy efficient manner ...
HuaLi (215-221) - Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition
... percentage of oleic acid can decrease low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-c) to high density lipoproteincholesterol ratio and so reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease7 and several cancers.8 Furthermore, the preferred ratio of n-6 to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in soybean9-11 may ...
... percentage of oleic acid can decrease low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-c) to high density lipoproteincholesterol ratio and so reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease7 and several cancers.8 Furthermore, the preferred ratio of n-6 to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in soybean9-11 may ...
Ch 16.4 Enzymes and rest
... Population studies from China (China Study) and Norway (WWII) correlate significant lower rates of breast and prostate cancer in dairy free ...
... Population studies from China (China Study) and Norway (WWII) correlate significant lower rates of breast and prostate cancer in dairy free ...
Chapter 7 7 The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes Mechanisms and
... by proteolysis. t l i § Holoenzyme: An active, complex enzyme consiting of an apoenzyme and a coenzyme Holoenzyme = apoenzyme +coenzyme (or cofactor) § Coenzyme: low molecular weight organic molecules (NAD+, FAD+…) § Cofactor: metal ions, ions is required for holoenzyme’s holoenzyme s ...
... by proteolysis. t l i § Holoenzyme: An active, complex enzyme consiting of an apoenzyme and a coenzyme Holoenzyme = apoenzyme +coenzyme (or cofactor) § Coenzyme: low molecular weight organic molecules (NAD+, FAD+…) § Cofactor: metal ions, ions is required for holoenzyme’s holoenzyme s ...
Product Description
... Product Description: Fulvic Green™ is a unique liquid concentrate of an Activated Monatomic Fulvic base with allnatural Hawaiian Spirulina. This powerful combination provides the natural healing benefits of Fulvic Acid with Spirulina's incredibly rich blend of proteins, amino acids, vitamins, and mi ...
... Product Description: Fulvic Green™ is a unique liquid concentrate of an Activated Monatomic Fulvic base with allnatural Hawaiian Spirulina. This powerful combination provides the natural healing benefits of Fulvic Acid with Spirulina's incredibly rich blend of proteins, amino acids, vitamins, and mi ...