genetics ch 7 [10-31
... o Tyrosemia type 2 (oculocutaneous tyrosinemia) – caused by deficiency of tyrosine aminotransferase; characterized by corneal erosions, thickening of skin on palms and soles, and variable mental retardation o Tyrosinemia type 3 associated with reduced activity of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase ...
... o Tyrosemia type 2 (oculocutaneous tyrosinemia) – caused by deficiency of tyrosine aminotransferase; characterized by corneal erosions, thickening of skin on palms and soles, and variable mental retardation o Tyrosinemia type 3 associated with reduced activity of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase ...
Fatty Acid Degradation Catabolism Overview TAG and FA
... Utilization Stage 2: Activation and Transport into Matrix • FA must be attached to CoA • High energy bond • Costs ATP AMP (2 ATP equivalents) ...
... Utilization Stage 2: Activation and Transport into Matrix • FA must be attached to CoA • High energy bond • Costs ATP AMP (2 ATP equivalents) ...
Systematically Assessing the Influence of 3
... intricate 3-dimensional (3D) structure of the protein. As such, the local structural context of amino acid residues within the protein should significantly affect the level of selective constraint operating on the residues. Although this notion is readily assumed by many investigators (Bao and Cui 2 ...
... intricate 3-dimensional (3D) structure of the protein. As such, the local structural context of amino acid residues within the protein should significantly affect the level of selective constraint operating on the residues. Although this notion is readily assumed by many investigators (Bao and Cui 2 ...
Aerobic Respiration
... Advantages of ATP as an intermediate energy carrier Only one enzyme is required to release ...
... Advantages of ATP as an intermediate energy carrier Only one enzyme is required to release ...
18,5 Primory structure of proteins 18.6 Secondory stractare of proteins
... shows, a corkscrew must be turned in a right-handed, or clockwise, direction to penetrate a cork. The alpha helixes of proteins are always righthanded. The helixes are held together by hydrogen bonds, shornmin Figure 18.4,formed between the hydrogen of an N-H of a peptide bond and the carbonyl oxyge ...
... shows, a corkscrew must be turned in a right-handed, or clockwise, direction to penetrate a cork. The alpha helixes of proteins are always righthanded. The helixes are held together by hydrogen bonds, shornmin Figure 18.4,formed between the hydrogen of an N-H of a peptide bond and the carbonyl oxyge ...
Protegrins: leukocyte antimicrobial peptides that combine features of
... His Arg Thr Ala Pro Tyr Val Met Ile Leu Phe ...
... His Arg Thr Ala Pro Tyr Val Met Ile Leu Phe ...
Nitrogen Balance With Sheep on Rations Containing Urea
... urea-N and ammonia-N of systemic blood following urea adm1n1atratlon (Dinnlng et al., MS.). It is evident, therefore, that ammonia formation sa one ot the predominating reactions taking place in the rumen of an1maJ8 fed urea. Consideration of the possibility that ammonia formed in the rumen contribu ...
... urea-N and ammonia-N of systemic blood following urea adm1n1atratlon (Dinnlng et al., MS.). It is evident, therefore, that ammonia formation sa one ot the predominating reactions taking place in the rumen of an1maJ8 fed urea. Consideration of the possibility that ammonia formed in the rumen contribu ...
Chapter 3
... – Removing an electron • Reduction – Addition of an electron • Oxidation and reduction are always coupled reactions • Often involves the transfer of hydrogen atoms rather than free electrons – Hydrogen atom contains one electron – A molecule that loses a hydrogen also loses an electron and therefore ...
... – Removing an electron • Reduction – Addition of an electron • Oxidation and reduction are always coupled reactions • Often involves the transfer of hydrogen atoms rather than free electrons – Hydrogen atom contains one electron – A molecule that loses a hydrogen also loses an electron and therefore ...
Exam #3 2 Problem 1. (25 points) You study ligand binding to two
... Carbon monoxide, an odorless gas, binds to hemoglobin to form CO-hemoglobin. Crystals of CO-hemoglobin are isomorphous with those of oxyhemoglobin, which suggests that COHb has the same conformation as oxyhemoglobin. Each heme in Hb can bind one CO molecule, but O2 and CO cannot simultaneously bind ...
... Carbon monoxide, an odorless gas, binds to hemoglobin to form CO-hemoglobin. Crystals of CO-hemoglobin are isomorphous with those of oxyhemoglobin, which suggests that COHb has the same conformation as oxyhemoglobin. Each heme in Hb can bind one CO molecule, but O2 and CO cannot simultaneously bind ...
Metabolism - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... biosynthesis of RNA, DNA, and coenzymes such as ATP, NAD+, FAD, and coenzyme A - required by rapidly growing cells such as those of bone marrow, skin and intestinal mucosa. ...
... biosynthesis of RNA, DNA, and coenzymes such as ATP, NAD+, FAD, and coenzyme A - required by rapidly growing cells such as those of bone marrow, skin and intestinal mucosa. ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... for T3 . The further proteins, binding thyroid hormones, are thyroxine binding prealbumin and albumin. More than 99% of T4 is bound on plasma proteins. • During this period the part of T4 is deionidated to T3 because this form is tentimes more metabolically active. Conversion of T4 to T3 is also obs ...
... for T3 . The further proteins, binding thyroid hormones, are thyroxine binding prealbumin and albumin. More than 99% of T4 is bound on plasma proteins. • During this period the part of T4 is deionidated to T3 because this form is tentimes more metabolically active. Conversion of T4 to T3 is also obs ...
on the enzyme
... place where the target molecule can attach. This place is called the active site. The target molecule/chemical is the substrate. ...
... place where the target molecule can attach. This place is called the active site. The target molecule/chemical is the substrate. ...
02b Basic equations two substrates
... In the second major class of bisubstrate reactions one of the products is released before the second can bind. A stable enzyme intermediate occurs in these reactions that reacts with the second substrate. Often the enzyme is transiently covalently modified in order to transfer a functional group fro ...
... In the second major class of bisubstrate reactions one of the products is released before the second can bind. A stable enzyme intermediate occurs in these reactions that reacts with the second substrate. Often the enzyme is transiently covalently modified in order to transfer a functional group fro ...
week 10_protein
... In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the protein that is linked to a b ...
... In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the protein that is linked to a b ...
protein - Portal UniMAP
... In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the protein that is linked to a b ...
... In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the protein that is linked to a b ...
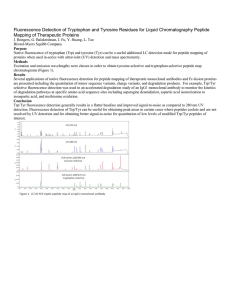
Fluorescence Detection of Tryptophan and Tyrosine Residues for
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
Pyruvic acid is chemically groomed for the Krebs cycle
... – Some are obtained directly from food – Others are made from intermediates in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle ...
... – Some are obtained directly from food – Others are made from intermediates in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle ...
Flux distributions in anaerobic, glucose-limited
... ments carried out in this work have shown that ADH I11 is active during anaerobic growth on glucose (see Results). Hence, the model includes two reactions where acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol but localized in different compartments (reactions 9 and 37). Two isoenzymes of aldehyde dehydrogenase e ...
... ments carried out in this work have shown that ADH I11 is active during anaerobic growth on glucose (see Results). Hence, the model includes two reactions where acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol but localized in different compartments (reactions 9 and 37). Two isoenzymes of aldehyde dehydrogenase e ...