Chapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During Exercise,
... oxygen captured from the air by the lungs, and they are fed by nutrients and oxygen carried through the bloodstream. It is essential to remember that a full understanding of muscle metabolism begins at the cellular level, but also includes hydration, nutrition, meal timing and maintenance of muscle ...
... oxygen captured from the air by the lungs, and they are fed by nutrients and oxygen carried through the bloodstream. It is essential to remember that a full understanding of muscle metabolism begins at the cellular level, but also includes hydration, nutrition, meal timing and maintenance of muscle ...
Review Packet CORRECT
... They move through the electron transport chain and are DE energized. d. Describe the movement of H+ ions (protons) in OP They are pumped from the matrix (low concentration) to the intermembrane space (high concentration) ...
... They move through the electron transport chain and are DE energized. d. Describe the movement of H+ ions (protons) in OP They are pumped from the matrix (low concentration) to the intermembrane space (high concentration) ...
Molecular Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere
... several PGPR Bacillus strains, including FZB42T (Borriss, 2011). The volatiles 3-hydroxy-2-butanone (acetoin) and 2,3 butandiol trigger enhanced plant growth. To synthesize 2,3-butanediol, pyruvate is firstly converted into acetolactate by acetolactate synthase (AlsS) under conditions of low pH and ...
... several PGPR Bacillus strains, including FZB42T (Borriss, 2011). The volatiles 3-hydroxy-2-butanone (acetoin) and 2,3 butandiol trigger enhanced plant growth. To synthesize 2,3-butanediol, pyruvate is firstly converted into acetolactate by acetolactate synthase (AlsS) under conditions of low pH and ...
Lab #8 Prelab: Protein, Triglycerides, and Esters Lab
... "Chemically, proteins are high polymers. They are polyamides, and the monomers from which they are derived are the α-amino carboxylic acids. A single protein molecule contains hundreds or even thousands of amino acids units; these units can be of twenty-odd different kinds. The number of different p ...
... "Chemically, proteins are high polymers. They are polyamides, and the monomers from which they are derived are the α-amino carboxylic acids. A single protein molecule contains hundreds or even thousands of amino acids units; these units can be of twenty-odd different kinds. The number of different p ...
enzymes lecture 1
... Active Site(catalytic site) • A restricted region of an enzyme molecule which binds to the substrate. Active Site • It is formed from Substrate Enzyme Amino acids sequences in the polypeptide chain . ...
... Active Site(catalytic site) • A restricted region of an enzyme molecule which binds to the substrate. Active Site • It is formed from Substrate Enzyme Amino acids sequences in the polypeptide chain . ...
Test Example
... Ans: (1) Hydrogen bonds: weak electrostatic attractions between one electronegative atom (such as oxygen or nitrogen) and a hydrogen atom covalently linked to a second electronegative atom; (2) electrostatic interactions: relatively weak charge-charge interactions (attractions of opposite charges, r ...
... Ans: (1) Hydrogen bonds: weak electrostatic attractions between one electronegative atom (such as oxygen or nitrogen) and a hydrogen atom covalently linked to a second electronegative atom; (2) electrostatic interactions: relatively weak charge-charge interactions (attractions of opposite charges, r ...
Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of the Toll
... to shrimp pathogens such as the yellow head (Boonyaratpalin et al., 1993) and white spot syndrome (Flegel, 1997) viruses. Shrimp immunity is similar to that in other invertebrate organisms, and consists of an innate immunity, which can be divided into humoral and cellular defenses (Lee and Soderhall ...
... to shrimp pathogens such as the yellow head (Boonyaratpalin et al., 1993) and white spot syndrome (Flegel, 1997) viruses. Shrimp immunity is similar to that in other invertebrate organisms, and consists of an innate immunity, which can be divided into humoral and cellular defenses (Lee and Soderhall ...
Lecture 17 Glycolysis (continued) Recap Phases: priming: glucose
... ΔGo’ =+6.3 kJ/mol ΔG’ = -1.29 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note that the acid C is oxidized (from aldehyde to acid) Reaction 7 ΔGo’ =-18.9 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.1 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note “substrate level phosphorylation” of ADP Reaction 8 ΔGo’ =+4.4 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.83 kJ/mol ...
... ΔGo’ =+6.3 kJ/mol ΔG’ = -1.29 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note that the acid C is oxidized (from aldehyde to acid) Reaction 7 ΔGo’ =-18.9 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.1 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note “substrate level phosphorylation” of ADP Reaction 8 ΔGo’ =+4.4 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.83 kJ/mol ...
Effect of Alanine-293 Replacement on the Activity, ATP Binding, and
... aminoacylation activity of LeuRS than any of the other substitutions A293D, A293R, A293G, A293I, A293Y and A293F. 293A is only involved in the binding of ATP, and all amino acid substitutions above caused stronger binding of ATP. Moreover, the negative charge at this site, induced by mutation A293D, ...
... aminoacylation activity of LeuRS than any of the other substitutions A293D, A293R, A293G, A293I, A293Y and A293F. 293A is only involved in the binding of ATP, and all amino acid substitutions above caused stronger binding of ATP. Moreover, the negative charge at this site, induced by mutation A293D, ...
MOLECULAR MEDICINE
... may have important biological effects, but they are rarely understood the same way drugs are. In the case of omega-3 fatty acids, studies have been hampered by the inconsistency of supplements that are not regulated like drugs and vary in content and quality. With Kang’s mice, he said, “you take awa ...
... may have important biological effects, but they are rarely understood the same way drugs are. In the case of omega-3 fatty acids, studies have been hampered by the inconsistency of supplements that are not regulated like drugs and vary in content and quality. With Kang’s mice, he said, “you take awa ...
Comparison of Rumen Amino Acid Protection Technologies
... Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine ...
... Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine ...
Biochemistry - Textbooks Online
... and maintenance of health (2) the understanding and treatment of ...
... and maintenance of health (2) the understanding and treatment of ...
Objectives 7
... - Energy is stored as glycogen (carbohydrates), protein (amino acids) or triacylglyercols (fatty acids) - The four circulating fuels are glucose (most important), lactate, free fatty acids, and ketone bodies; these provide fuel in response to specific physiological conditions - In fed and early star ...
... - Energy is stored as glycogen (carbohydrates), protein (amino acids) or triacylglyercols (fatty acids) - The four circulating fuels are glucose (most important), lactate, free fatty acids, and ketone bodies; these provide fuel in response to specific physiological conditions - In fed and early star ...
very new glucogen me..
... Any substance can join to common pathway of gluconeogenesis is glycogenic ...
... Any substance can join to common pathway of gluconeogenesis is glycogenic ...
Influence of Metal Ions on Ruminal Enzyme Activities Nutritional
... nitrogen in ammonia or other nitrogen source and carbon skeletons and sulphur precursors. Ammonia assimilation by rumen microbes depends on rumen pH (V e t h et al. 1999), rumen ammonia concentration (M e h r e z et al. 1977) and ruminal ammonia-assimilating enzyme activity. Several ammonia-assimila ...
... nitrogen in ammonia or other nitrogen source and carbon skeletons and sulphur precursors. Ammonia assimilation by rumen microbes depends on rumen pH (V e t h et al. 1999), rumen ammonia concentration (M e h r e z et al. 1977) and ruminal ammonia-assimilating enzyme activity. Several ammonia-assimila ...
RESPIRATION Production of ATP and CO2 by O2 and organic
... In sugar, starch, glycogen, fat, protein NAD+ is Respiratory Electron Carrier Reduced NADH results from addition of 2 e- and 1 H+ Contains nearly all the energy from the original organic molecule bond Key: Ea keeps us from burning up Without it, all these reactions would occur spontaneously Exergoni ...
... In sugar, starch, glycogen, fat, protein NAD+ is Respiratory Electron Carrier Reduced NADH results from addition of 2 e- and 1 H+ Contains nearly all the energy from the original organic molecule bond Key: Ea keeps us from burning up Without it, all these reactions would occur spontaneously Exergoni ...
Use of infrared and visible light radiation as modulator of protein
... Furthermore, it was also shown that proteins and their targets share a characteristic frequency. Thus it can be further postulated that RRM frequencies characterize not only a general function but also recognition/interaction between ...
... Furthermore, it was also shown that proteins and their targets share a characteristic frequency. Thus it can be further postulated that RRM frequencies characterize not only a general function but also recognition/interaction between ...
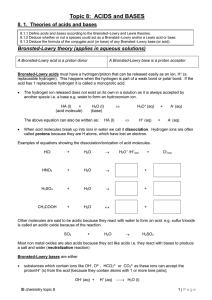
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
Unit: Enzymes II
... Procedure III Isoenzymes With the improved techniques for analyzing proteins, developed over the last twenty years, it has been demonstrated that a particular type of catalytic activity (enzymes) is frequently due to the existence of several distinct forms of an enzyme rather than to only one type o ...
... Procedure III Isoenzymes With the improved techniques for analyzing proteins, developed over the last twenty years, it has been demonstrated that a particular type of catalytic activity (enzymes) is frequently due to the existence of several distinct forms of an enzyme rather than to only one type o ...
Lipids (lec 1, 2, 3)..
... - Fats rich in saturated fatty acids (e.g butter) are solid in nature due to high melting point of saturated fatty acids. ...
... - Fats rich in saturated fatty acids (e.g butter) are solid in nature due to high melting point of saturated fatty acids. ...
Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Additives and Products or
... the detoxification of ammonia has been recognized since the discovery of the urea (ornithine) cycle in 1932 (Krebs and Henseleit, 1932). In the past decades, additional vital roles of L-arginine in physiology, nutrition and metabolic pathways as: the precursor of proline, glutamate, creatine, nitric ...
... the detoxification of ammonia has been recognized since the discovery of the urea (ornithine) cycle in 1932 (Krebs and Henseleit, 1932). In the past decades, additional vital roles of L-arginine in physiology, nutrition and metabolic pathways as: the precursor of proline, glutamate, creatine, nitric ...