video slide - Mr. Patrick Wagner's Teacher Web Site
... The nuclear envelope w/ pores encloses the nucleus, separating its contents (nucleolus, chromatin) from the cytoplasm ...
... The nuclear envelope w/ pores encloses the nucleus, separating its contents (nucleolus, chromatin) from the cytoplasm ...
Unit 5 Anatomy and Physiology Cells
... • This is the fluid that fills the cell. • The cells organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm. ...
... • This is the fluid that fills the cell. • The cells organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm. ...
Ch 3 Cells - Review Cell theory The cell is the smallest unit of life
... 1. maintain the cell’s integrity The phospholipid bilayer is a semipermeable membrane that separates intracellular from extracellular fluids and chemicals. It is permeable to lipids and some water. Cholesterol is present in and gives strength to all plasma membranes. 2. control transport in/out of c ...
... 1. maintain the cell’s integrity The phospholipid bilayer is a semipermeable membrane that separates intracellular from extracellular fluids and chemicals. It is permeable to lipids and some water. Cholesterol is present in and gives strength to all plasma membranes. 2. control transport in/out of c ...
The Endomembrane System
... to proteins in ER. Exocytosis, or stay as part of cell (e.g. lysosomes). ...
... to proteins in ER. Exocytosis, or stay as part of cell (e.g. lysosomes). ...
Cells - ckcary
... • Ribosomes help make protiens • Mitochondria change food into a form the cell can use for energy (ATP) • The vacuole stores water and nutrients, and may help digest food • The nucleus directs activities and stores information • The cell membrane holds the cell together and lets things go in and out ...
... • Ribosomes help make protiens • Mitochondria change food into a form the cell can use for energy (ATP) • The vacuole stores water and nutrients, and may help digest food • The nucleus directs activities and stores information • The cell membrane holds the cell together and lets things go in and out ...
Cell Structure - Brooklyn High School
... • Schwann – looked at animals and determined they were all made of cells • Remak, Virchow, Redi – biogenesis – “life comes from life” ...
... • Schwann – looked at animals and determined they were all made of cells • Remak, Virchow, Redi – biogenesis – “life comes from life” ...
(a) The structure of a cholera bacterium is different
... When pieces of carrot are placed in water, chloride ions are released from the cell vacuoles. Identical pieces of carrot were placed in water at different temperatures. The concentration of chloride ions in the water was measured after a set period of time. The graph shows the results. ...
... When pieces of carrot are placed in water, chloride ions are released from the cell vacuoles. Identical pieces of carrot were placed in water at different temperatures. The concentration of chloride ions in the water was measured after a set period of time. The graph shows the results. ...
Chapter 7 - Leon County Schools
... Prokaryote cells have a nucleus. The first organisms were all plantlike. Prokaryote cells have no nucleus. They have membrane-bound organelles. ...
... Prokaryote cells have a nucleus. The first organisms were all plantlike. Prokaryote cells have no nucleus. They have membrane-bound organelles. ...
1 - OG-Science
... theory by Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. ...
... theory by Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. ...
Membrane Transport
... D. The rate of diffusion through a membrane is also directly proportional to the surface area of the membrane, which can be increased by such adaptations as microvilli. III. Simple diffusion is the type of passive transport in which small molecules and inorganic ions move through the cell membrane. ...
... D. The rate of diffusion through a membrane is also directly proportional to the surface area of the membrane, which can be increased by such adaptations as microvilli. III. Simple diffusion is the type of passive transport in which small molecules and inorganic ions move through the cell membrane. ...
Essays Chapters 7, 8, and 12
... b. list the parts of the cell and give the function of that structure. 2. Explain the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. Be sure to identify and explain the two experiments that helped prove that the membrane is fluid and a mosaic. 3. What are the six major types of proteins found in the cell ...
... b. list the parts of the cell and give the function of that structure. 2. Explain the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. Be sure to identify and explain the two experiments that helped prove that the membrane is fluid and a mosaic. 3. What are the six major types of proteins found in the cell ...
CELL ORGANELLES
... storage area for food, enzymes, other materials needed by the cell and waste products. In plant cells there is a large vacuole that plays a part in the rigidity of the plant and in animal cells the vacuoles are small. Lysosomes - Lysosomes are small membrane-bound organelles that contain hydrolytic ...
... storage area for food, enzymes, other materials needed by the cell and waste products. In plant cells there is a large vacuole that plays a part in the rigidity of the plant and in animal cells the vacuoles are small. Lysosomes - Lysosomes are small membrane-bound organelles that contain hydrolytic ...
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW Cell Biology
... jelly-like material around organelles finish & ship proteins make ATP in cellular respiration cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals ...
... jelly-like material around organelles finish & ship proteins make ATP in cellular respiration cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals ...
Warm-Up - Alvin ISD
... 4. According to Bonnie Bassler (Princeton University), what are scientists hoping to use as the next class of antibiotics? ...
... 4. According to Bonnie Bassler (Princeton University), what are scientists hoping to use as the next class of antibiotics? ...
Parts of the Animal Cell
... envelope is an extra layer of protection for the DNA from anything harmful that might enter the cell. Since the DNA has all the instructions for the cell to follow, the DNA must communicate with the rest of the cell. Large pores within the nuclear membrane allow messenger molecules to enter and exit ...
... envelope is an extra layer of protection for the DNA from anything harmful that might enter the cell. Since the DNA has all the instructions for the cell to follow, the DNA must communicate with the rest of the cell. Large pores within the nuclear membrane allow messenger molecules to enter and exit ...
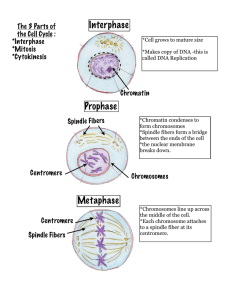
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
12. Cell Test Review
... bilayer, triglyceride, phospholipid, phosphate group, PO4, polar head, nonpolar tails, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, fluid mosaic model, aqueous, transport protein, carbohydrate, cholesterol, cell wall, cellular membrane, vacuole, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, chloroplast, mitochondria, chytopla ...
... bilayer, triglyceride, phospholipid, phosphate group, PO4, polar head, nonpolar tails, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, fluid mosaic model, aqueous, transport protein, carbohydrate, cholesterol, cell wall, cellular membrane, vacuole, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, chloroplast, mitochondria, chytopla ...
Cell organelles and functions
... Nuclear membrane is double layered and porous in nature. This allows the nucleoplasm to communicate (exchange of material) with the cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm is a gel like substance that contains large quantities of DNA, which forms the gene. One or more nucleoli are present in each nucleus. Th ...
... Nuclear membrane is double layered and porous in nature. This allows the nucleoplasm to communicate (exchange of material) with the cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm is a gel like substance that contains large quantities of DNA, which forms the gene. One or more nucleoli are present in each nucleus. Th ...
UNIT 2 Part A - Loudoun County Public Schools
... lysosome, cell membrane, cell wall, nucleolus, cilia/flagella, vacuoles, microtubules, centrioles and nuclear membrane. a) Nucleus controls cell’s activities and contains DNA. Only found in eukaryotic cells. b) Nucleolus located inside the nucleolus, makes the ribosomes for the cell. c) Nuclear Memb ...
... lysosome, cell membrane, cell wall, nucleolus, cilia/flagella, vacuoles, microtubules, centrioles and nuclear membrane. a) Nucleus controls cell’s activities and contains DNA. Only found in eukaryotic cells. b) Nucleolus located inside the nucleolus, makes the ribosomes for the cell. c) Nuclear Memb ...
Slide ()
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
Protista
... Member of Protista Kingdom. Unicellular microscopic organism found at the bottom of freshwater ponds or muddy soil. ...
... Member of Protista Kingdom. Unicellular microscopic organism found at the bottom of freshwater ponds or muddy soil. ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.