Level 2 Biology (90464) 2010 Assessment Schedule
... phosphate heads and fatty acid tails / phosphates with lipids. Semi permeable – also acceptable are: selectively permeable partially permeable differentiall permeable. (Some candidates may refer to the structure as a fluid-mosaic model, but without a description of the model, this is an inappropriat ...
... phosphate heads and fatty acid tails / phosphates with lipids. Semi permeable – also acceptable are: selectively permeable partially permeable differentiall permeable. (Some candidates may refer to the structure as a fluid-mosaic model, but without a description of the model, this is an inappropriat ...
What to Know for the Evolution Test
... Know the basic characteristics and possible functions of the following organic molecules: carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides), lipids, proteins (building blocks= amino acid) Enzyme, active site, substrate. Know that each type of enzyme is specific to a certain che ...
... Know the basic characteristics and possible functions of the following organic molecules: carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides), lipids, proteins (building blocks= amino acid) Enzyme, active site, substrate. Know that each type of enzyme is specific to a certain che ...
3/10 Kingdom PROTISTA •algae, protozoa, and slime molds •have
... • cilia and a coordinated mechanism for movement • usually have two nuclei • highly complex organelles - gullet, anus, contractile fibers • reproduction by fission or conjugation • heterotrophic (although some autotrophs are known), decomposer, food chains, some pathogenic • marine and freshwater sp ...
... • cilia and a coordinated mechanism for movement • usually have two nuclei • highly complex organelles - gullet, anus, contractile fibers • reproduction by fission or conjugation • heterotrophic (although some autotrophs are known), decomposer, food chains, some pathogenic • marine and freshwater sp ...
Part 1: The Paper
... best represent each cell part. Food items should look similar to the structure of the organelles i.e. a nucleus is round and has a nucleolus inside so a jawbreaker cut in half with the small round center exposed would best represent the nucleus and nucleolus. The key must contain two parts in order ...
... best represent each cell part. Food items should look similar to the structure of the organelles i.e. a nucleus is round and has a nucleolus inside so a jawbreaker cut in half with the small round center exposed would best represent the nucleus and nucleolus. The key must contain two parts in order ...
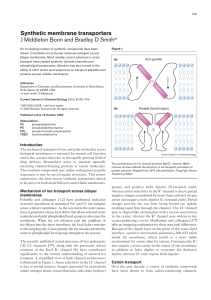
Synthetic membrane transporters J Middleton Boon and Bradley D
... head-group because of the increased acidity of the sulfonamide NH groups, and a molecular geometry that is able to form a tridentate complex with one of the phosphate oxygens on the head-group. Both sulfonamide 6 and amide 7 facilitate PC transport across human red blood cell membranes [31]. The TRE ...
... head-group because of the increased acidity of the sulfonamide NH groups, and a molecular geometry that is able to form a tridentate complex with one of the phosphate oxygens on the head-group. Both sulfonamide 6 and amide 7 facilitate PC transport across human red blood cell membranes [31]. The TRE ...
Folate Production and Lysis
... ldcA deletion ldcA encodes a cytoplasmic L,D-carboxypeptidase which creates peptide bonds ...
... ldcA deletion ldcA encodes a cytoplasmic L,D-carboxypeptidase which creates peptide bonds ...
CellLab06
... What evidence do you have that living things (or once living things) are composed of basic units called cells? _____________________________________________ ...
... What evidence do you have that living things (or once living things) are composed of basic units called cells? _____________________________________________ ...
Chapter 12 Notes Part 3 File
... • When synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects can summate over a brief period of time to produce an action potential ...
... • When synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects can summate over a brief period of time to produce an action potential ...
Syllabus for Medical Cell Biology
... The medical cell biology is a subject concerned with life activities, its mechanisms and principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using diffe ...
... The medical cell biology is a subject concerned with life activities, its mechanisms and principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using diffe ...
changes in DNA AT14A mediates the cell wall–plasma membrane
... This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/bync/3.0), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly ci ...
... This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/bync/3.0), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly ci ...
Unit 2 Notes - heckgrammar.co.uk
... 1. The middle lamella is a layer of pectins on the outside of the cell wall that glues adjacent cells together. 2. The primary cell wall is a thin layer of cellulose microbfibrils (unit 1), laid down while the cell is growing. The primary cell wall is flexible, so that is can expand as the cell grow ...
... 1. The middle lamella is a layer of pectins on the outside of the cell wall that glues adjacent cells together. 2. The primary cell wall is a thin layer of cellulose microbfibrils (unit 1), laid down while the cell is growing. The primary cell wall is flexible, so that is can expand as the cell grow ...
Chapter_06
... Chloroplasts are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae ANIMALS DO NOT HAVE CHLOROPLASTS ...
... Chloroplasts are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae ANIMALS DO NOT HAVE CHLOROPLASTS ...
Unit 2 - Mini Test
... transport. During osmosis, water always moves from the side of the membrane that has more water to the side of the membrane that has less water. The only thing that moves by osmosis is water. This means that choice B can be eliminated because solutes are not moving by osmosis. If there is a concentr ...
... transport. During osmosis, water always moves from the side of the membrane that has more water to the side of the membrane that has less water. The only thing that moves by osmosis is water. This means that choice B can be eliminated because solutes are not moving by osmosis. If there is a concentr ...
Work Plan and Methodology: A)Work Plan: B) Methodology:
... Two plastic bottles were used as chambers of an MFC. Two holes were drilled from the sides of the two plastic bottles such that a PVC pipe can be connected rigidly. Each container was about 7 cm high and about 0.5 cm in diameter. Two holes were also made on the lids of the bottles such that a copper ...
... Two plastic bottles were used as chambers of an MFC. Two holes were drilled from the sides of the two plastic bottles such that a PVC pipe can be connected rigidly. Each container was about 7 cm high and about 0.5 cm in diameter. Two holes were also made on the lids of the bottles such that a copper ...
•Deposition of unique membrane/cell wall material at rhizoid end
... • cytoskelton is organized so that vesicles fuse at rhizoid end •If stop secretion using brefaldinA, no axis fixation Belanger and Quatrano, 2000 ...
... • cytoskelton is organized so that vesicles fuse at rhizoid end •If stop secretion using brefaldinA, no axis fixation Belanger and Quatrano, 2000 ...
Cell Junctions - Mrs. Blackmon`s Science Blackboard
... desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, and adherens. Desmosomes occur in patches on the membranes of cells. The patches are structural proteins on the inner surface of the cell’s membrane. The adhesion molecule, cadherin, is embedded in these patches and projects through the cell membrane to link with the cad ...
... desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, and adherens. Desmosomes occur in patches on the membranes of cells. The patches are structural proteins on the inner surface of the cell’s membrane. The adhesion molecule, cadherin, is embedded in these patches and projects through the cell membrane to link with the cad ...
Basics of biological cells - Department of Mechanical Engineering
... transformations, none of which occurs at any significant rate in the inanimate world. Virtually all chemical changes that take place in cells require enzymes-molecules that greatly increase the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The sum total of the chemical reactions in a cell represents tha ...
... transformations, none of which occurs at any significant rate in the inanimate world. Virtually all chemical changes that take place in cells require enzymes-molecules that greatly increase the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The sum total of the chemical reactions in a cell represents tha ...
10ProjectINBPages
... 2. Have I built a 3-dimensional model of my assigned organelle that is accurately sized in all dimensions? 3. Does my model show the detailed exterior AND interior structure of my assigned organelle? 4. Do I know how many of my organelles would be present and where they’d be found in the cell? 5. Ha ...
... 2. Have I built a 3-dimensional model of my assigned organelle that is accurately sized in all dimensions? 3. Does my model show the detailed exterior AND interior structure of my assigned organelle? 4. Do I know how many of my organelles would be present and where they’d be found in the cell? 5. Ha ...
Kingdom Protista Review
... Label the following terms seen in the paramecium diagram below: macronucleus , micronucleus , contractile vacuole , food vacuole , cilia , oral groove ...
... Label the following terms seen in the paramecium diagram below: macronucleus , micronucleus , contractile vacuole , food vacuole , cilia , oral groove ...
Joy of Science
... - A cellular “skeleton” contained within the cytoplasm (fluid) and is made of protein - Gives the cell its shape and keeps things anchored in place - Plays important roles in both intracellular transport (the movement of vesicles and organelles, for example) and cellular division ...
... - A cellular “skeleton” contained within the cytoplasm (fluid) and is made of protein - Gives the cell its shape and keeps things anchored in place - Plays important roles in both intracellular transport (the movement of vesicles and organelles, for example) and cellular division ...
Plant Communication PPT
... The Discovery of Plant Hormones • Any response resulting in curvature of organs toward or away from a stimulus is called a tropism • In the late 1800s, Charles Darwin and his son Francis conducted experiments on phototropism, a plant’s response to light • They observed that a grass seedling could b ...
... The Discovery of Plant Hormones • Any response resulting in curvature of organs toward or away from a stimulus is called a tropism • In the late 1800s, Charles Darwin and his son Francis conducted experiments on phototropism, a plant’s response to light • They observed that a grass seedling could b ...
Protein Synthesis and Quality Control at the Endoplasmic Reticulum
... (Figure 1A). However, experimental confirmation of this hypothesis proved very difficult to obtain, and alternative models involving direct movement of the nascent chain through the non-polar core of the ER membrane (Figure 1B) were also proposed (e.g. [7]). These competing models were debated vigor ...
... (Figure 1A). However, experimental confirmation of this hypothesis proved very difficult to obtain, and alternative models involving direct movement of the nascent chain through the non-polar core of the ER membrane (Figure 1B) were also proposed (e.g. [7]). These competing models were debated vigor ...
Developing a CLIL Learning Unit
... • To explain passive transport across membranes by diffusion and osmosis • To explain turgor and plasmolysis in plant cells • To explain the meaning of the words hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic ...
... • To explain passive transport across membranes by diffusion and osmosis • To explain turgor and plasmolysis in plant cells • To explain the meaning of the words hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic ...
Organization of the Human Body
... organization within the human body and to begin to use the medical and anatomical terms to describe the body and its relative positions and structures. ...
... organization within the human body and to begin to use the medical and anatomical terms to describe the body and its relative positions and structures. ...
Cell Division Flash Cards - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... A DNA molecule that codes for your genetic traits. An organelle that is part of cell division that has an aster form around it and has spindle fibers attach to it. The structure that holds the two sister chromatids together in a replicated chromosome. The structure that forms in the cell during cell ...
... A DNA molecule that codes for your genetic traits. An organelle that is part of cell division that has an aster form around it and has spindle fibers attach to it. The structure that holds the two sister chromatids together in a replicated chromosome. The structure that forms in the cell during cell ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.