PDF
... monolayer and the rate of adhesion is determined from the amount of radioactivity present in the monolayer and adherent cells after removal of the cell suspension. In this type of assay, cell-substrate and cell-cell contacts within the monolayer may give rise to difficulties with interpretation of t ...
... monolayer and the rate of adhesion is determined from the amount of radioactivity present in the monolayer and adherent cells after removal of the cell suspension. In this type of assay, cell-substrate and cell-cell contacts within the monolayer may give rise to difficulties with interpretation of t ...
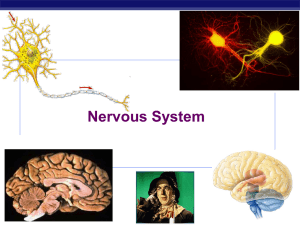
Nervous system 12-13
... wave of opening ion channels moves down neuron signal moves in one direction flow of K+ out of cell stops activation of Na+ channels in wrong direction ...
... wave of opening ion channels moves down neuron signal moves in one direction flow of K+ out of cell stops activation of Na+ channels in wrong direction ...
Meeting the Design Challenges of nano
... [3] A. R. Brown, G. Roy, and A. Asenov, “Poly-si-gate-related variability in decananometer mosfets with conventional architecture,” Electron Devices, IEEE Transactions on, vol. 54, no. 11, ...
... [3] A. R. Brown, G. Roy, and A. Asenov, “Poly-si-gate-related variability in decananometer mosfets with conventional architecture,” Electron Devices, IEEE Transactions on, vol. 54, no. 11, ...
The Exocytic/Lysosomal Transport Pathway
... Secretory Vesicles/Granules • Material in secretory vesicle aggregates due to decreased pH and divalent cations • Membrane recycling to TGN directly or via endosome reduced vesicle size ...
... Secretory Vesicles/Granules • Material in secretory vesicle aggregates due to decreased pH and divalent cations • Membrane recycling to TGN directly or via endosome reduced vesicle size ...
Cell Signaling and Cancer
... conjunction with Fos and serves to “turn on” the expression of specific genes needed in the cell response to the chemical signal received by the cell. Kinase - An enzyme that phosphorylates its substrate. The source of the phosphate is ATP Ras – A key protein found in signaling pathways. Ras is foun ...
... conjunction with Fos and serves to “turn on” the expression of specific genes needed in the cell response to the chemical signal received by the cell. Kinase - An enzyme that phosphorylates its substrate. The source of the phosphate is ATP Ras – A key protein found in signaling pathways. Ras is foun ...
Osmosis
... – Water is a small but extremely important molecule that makes up most of the liquid part of the cytoplasm in living things. – Deals ONLY with the diffusion of WATER – The molecules (in this case, water - not solute molecules) will tend to move from an area of high (water) concentration to an area o ...
... – Water is a small but extremely important molecule that makes up most of the liquid part of the cytoplasm in living things. – Deals ONLY with the diffusion of WATER – The molecules (in this case, water - not solute molecules) will tend to move from an area of high (water) concentration to an area o ...
Production of Outer Membrane Vesicles in a Clinical
... added and allowed to solidify; subsequently, a small block of bacterial growth was cut and processed for TEM. Furthermore, 20 µl of the sample obtained from the OMV purification technique was taken and placed on a formvar-coated grid, where it was allowed to adsorb for 1 min and the excess was elimi ...
... added and allowed to solidify; subsequently, a small block of bacterial growth was cut and processed for TEM. Furthermore, 20 µl of the sample obtained from the OMV purification technique was taken and placed on a formvar-coated grid, where it was allowed to adsorb for 1 min and the excess was elimi ...
Edible Cell Lab
... candy is a good representation, and explain what the organelle does. Organelle Nucleus ...
... candy is a good representation, and explain what the organelle does. Organelle Nucleus ...
Inside and Out!—A Look From Within
... Cells are often uniquely suited to perform a particular function within the organism – Nerve Cells – Muscle Cells – Rods and Cones in the eye – Sex cells – Determined by complex processes of turning on ...
... Cells are often uniquely suited to perform a particular function within the organism – Nerve Cells – Muscle Cells – Rods and Cones in the eye – Sex cells – Determined by complex processes of turning on ...
Transcription- and translation-dependent changes in membrane
... the anisotropy value of untreated cells, which was 0.165 6 0.004 (SD; n ¼ 50) for E. coli and 0.150 6 0.003 (SD; n ¼ 25) for B. subtilis. The basic anisotropy value may vary slightly from culture to culture, but the relative effect of drugs was easily reproducible. An average of relative drug effect ...
... the anisotropy value of untreated cells, which was 0.165 6 0.004 (SD; n ¼ 50) for E. coli and 0.150 6 0.003 (SD; n ¼ 25) for B. subtilis. The basic anisotropy value may vary slightly from culture to culture, but the relative effect of drugs was easily reproducible. An average of relative drug effect ...
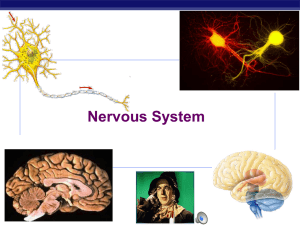
Nervous System
... wave of opening ion channels moves down neuron signal moves in one direction flow of K+ out of cell stops activation of Na+ channels in wrong direction ...
... wave of opening ion channels moves down neuron signal moves in one direction flow of K+ out of cell stops activation of Na+ channels in wrong direction ...
DAB photo-oxidation as a tool for detecting low amounts of free and
... microscopy (Figure 4). With this technique, it is not only possible to visualize Ca2+ ions but also to stabilize their intracellular presence, thus limiting the loss of ions. Interestingly enough, the final yield in terms of cells which can then be processed for electron microscopy is rather large, ...
... microscopy (Figure 4). With this technique, it is not only possible to visualize Ca2+ ions but also to stabilize their intracellular presence, thus limiting the loss of ions. Interestingly enough, the final yield in terms of cells which can then be processed for electron microscopy is rather large, ...
Document
... 1. Were any of the cells you observed today prokaryotic? If so, which ones? 2. Were any of the cells you observed today eukaryotic? If so, which ones? 3. Are all cells the same shape? Why or why not? 4. What types of organisms are not made of cells? 5. What part of the cell is “in charge” of allowin ...
... 1. Were any of the cells you observed today prokaryotic? If so, which ones? 2. Were any of the cells you observed today eukaryotic? If so, which ones? 3. Are all cells the same shape? Why or why not? 4. What types of organisms are not made of cells? 5. What part of the cell is “in charge” of allowin ...
Triton X-100 Extraction of P815 Tumor Cells
... vesicles they were isolated from (22). The material appeared relatively amorphous in thin section and had little or no lipid bilayer structure remaining. Vectorial labeling studies indicated that this set of proteins was present at the inner (cytoplasmic) face of the membrane. The presence here and ...
... vesicles they were isolated from (22). The material appeared relatively amorphous in thin section and had little or no lipid bilayer structure remaining. Vectorial labeling studies indicated that this set of proteins was present at the inner (cytoplasmic) face of the membrane. The presence here and ...
Experiment - 11 Binary fission (Amoeba) Budding (Yeast)
... Shubhankar was given two permanent slides, one of binary fission in amoeba and the other of budding in yeast. He was asked to determine any one difference in the nucleus of the two. One such difference is (a) presence of single nucleus each in amoeba, yeast cell and its attatched bud. (b) presence o ...
... Shubhankar was given two permanent slides, one of binary fission in amoeba and the other of budding in yeast. He was asked to determine any one difference in the nucleus of the two. One such difference is (a) presence of single nucleus each in amoeba, yeast cell and its attatched bud. (b) presence o ...
4042 Animal and plant cell culture
... Understanding principals of growth and development of cells and tissues Understanding the possibilities and obstacles during cell growth and development manipulation Ability of independent work on establishment and directioning of cell culture growth Ability of genetic manipulation with cells and ti ...
... Understanding principals of growth and development of cells and tissues Understanding the possibilities and obstacles during cell growth and development manipulation Ability of independent work on establishment and directioning of cell culture growth Ability of genetic manipulation with cells and ti ...
Cells
... on Two main types of cells: plant cells & animal cells • Some organelles are found in both cell types while some are found only in plant cells • These special organelles are needed for the plant to carry out special functions needed by the plant ...
... on Two main types of cells: plant cells & animal cells • Some organelles are found in both cell types while some are found only in plant cells • These special organelles are needed for the plant to carry out special functions needed by the plant ...
post-doctoral position
... JOB TITLE: molecular and cellular studies of two new ABC transporters of Streptococcus pneumoniae : a possible link between virulence and multidrug resistance. POSITION OPENED: This position will involve two teams of the Institute for Structural Biology (IBS) in Grenoble, with complementary expertis ...
... JOB TITLE: molecular and cellular studies of two new ABC transporters of Streptococcus pneumoniae : a possible link between virulence and multidrug resistance. POSITION OPENED: This position will involve two teams of the Institute for Structural Biology (IBS) in Grenoble, with complementary expertis ...
Notes: Cell Division & the Cell Cycle (Ch. 12)
... (DNA) before they divide, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material ● A dividing cell duplicates its DNA, allocates the two copies to opposite ends of the cell, and only then splits into ...
... (DNA) before they divide, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material ● A dividing cell duplicates its DNA, allocates the two copies to opposite ends of the cell, and only then splits into ...
29.9 Tanaka
... Lipid-bilayer membranes supported on solid substrates are widely used as cell-surface models that connect biological and artificial materials. They can be placed either directly on solids or on ultrathin polymer supports that mimic the generic role of the extracellular matrix. The tools of modern ge ...
... Lipid-bilayer membranes supported on solid substrates are widely used as cell-surface models that connect biological and artificial materials. They can be placed either directly on solids or on ultrathin polymer supports that mimic the generic role of the extracellular matrix. The tools of modern ge ...
Introduction to Virology II
... The plasma membrane of every cell type is composed of a similar phospholipid - glycolipid bilayer, but different sets of membrane proteins and lipids allow the cells of different tissues to carry out their specialized functions. The lipid bilayer consists of molecules that possess both hydrophilic a ...
... The plasma membrane of every cell type is composed of a similar phospholipid - glycolipid bilayer, but different sets of membrane proteins and lipids allow the cells of different tissues to carry out their specialized functions. The lipid bilayer consists of molecules that possess both hydrophilic a ...
Lipids
... • The name lipid is used to describe a range of substances. Some of the most important of these are triglycerides, usually known as fats and oils ...
... • The name lipid is used to describe a range of substances. Some of the most important of these are triglycerides, usually known as fats and oils ...
Cell Cycle - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... It is necessary that the cell copies its DNA so that each of the daughter cells will have one complete copy. When a cell divides, it replicates a new complete set of chromosomes so that these instructions can be passed on to the daughter cells. In humans, we start out with _______ chromosomes in our ...
... It is necessary that the cell copies its DNA so that each of the daughter cells will have one complete copy. When a cell divides, it replicates a new complete set of chromosomes so that these instructions can be passed on to the daughter cells. In humans, we start out with _______ chromosomes in our ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.