In the preparation of the esters given in this experiment
... In the preparation of the esters given in this experiment, the reaction product was extracted with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution (NaHCO 3) in the isolation step. Why? What gas was evolved during this washing step? Write a balanced equation for the reaction that produced it. 2. Why is a large excess ...
... In the preparation of the esters given in this experiment, the reaction product was extracted with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution (NaHCO 3) in the isolation step. Why? What gas was evolved during this washing step? Write a balanced equation for the reaction that produced it. 2. Why is a large excess ...
18 Important and sometimes forgotten) organic transformations
... •Phosphines can also be used •DMAP and DBU are better in some cases ...
... •Phosphines can also be used •DMAP and DBU are better in some cases ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... ii. reaction with Ketones and Aldehydes iii. reaction with acid chlorides or esters (double addition) iv. reaction with epoxides (Anti stereoselective; SN2-like regioselectivity) v. Side reactions with acidic compounds d. Via reduction of carbonyls or epoxides with Hydride Reducing reagents i. Reduc ...
... ii. reaction with Ketones and Aldehydes iii. reaction with acid chlorides or esters (double addition) iv. reaction with epoxides (Anti stereoselective; SN2-like regioselectivity) v. Side reactions with acidic compounds d. Via reduction of carbonyls or epoxides with Hydride Reducing reagents i. Reduc ...
Chemical Equations Balancing Chemical Equations Try One…
... To begin our study of equations, we must first review writing, balancing and naming the reaction type. In a chemical reaction, only 2 things are conserved the number of atoms and the conserved... number of grams. an arrow is used to separate reactants (the starting substances) and the products ( ...
... To begin our study of equations, we must first review writing, balancing and naming the reaction type. In a chemical reaction, only 2 things are conserved the number of atoms and the conserved... number of grams. an arrow is used to separate reactants (the starting substances) and the products ( ...
Synthesis of Oil of Wintergreen - Cornell University
... Students can choose a particular isomer and draw as many structures possible and discuss their physical and chemical properties. Supplemental Information: Advanced students can be exposed to chiral centers and chirality of molecules. Handedness also plays a role in organic chemistry due to the tetra ...
... Students can choose a particular isomer and draw as many structures possible and discuss their physical and chemical properties. Supplemental Information: Advanced students can be exposed to chiral centers and chirality of molecules. Handedness also plays a role in organic chemistry due to the tetra ...
Lecture 1: Key Concepts in Stereoselective Synthesis
... The development of novel catalyst systems for hydroamination has seen significant progress in the last two decades but the intermolecular hydroamination of unactivated alkenes with simple amines remains very challenging. It is not surprising that asymmetric hydroamination reactions have been studied ...
... The development of novel catalyst systems for hydroamination has seen significant progress in the last two decades but the intermolecular hydroamination of unactivated alkenes with simple amines remains very challenging. It is not surprising that asymmetric hydroamination reactions have been studied ...
Highlights IACChE`s James Y. Oldshue Lecture Tuesday, November
... the solvent effect on catalyst activity and selectivity for the liquid-phase hydrogenation of acetophenone to 1-phenylethanol was thoroughly investigated over Ni/SiO2. Solvents of different properties and polarities were used: i) protic solvents: methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol and 2-propanol; ii) apr ...
... the solvent effect on catalyst activity and selectivity for the liquid-phase hydrogenation of acetophenone to 1-phenylethanol was thoroughly investigated over Ni/SiO2. Solvents of different properties and polarities were used: i) protic solvents: methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol and 2-propanol; ii) apr ...
Slide 1
... If a compound has two functional groups, the one with the lowest priority is indicated by its prefix ...
... If a compound has two functional groups, the one with the lowest priority is indicated by its prefix ...
Lectures 32-33 - U of L Class Index
... morning sickness in the late 1950s and early 1960s. One enantiomer of this drug was effective in combating morning sickness; however, the other enantiomer caused severe birth defects in the children of the women who took it. It was pulled from the market 4 years after its release, but not before man ...
... morning sickness in the late 1950s and early 1960s. One enantiomer of this drug was effective in combating morning sickness; however, the other enantiomer caused severe birth defects in the children of the women who took it. It was pulled from the market 4 years after its release, but not before man ...
Carbohydrates important reactions
... an aldonic acid. Because of the 2º hydroxyl functions that are also present in these compounds, a mild oxidizing agent such as hypobromite must be used for this conversion (equation 1). If both ends of an aldose chain are oxidized to carboxylic acids the product is called an aldaric acid. By convert ...
... an aldonic acid. Because of the 2º hydroxyl functions that are also present in these compounds, a mild oxidizing agent such as hypobromite must be used for this conversion (equation 1). If both ends of an aldose chain are oxidized to carboxylic acids the product is called an aldaric acid. By convert ...
Microwave-Assisted Sulfamide Synthesis
... selective [1,5]. A novel transition-metal-catalyzed process for making unsymmetric sulfamides that was recently reported has several limitations, especially with ortho-isomers [1]. Even though other available methods report high yields, they either require reagents that are not readily accessible or ...
... selective [1,5]. A novel transition-metal-catalyzed process for making unsymmetric sulfamides that was recently reported has several limitations, especially with ortho-isomers [1]. Even though other available methods report high yields, they either require reagents that are not readily accessible or ...
ch-22 HW answers - HCC Learning Web
... 23. Which one of the following functional groups is found in ketones? Ans: C ...
... 23. Which one of the following functional groups is found in ketones? Ans: C ...
Communications to the Editor - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... also be converted to a mixture in which 6b predominated by base treatment. We assumed that 6a and 6b are the endo (syn to carbonyl) and exo (anti to carbonyl) isomers, respectively. However, the correctness of this assignment was not proven until the completion of the synthesis when the synthetic pr ...
... also be converted to a mixture in which 6b predominated by base treatment. We assumed that 6a and 6b are the endo (syn to carbonyl) and exo (anti to carbonyl) isomers, respectively. However, the correctness of this assignment was not proven until the completion of the synthesis when the synthetic pr ...
Amide Uses
... as a reagent in the Bouveault aldehyde synthesis and in the Vilsmeier-Haack reaction, another useful method of forming aldehydes. It is also a common catalyst used in the synthesis of acyl halides, in particular the synthesis of acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids using oxalyl or thionyl chloride. ...
... as a reagent in the Bouveault aldehyde synthesis and in the Vilsmeier-Haack reaction, another useful method of forming aldehydes. It is also a common catalyst used in the synthesis of acyl halides, in particular the synthesis of acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids using oxalyl or thionyl chloride. ...
F324 : Rings, Polymers and Analysis
... describe the oxidation of alcohols (see also unit F322: 2.2.1.f) using Cr2O72-/H+ (ie K2Cr2O7/H2SO4), including: (i) the oxidation of primary alcohols to form aldehydes and carboxylic acids; the control of the oxidation product using different reaction conditions, (ii) the oxidation of secondary alc ...
... describe the oxidation of alcohols (see also unit F322: 2.2.1.f) using Cr2O72-/H+ (ie K2Cr2O7/H2SO4), including: (i) the oxidation of primary alcohols to form aldehydes and carboxylic acids; the control of the oxidation product using different reaction conditions, (ii) the oxidation of secondary alc ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Spontaneous reactions—occur naturally, the process is unaided. • Example: –Decomposition of dead matter = spontaneous endothermic reactions. (absorbs heat energy) –Forest fire = spontaneous exothermic reactions. (releases heat energy) ...
... • Spontaneous reactions—occur naturally, the process is unaided. • Example: –Decomposition of dead matter = spontaneous endothermic reactions. (absorbs heat energy) –Forest fire = spontaneous exothermic reactions. (releases heat energy) ...
Azetidinone : A bioactive moiety
... carbapenems, nocardicin and monobactams which have been widely used as chemotherapeutic agents to treat bacterial infection and microbial diseases.2,3 These molecules operate by forming a covalent adduct with membrane bound bacterial transpeptidases which are also known as penicillin binding protein ...
... carbapenems, nocardicin and monobactams which have been widely used as chemotherapeutic agents to treat bacterial infection and microbial diseases.2,3 These molecules operate by forming a covalent adduct with membrane bound bacterial transpeptidases which are also known as penicillin binding protein ...
4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... a. Structural: different arrangement of the same atoms b. Geometric: same atoms bound but a different arrangement across a double bond c. Enantiomers i. Also called stereoisomers, chiral compounds and optical isomers ...
... a. Structural: different arrangement of the same atoms b. Geometric: same atoms bound but a different arrangement across a double bond c. Enantiomers i. Also called stereoisomers, chiral compounds and optical isomers ...
OXAZOLINES: THEIR SYNTHESIS AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY
... reported wide range of biological activities such as antibacterial, antifungal, antimicrobial, antioxidant, antipyretic, anti-HIV, anti malarial, anti tumour, anti viral, anti-inflammatory, CNS stimulant activity etc. Oxazolines synthesized by the reaction of various aromatic substitutes like acids, ...
... reported wide range of biological activities such as antibacterial, antifungal, antimicrobial, antioxidant, antipyretic, anti-HIV, anti malarial, anti tumour, anti viral, anti-inflammatory, CNS stimulant activity etc. Oxazolines synthesized by the reaction of various aromatic substitutes like acids, ...
Catalytic hydrogenation
... Metal-ligand bifunctional catalysts. Noyori has coined the term “metal-ligand bifunctional catalysts, describing systems containing an ancillary ligand cis to the hydride that assists in the hydride transfer step and this ligand must have an NH or OH (protic) group. ...
... Metal-ligand bifunctional catalysts. Noyori has coined the term “metal-ligand bifunctional catalysts, describing systems containing an ancillary ligand cis to the hydride that assists in the hydride transfer step and this ligand must have an NH or OH (protic) group. ...
Chapter 11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Part 2
... 5. The two isomers, configurations (a) and (b), are enantiomers because each molecule contains two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbon atoms) and their mirror images are non-superimposable to each other. 6. A. ...
... 5. The two isomers, configurations (a) and (b), are enantiomers because each molecule contains two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbon atoms) and their mirror images are non-superimposable to each other. 6. A. ...
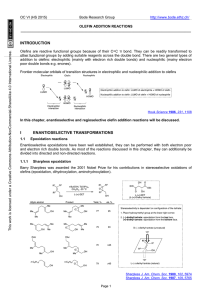
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.