Packet
... v. Act as signals to ___________________________________________ vi. Control chemical reaction in cells b. Once you are sure you have a correct arrangement, sketch a picture of the pieces down and use a marker to label it as a 5-monomer protein Then, denature it (denature- __________________________ ...
... v. Act as signals to ___________________________________________ vi. Control chemical reaction in cells b. Once you are sure you have a correct arrangement, sketch a picture of the pieces down and use a marker to label it as a 5-monomer protein Then, denature it (denature- __________________________ ...
Quiz 22
... and cell A is a body cell / diploid cell. (1) [give 0 mark for the whole question if “cell C is haploid” is given in the answer] (c) Because the cytoplasm of many cells of D is formed by repeated divisions (1) of the cytoplasm of the same one cell C (1). (d) Sheep X (1) because the body characterist ...
... and cell A is a body cell / diploid cell. (1) [give 0 mark for the whole question if “cell C is haploid” is given in the answer] (c) Because the cytoplasm of many cells of D is formed by repeated divisions (1) of the cytoplasm of the same one cell C (1). (d) Sheep X (1) because the body characterist ...
Document
... -More material with less exposure to solute.- advantage because fighting for stability against aqueous environment. 2. Exclusion of mutated proteins -If have mutation, subunit will not be incorporated into 4° structure-exception: collagen or other structural proteins- If mutated then nonfunctional 3 ...
... -More material with less exposure to solute.- advantage because fighting for stability against aqueous environment. 2. Exclusion of mutated proteins -If have mutation, subunit will not be incorporated into 4° structure-exception: collagen or other structural proteins- If mutated then nonfunctional 3 ...
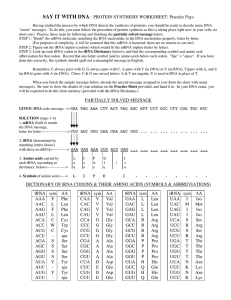
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
DETERMINATIVE DEGREE AND NUCLEOTIDE CONTENT OF DNA
... amino acids. For latter the analogous, but passive characteristics “predeterminativity” is also proposed, and it is shown that it correlates with the interaction energy of nitrous bases in corresponding DNA triplets. Purine-pyrimidine content of DNA sequences is considered in terms of the determinat ...
... amino acids. For latter the analogous, but passive characteristics “predeterminativity” is also proposed, and it is shown that it correlates with the interaction energy of nitrous bases in corresponding DNA triplets. Purine-pyrimidine content of DNA sequences is considered in terms of the determinat ...
UNIT 9 NOTES Genetics
... A substitution is a mutation that exchanges one base for another. (Ex. switching an A to a G) -sickle cell anemia is caused by a substitution in the betahemoglobin gene. -change a codon to one that encodes the same amino acid and causes no change in the protein produced. These are called silent muta ...
... A substitution is a mutation that exchanges one base for another. (Ex. switching an A to a G) -sickle cell anemia is caused by a substitution in the betahemoglobin gene. -change a codon to one that encodes the same amino acid and causes no change in the protein produced. These are called silent muta ...
homology modeling
... Levels of Description • protein structure is often described at four different scales – primary structure – secondary structure – tertiary structure – quaternary structure ...
... Levels of Description • protein structure is often described at four different scales – primary structure – secondary structure – tertiary structure – quaternary structure ...
Biosimilars PPTX
... The most common DNA shape illustrated by artists and scientists looks a lot like a twisting ladder that scientists call a double helix. DNA also folds and coils itself into more complex shapes. The coiled shape makes it very small. In fact, it is small enough to easily fit inside and any of our cell ...
... The most common DNA shape illustrated by artists and scientists looks a lot like a twisting ladder that scientists call a double helix. DNA also folds and coils itself into more complex shapes. The coiled shape makes it very small. In fact, it is small enough to easily fit inside and any of our cell ...
Molecular Abnormality of Erythrocyte Pyruvate
... reticulocyte mRNA is the appropriate source for cloning and sequencing the R-PK cDNA, the genomic DNA is more convenient for handling. Recently,we have clarified thestructure of the humanGtype PK (GPK) gene, and it becomes possible to search the mutation in the genomic DNA analysis.' In 1963, five P ...
... reticulocyte mRNA is the appropriate source for cloning and sequencing the R-PK cDNA, the genomic DNA is more convenient for handling. Recently,we have clarified thestructure of the humanGtype PK (GPK) gene, and it becomes possible to search the mutation in the genomic DNA analysis.' In 1963, five P ...
2017 N3 Week 2
... 3. In some chickens, the gene for feather color is controlled by codominance. The allele for black is B and the allele for white is W. The heterozygous phenotype is known as ...
... 3. In some chickens, the gene for feather color is controlled by codominance. The allele for black is B and the allele for white is W. The heterozygous phenotype is known as ...
Part 1 – History, DNA Structure, DNA Replication
... Part 1 – History, DNA Structure, DNA Replication DNA History http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Read the text and answer the following questions. 1. What have people wondered since the beginning of human history? _________________________________ 2. Who discovered that individual trai ...
... Part 1 – History, DNA Structure, DNA Replication DNA History http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Read the text and answer the following questions. 1. What have people wondered since the beginning of human history? _________________________________ 2. Who discovered that individual trai ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... 2. List and define the four patterns of natural selection. Answer: Directional selection – This pattern of selection favors individuals at one extreme of a phenotypic distribution that have greater reproductive success in a particular environment.. Stabilizing selection – This pattern of selecti ...
... 2. List and define the four patterns of natural selection. Answer: Directional selection – This pattern of selection favors individuals at one extreme of a phenotypic distribution that have greater reproductive success in a particular environment.. Stabilizing selection – This pattern of selecti ...
Cover Page In-silico study of Neural Tube Defect in relation to
... 1986). Polymorphism has been observed in exon 13 H475Y (1561C→T) in the catalytic domain of GCPII. The presence of this polymorphism is known to down regulate the FGCP activity, thereby block the intestinal absorption of folate (Halsted et al, 1998). This prompted us to focus on the systematic analy ...
... 1986). Polymorphism has been observed in exon 13 H475Y (1561C→T) in the catalytic domain of GCPII. The presence of this polymorphism is known to down regulate the FGCP activity, thereby block the intestinal absorption of folate (Halsted et al, 1998). This prompted us to focus on the systematic analy ...
BOLIVARIAN REPUBLIC OF VENEZUELA
... above consideration, the element can rise to fixation in the population. By definition, a selfish gene works only for itself, using any mean necessary for its survival in the next generations1. And by any mean, it includes the destruction of other genes while it is inserted in the DNA, and, the uniq ...
... above consideration, the element can rise to fixation in the population. By definition, a selfish gene works only for itself, using any mean necessary for its survival in the next generations1. And by any mean, it includes the destruction of other genes while it is inserted in the DNA, and, the uniq ...
Lecture 13
... population. The term “single nucleotide polymorphism” refers to the situation where, at a single specific nucleotide site on the chromosome, two or more different nucleotides are found in different members of the population---or even on the two homologous chromosomes present in each (diploid) indivi ...
... population. The term “single nucleotide polymorphism” refers to the situation where, at a single specific nucleotide site on the chromosome, two or more different nucleotides are found in different members of the population---or even on the two homologous chromosomes present in each (diploid) indivi ...
Gene7-17
... 17.4 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type 17.5 The MAT locus codes for regulator proteins 17.6 Silent cassettes at HML and HMR are repressed 17.7 Unidirectional transposition is initiated by the recipient MAT locus 17.8 Regulation of HO expression 17.9 Trypanosomes switch the VSG ...
... 17.4 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type 17.5 The MAT locus codes for regulator proteins 17.6 Silent cassettes at HML and HMR are repressed 17.7 Unidirectional transposition is initiated by the recipient MAT locus 17.8 Regulation of HO expression 17.9 Trypanosomes switch the VSG ...
Plant Physiology
... of this homology is unclear. The deduced MsLECl protein is 92% identical with and 96% homologous to the deduced MtLECl protein, and MsLECl is highly homologous to other legume lectins. Especially highly conserved amino acid residues in legume lectins are known to be important in sugar binding (van E ...
... of this homology is unclear. The deduced MsLECl protein is 92% identical with and 96% homologous to the deduced MtLECl protein, and MsLECl is highly homologous to other legume lectins. Especially highly conserved amino acid residues in legume lectins are known to be important in sugar binding (van E ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for palmitic acid oxidation. 8. List the possible enzymes that are involved in DNA replication. 9. Define Homeostasis. 10. Name the enzymes responsible for regulating the water balance in our system. Par ...
... 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for palmitic acid oxidation. 8. List the possible enzymes that are involved in DNA replication. 9. Define Homeostasis. 10. Name the enzymes responsible for regulating the water balance in our system. Par ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.