Schindler Disease - Great Ormond Street Hospital Laboratory
... disease, which is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme, alpha-Nacetylgalactosaminidase (NAGA). NAGA is a lysosomal glycohydrolase that cleaves alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase moieties from glycoconjugates inside lysosomes. Schindler disease is clinically heterogeneous with 3 main phenotypes; type 1 ...
... disease, which is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme, alpha-Nacetylgalactosaminidase (NAGA). NAGA is a lysosomal glycohydrolase that cleaves alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase moieties from glycoconjugates inside lysosomes. Schindler disease is clinically heterogeneous with 3 main phenotypes; type 1 ...
Job Description - Faculty of Biological Sciences
... mislocalisation in sarcomeres contributing towards a pathological phenotype. The main aim of this project is to study the influence of single amino acid substitution mutations in the S2 region of beta-cardiac myosin on its secondary structure and its localization in cardiomyocytes. Examining the eff ...
... mislocalisation in sarcomeres contributing towards a pathological phenotype. The main aim of this project is to study the influence of single amino acid substitution mutations in the S2 region of beta-cardiac myosin on its secondary structure and its localization in cardiomyocytes. Examining the eff ...
Basics Terms of Life Science Cells
... • All living organisms contain cells, which are the fundamental working units of life. • A cell can be divided into two parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm . ...
... • All living organisms contain cells, which are the fundamental working units of life. • A cell can be divided into two parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm . ...
Protein Synthesis
... Purpose: to convert the instructions of RNA (order of bases) into amino acids, this will make up the protein. Events of translation: 1.) The first three bases of mRNA (codon) join the ribosome. AUG – is the start codon 2.) tRNA brings the amino acid down to the ribosome. The three bases on tRNA, or ...
... Purpose: to convert the instructions of RNA (order of bases) into amino acids, this will make up the protein. Events of translation: 1.) The first three bases of mRNA (codon) join the ribosome. AUG – is the start codon 2.) tRNA brings the amino acid down to the ribosome. The three bases on tRNA, or ...
Biochemistry Review Worksheet - CHS Science Department Mrs
... Transcription occurs in the _____________. The enzyme helicase “unzips” the DNA strands and RNA polymerase copies one strand of DNA into a complementary mRNA strand. The mRNA travels out of the nucleus to the ribosome. The Process of Translation: Translation occurs at the ________________. The ribos ...
... Transcription occurs in the _____________. The enzyme helicase “unzips” the DNA strands and RNA polymerase copies one strand of DNA into a complementary mRNA strand. The mRNA travels out of the nucleus to the ribosome. The Process of Translation: Translation occurs at the ________________. The ribos ...
Station #3: DNA structure, replication, protein synthesis, mutation
... Provide a scientific explanation for the trend in the data. ...
... Provide a scientific explanation for the trend in the data. ...
chloroplasts passive transport active transport osmosis
... What are the functions of each of the cells organelle? How do materials get into and out of cells? What makes up the cell membrane? Unit 3: DNA and genetics Vocab: DNA base pair complementary mutation ...
... What are the functions of each of the cells organelle? How do materials get into and out of cells? What makes up the cell membrane? Unit 3: DNA and genetics Vocab: DNA base pair complementary mutation ...
ChannelopQues
... 1. What are channelopathies? What channels are involved? What properties of channels are altered by channel mutations. How would you know a patient’s symptoms were caused by a channelopathy? 2. How can mutations in one gene cause several different phenotypic syndromes in patients? Give examples of t ...
... 1. What are channelopathies? What channels are involved? What properties of channels are altered by channel mutations. How would you know a patient’s symptoms were caused by a channelopathy? 2. How can mutations in one gene cause several different phenotypic syndromes in patients? Give examples of t ...
answers
... Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON? __t-RNA____ What kind of molecules make up ribosomes? ___PROTEINS______ & ___r-RNA__________ Which cell part makes r-RNA? ___NUCLEOLUS__ Which cell part makes proteins? _RIBOSOMES______________ The ribosome makes sure the amino acid is put in the right spot by mat ...
... Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON? __t-RNA____ What kind of molecules make up ribosomes? ___PROTEINS______ & ___r-RNA__________ Which cell part makes r-RNA? ___NUCLEOLUS__ Which cell part makes proteins? _RIBOSOMES______________ The ribosome makes sure the amino acid is put in the right spot by mat ...
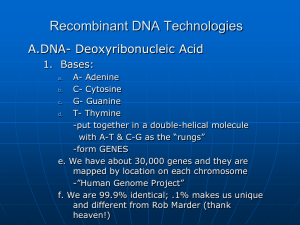
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... C. Gene Therapy 1. Problems with gene expression lead to faulty molecules, especially enzymes -cannot do their jobs 2. examples: Cystic Fibrosis & Tay Sachs diseases 3. Idea: replace bad genes with good ones that make the proper molecule And theoretically “fix” the problem 4. How can we deliver t ...
... C. Gene Therapy 1. Problems with gene expression lead to faulty molecules, especially enzymes -cannot do their jobs 2. examples: Cystic Fibrosis & Tay Sachs diseases 3. Idea: replace bad genes with good ones that make the proper molecule And theoretically “fix” the problem 4. How can we deliver t ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
Genetic Variation - Nicholls State University
... sequence off bbases within ithi one off the th genes. Huntington’s disease - a fatal neurological disorder - is due to an excessive number of repeats of the sequence CAG - normal forms of the genes have 10 to 30 repeats, mutants have more than 75 ...
... sequence off bbases within ithi one off the th genes. Huntington’s disease - a fatal neurological disorder - is due to an excessive number of repeats of the sequence CAG - normal forms of the genes have 10 to 30 repeats, mutants have more than 75 ...
Extranuclear Inheritance
... • Infectious heredity – comes about from the symbiotic (parasitic) relationship associated with a microorganism; inherited phenotype is affected by the presence of the microorganism living in the cell’s cytoplasm • Maternal effect – nuclear gene products are stored in the egg and then transmitted th ...
... • Infectious heredity – comes about from the symbiotic (parasitic) relationship associated with a microorganism; inherited phenotype is affected by the presence of the microorganism living in the cell’s cytoplasm • Maternal effect – nuclear gene products are stored in the egg and then transmitted th ...
mutations
... (2) Therefore, a base substitution in DNA might not result in any amino acid change in a protein c) Missense mutation resulting in the replacement of an amino acid with a similar amino acid (1) A substitution of one hydrophobic amino acid for another hydrophobic amino acid might not disrupt the stru ...
... (2) Therefore, a base substitution in DNA might not result in any amino acid change in a protein c) Missense mutation resulting in the replacement of an amino acid with a similar amino acid (1) A substitution of one hydrophobic amino acid for another hydrophobic amino acid might not disrupt the stru ...
CS4030: Tutorial 1- Biological Issues (from Bioinformatics ch 1)
... the nitrogenous base uracil in place of DNA’s thymine, and (2) the hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the 2’ carbon of the deoxyribose sugar of RNA is replaced with just a hydrogen (H) in DNA. Sketch the chemical structure of the deoxyribose sugar used by DNA in the ribose sugar used in RNA. 2. Diagram ...
... the nitrogenous base uracil in place of DNA’s thymine, and (2) the hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the 2’ carbon of the deoxyribose sugar of RNA is replaced with just a hydrogen (H) in DNA. Sketch the chemical structure of the deoxyribose sugar used by DNA in the ribose sugar used in RNA. 2. Diagram ...
Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... genes that are vital for normal development, no baby has been born a. without an X chromosome. b. with one X chromosome. c. with four X chromosomes. d. with three X chromosomes. ...
... genes that are vital for normal development, no baby has been born a. without an X chromosome. b. with one X chromosome. c. with four X chromosomes. d. with three X chromosomes. ...
The DNA Connection
... 1. Protein molecule grows longer as each transfer RNA adds an amino acid 2. When done the transfer RNA is released into the cytoplasm and can pick up another amino acid 3. Each transfer amino acid picks up the same type of amino acid ...
... 1. Protein molecule grows longer as each transfer RNA adds an amino acid 2. When done the transfer RNA is released into the cytoplasm and can pick up another amino acid 3. Each transfer amino acid picks up the same type of amino acid ...
mutations - s3.amazonaws.com
... What Causes Mutations? There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
... What Causes Mutations? There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
DNA Discovery
... – If two nucleotides coded for one amino acid, we still would not have enough combinations. – So we have three nitrogenous bases to code for one amino acid (although there are now 64 different combinations). • However, in some cases two or more codons code for the same amino acid ...
... – If two nucleotides coded for one amino acid, we still would not have enough combinations. – So we have three nitrogenous bases to code for one amino acid (although there are now 64 different combinations). • However, in some cases two or more codons code for the same amino acid ...
Genetic Mutation
... • In humans, it can be a different set of circumstances… Here’s an example: • Sickle-Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder in which there is a defect in the structure of red blood cells. This leads to fatigue and anemia when not treated. • However, it has been found that people who are carriers for Sick ...
... • In humans, it can be a different set of circumstances… Here’s an example: • Sickle-Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder in which there is a defect in the structure of red blood cells. This leads to fatigue and anemia when not treated. • However, it has been found that people who are carriers for Sick ...
DNA Ligase Joke (insert laughter here)
... following replication-both strands are identical—recall semi-conservative:— each new DNA double-helix has one parental strand and one newly-formed strand No enzyme activity necessary ...
... following replication-both strands are identical—recall semi-conservative:— each new DNA double-helix has one parental strand and one newly-formed strand No enzyme activity necessary ...
A substance formed by the chemical joining of two or more elements
... been born without which chromosome X ...
... been born without which chromosome X ...
AIR Genetics Review PPT
... – tRNA, that contains an amino acid (anticodon), base pairs with mRNA strand (codon). Amino acids are linked together. – Stop codon reached and amino acid sequence is released to fold (protein) ...
... – tRNA, that contains an amino acid (anticodon), base pairs with mRNA strand (codon). Amino acids are linked together. – Stop codon reached and amino acid sequence is released to fold (protein) ...
Nutrition and Gene Expression Jan 29, 2015
... The goal is to provide that for less than $1,000 (certain to be achieved soon). Of course, if your doctor has your COMPLETE DNA sequence, what use can be made of that? VERY CONTROVERSIAL. For example: we have lists of thousands of recessive and dominant mutations that cause health disorders. This te ...
... The goal is to provide that for less than $1,000 (certain to be achieved soon). Of course, if your doctor has your COMPLETE DNA sequence, what use can be made of that? VERY CONTROVERSIAL. For example: we have lists of thousands of recessive and dominant mutations that cause health disorders. This te ...
Extend Your Understanding of the Bacterial
... 3-dimentional structure; the other molecules the protein may interact with or bind to; the protein activity (i.e., enzymatic, catalytic, structural, signaling, etc.); where the protein is located, or expressed, within a cell or within tissues in a multi-cellular organism; and a broad range of other ...
... 3-dimentional structure; the other molecules the protein may interact with or bind to; the protein activity (i.e., enzymatic, catalytic, structural, signaling, etc.); where the protein is located, or expressed, within a cell or within tissues in a multi-cellular organism; and a broad range of other ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.