psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... 6. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a neuron, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ pe ...
... 6. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a neuron, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ pe ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... Magnetoencephalography (MEG) scans use magnetic fields to measure brain activity ...
... Magnetoencephalography (MEG) scans use magnetic fields to measure brain activity ...
Principles of Pharmacolgy
... Study of actions of the drug & changes that drugs undergo from absorption to excretion Receptor, Agonist, Antagonist propranolol (Inderal) beta adrenergic antagonist ...
... Study of actions of the drug & changes that drugs undergo from absorption to excretion Receptor, Agonist, Antagonist propranolol (Inderal) beta adrenergic antagonist ...
Stimulus space topology and geometry from neural activity
... generated in our brains. How do we do this? Many studies have investigated how the electrical activity of neurons (action potentials) is related to outside stimuli, and maps of these relationships – often called receptive fields – are routinely computed from data collected in neuroscience experiment ...
... generated in our brains. How do we do this? Many studies have investigated how the electrical activity of neurons (action potentials) is related to outside stimuli, and maps of these relationships – often called receptive fields – are routinely computed from data collected in neuroscience experiment ...
cholinergic drugs
... control muscular tension, including peristalsis and motor control. Cholinergic neurons are dominant in inhibitory activity inherent to so-called parasympathetic neurons whic comlpement dopamine/norepinephrine based neurons in parallel sympathtic structures. Two cholinergic receptor subtypes have bee ...
... control muscular tension, including peristalsis and motor control. Cholinergic neurons are dominant in inhibitory activity inherent to so-called parasympathetic neurons whic comlpement dopamine/norepinephrine based neurons in parallel sympathtic structures. Two cholinergic receptor subtypes have bee ...
The Brain and Its Disorders
... releases neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters cross the synapse and bind to receptors on another neuron • Neurotransmitters released, taken up again by first neuron ...
... releases neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters cross the synapse and bind to receptors on another neuron • Neurotransmitters released, taken up again by first neuron ...
Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... The presynaptic neuron releases the enzyme cholinesterase which breaks down acetylcholine, allowing the sodium channels to close, and repolarization to take place. Why is this important to neuron function? ...
... The presynaptic neuron releases the enzyme cholinesterase which breaks down acetylcholine, allowing the sodium channels to close, and repolarization to take place. Why is this important to neuron function? ...
Pharmacology
... order to learn how drugs work. Pharmacologists also study the ways in which drugs are modified within organisms. In most of the pharmacologic specialties, drugs are also used today as tools to gain insight into both normal and abnormal function. ...
... order to learn how drugs work. Pharmacologists also study the ways in which drugs are modified within organisms. In most of the pharmacologic specialties, drugs are also used today as tools to gain insight into both normal and abnormal function. ...
Lecture 15- Nervous systems (continued), Sensory and motor
... Norepinephrine/serotonin and depression • Catecholamine hypothesis - depression represented a decreased availability of norepinephrine and/or serotonin • Treatments are electroshock therapy and drugs to increase norepinephrine and/or ...
... Norepinephrine/serotonin and depression • Catecholamine hypothesis - depression represented a decreased availability of norepinephrine and/or serotonin • Treatments are electroshock therapy and drugs to increase norepinephrine and/or ...
Pharmacology 2a – Mechanisms of Drug action
... Pharmacology 2a – Mechanisms of Drug action 2 Anil Chopra 1. Briefly explain what you understand by the term 'structure-activity relationship'. 2. Differentiate between the four principal types of drug antagonism. Give one example of each type of antagonist. 3. Name the four main families of recepto ...
... Pharmacology 2a – Mechanisms of Drug action 2 Anil Chopra 1. Briefly explain what you understand by the term 'structure-activity relationship'. 2. Differentiate between the four principal types of drug antagonism. Give one example of each type of antagonist. 3. Name the four main families of recepto ...
Невротрансмитери в ЦНС
... Glutamate is the excitatory amino acid transmitter in the CNS. It acts at NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) and other receptors. NMDA receptors are involved in the development of adaptive responses that modulate synaptic transmission, known as synaptic plasticity.These responses have a role in both physi ...
... Glutamate is the excitatory amino acid transmitter in the CNS. It acts at NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) and other receptors. NMDA receptors are involved in the development of adaptive responses that modulate synaptic transmission, known as synaptic plasticity.These responses have a role in both physi ...
The Nervous System
... either too stiff or too floppy. Cerebral palsy can’t be cured, but treatment will often improve a child's capabilities. ...
... either too stiff or too floppy. Cerebral palsy can’t be cured, but treatment will often improve a child's capabilities. ...
Chapter 4
... IPSPs – If membrane is depolarized sufficiently it will generate a sudden change in the electrical state of the cell • Action Potential ...
... IPSPs – If membrane is depolarized sufficiently it will generate a sudden change in the electrical state of the cell • Action Potential ...
Slide ()
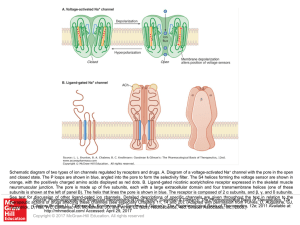
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
Slide 1
... •Metabolized by MAO •14 known 5 HT receptors •All are G- protein coupled except 5 -HT3 5- HT 1A – important target in the action of antidepressants 5- HT 2A – sensory perception 5- HT 2c- when activated reduce food intake, induce anxiety/panic 5- HT3 – antagonists have antiemetic action - regula ...
... •Metabolized by MAO •14 known 5 HT receptors •All are G- protein coupled except 5 -HT3 5- HT 1A – important target in the action of antidepressants 5- HT 2A – sensory perception 5- HT 2c- when activated reduce food intake, induce anxiety/panic 5- HT3 – antagonists have antiemetic action - regula ...
Psychopharmacology
... Sites of action - located on or in particular cells in the central nervous system One of the factors determining the rate at which the drug that is present in the bloodstream reaches sites of action within the brain is lipid solubility All are eventually excreted – primarily by the kidneys Enzymatic ...
... Sites of action - located on or in particular cells in the central nervous system One of the factors determining the rate at which the drug that is present in the bloodstream reaches sites of action within the brain is lipid solubility All are eventually excreted – primarily by the kidneys Enzymatic ...
Myers Module Fifty Four
... Administration by patch bypasses the intestines and liver, helping to reduce such side effects. (Bodkin & Amsterdam, ...
... Administration by patch bypasses the intestines and liver, helping to reduce such side effects. (Bodkin & Amsterdam, ...
WARM UP 4/20
... neurons that bring messages to the brain efferent neurons bring messages away from the brain -afferent neurons within the brain - interneurons ...
... neurons that bring messages to the brain efferent neurons bring messages away from the brain -afferent neurons within the brain - interneurons ...
Psychology 300 Instructor: Sylvia S. Spencer Ph.D. TEST 1 REVIEW
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...