Design a Neuron
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
Cell Signalling
... survive (blue arrows) and additional signals to divide (red arrow) or differentiate (green arrows). If deprived of appropriate survival signals, a cell will undergo a form of cell suicide known as programmed cell death, or apoptosis. ...
... survive (blue arrows) and additional signals to divide (red arrow) or differentiate (green arrows). If deprived of appropriate survival signals, a cell will undergo a form of cell suicide known as programmed cell death, or apoptosis. ...
HP Authorized Customer
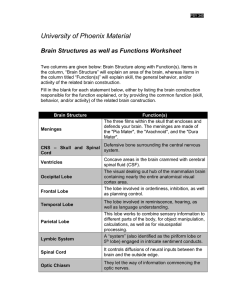
... sensory signs between the brain and body. Involved in damaged by Alzheimer’s disease, spatial memory, short term memory, and learning. ...
... sensory signs between the brain and body. Involved in damaged by Alzheimer’s disease, spatial memory, short term memory, and learning. ...
Nervous Systems
... Propagation of Action Potential • Action potential are very localized events • DO NOT travel down membrane • Are generated anew in a sequence along the neuron ...
... Propagation of Action Potential • Action potential are very localized events • DO NOT travel down membrane • Are generated anew in a sequence along the neuron ...
Direct cholinergic agonists
... The competitive neuromuscular blocking drugs are used to produce skeletal muscle relaxation. Succinylcholine is a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker. Botulinum toxin blocks the release of acetylcholine at all cholinergic synapses. Tubocurarine: is among the drugs that compete with acetylcholine for ...
... The competitive neuromuscular blocking drugs are used to produce skeletal muscle relaxation. Succinylcholine is a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker. Botulinum toxin blocks the release of acetylcholine at all cholinergic synapses. Tubocurarine: is among the drugs that compete with acetylcholine for ...
Extracting Single-trialViews of Brain Activity
... ABSTRACT Advances in neural recording technologies (including multi-electrode arrays and optical imaging techniques) have transformed systems neuroscience from a field that is data-limited to one that is limited by the available analytical methods. While we have well-established methods for studying ...
... ABSTRACT Advances in neural recording technologies (including multi-electrode arrays and optical imaging techniques) have transformed systems neuroscience from a field that is data-limited to one that is limited by the available analytical methods. While we have well-established methods for studying ...
chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... Read the paragraph in the box and study the diagram. Then answer the questions. The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, o ...
... Read the paragraph in the box and study the diagram. Then answer the questions. The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, o ...
General design of the nervous system
... The incoming signal enters the neuron throught synapses mainly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. The output signal travels by way of a single axon, leaving the neuron, but this axon has many separate branches to other parts of the nervous system or peripheral body. ...
... The incoming signal enters the neuron throught synapses mainly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. The output signal travels by way of a single axon, leaving the neuron, but this axon has many separate branches to other parts of the nervous system or peripheral body. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
Chapter 2 Notes Packet (Part 1)
... Endorphins: inhibition of pain, released during strenuous exercise Responsible for “runner’s high”. Psychopharmacology o Most psychoactive drugs and toxins work by either blocking or enhancing the transmission of chemicals across synapses o Others do the exact opposite ________________________ ...
... Endorphins: inhibition of pain, released during strenuous exercise Responsible for “runner’s high”. Psychopharmacology o Most psychoactive drugs and toxins work by either blocking or enhancing the transmission of chemicals across synapses o Others do the exact opposite ________________________ ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... Nerve Cells employ both electrical and chemical signals to process and transmit information. P.74 Synaptic vesicle: Neurotransmitters: ...
... Nerve Cells employ both electrical and chemical signals to process and transmit information. P.74 Synaptic vesicle: Neurotransmitters: ...
Nervous System Outline 1
... C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands or muscles to “create” a response. 1. The response is carried out by Effector Cells. a. Effectors are Muscles or Glands. These structures can have an effect on your body. D. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. This incl ...
... C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands or muscles to “create” a response. 1. The response is carried out by Effector Cells. a. Effectors are Muscles or Glands. These structures can have an effect on your body. D. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. This incl ...
Harnessing Plasticity to Reset Dysfunctional Neurons
... circuits were laid down and their functions assigned, little change was possible. This notion is no longer tenable. The brain has a lifelong inherent ability to change and adapt: individual neurons and neural circuits can change their “job descriptions” and their allegiance in response to demands. T ...
... circuits were laid down and their functions assigned, little change was possible. This notion is no longer tenable. The brain has a lifelong inherent ability to change and adapt: individual neurons and neural circuits can change their “job descriptions” and their allegiance in response to demands. T ...
Nervous System
... The cranial nerves, spinal nerves and ganglia make up the PNS. The cranial nerves connect to the brain. The cranial and spinal nerves contain the axons (fibres) of sensory and motor nerve cells. Nerve cells are also known as neurons. ...
... The cranial nerves, spinal nerves and ganglia make up the PNS. The cranial nerves connect to the brain. The cranial and spinal nerves contain the axons (fibres) of sensory and motor nerve cells. Nerve cells are also known as neurons. ...
Trigeminal Ganglion Cell
... trillion glia Cells. Each neuron receives and combines multiple inputs to determine, whether to transmit an action potential to the next target in its network (Neuron, Muscle, Gland, or Organ). ...
... trillion glia Cells. Each neuron receives and combines multiple inputs to determine, whether to transmit an action potential to the next target in its network (Neuron, Muscle, Gland, or Organ). ...
The Brain - Science Leadership Academy
... Along with the hypothalamus the pituitary gland is responsible for visceral functions. ...
... Along with the hypothalamus the pituitary gland is responsible for visceral functions. ...
Organization of Nervous System
... As it turns out, there are also receptors on the bouton itself. These receptors modulate the release of neurotransmitters. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that acts on the presynaptic receptor. It inhibits the release of glutamate. ...
... As it turns out, there are also receptors on the bouton itself. These receptors modulate the release of neurotransmitters. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that acts on the presynaptic receptor. It inhibits the release of glutamate. ...
Drugs and the Brain
... The limbic system contains the brain's reward circuit - it links together a number of brain structures that control and regulate our ability to feel pleasure. Feeling pleasure motivates us to repeat behaviors such as eating - actions that are critical to our existence. The limbic system is activated ...
... The limbic system contains the brain's reward circuit - it links together a number of brain structures that control and regulate our ability to feel pleasure. Feeling pleasure motivates us to repeat behaviors such as eating - actions that are critical to our existence. The limbic system is activated ...
Sensory Systems
... Pressure and Temperature: Mechanoreceptors in the skin make it possible to sense touch, ___________, and tension. For humans, touch receptors are concentrated in the face, tongue, and ________________. Body hair helps to sense touch because bending a hair stimulates mechanoreceptors at the base o ...
... Pressure and Temperature: Mechanoreceptors in the skin make it possible to sense touch, ___________, and tension. For humans, touch receptors are concentrated in the face, tongue, and ________________. Body hair helps to sense touch because bending a hair stimulates mechanoreceptors at the base o ...
SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... neural impulses that the brain processes into what we consciously see. 1. Cornea-transparent, protective outer membrane of the eye. 2. Pupil-The small opening in the middle of the iris, which changes size to let in different amounts of light. 3. Iris-the colored part of the eye is a ring of muscle. ...
... neural impulses that the brain processes into what we consciously see. 1. Cornea-transparent, protective outer membrane of the eye. 2. Pupil-The small opening in the middle of the iris, which changes size to let in different amounts of light. 3. Iris-the colored part of the eye is a ring of muscle. ...
E4 Neurotransmitters and synapses trs
... is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter. •Inhibitory NTs cause hyperpolarization of post synaptic neuron (makes neuron more negative), thereby inhibiting action potentials. •When inhibitory NTs bind to receptors, either K+ ions move out of the cell, or Clions move in. ...
... is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter. •Inhibitory NTs cause hyperpolarization of post synaptic neuron (makes neuron more negative), thereby inhibiting action potentials. •When inhibitory NTs bind to receptors, either K+ ions move out of the cell, or Clions move in. ...