OL Chapter 2 overview
... feel most mentally confused and uncoordinated (groggiest) about halfway through the night. But we may feel more lively and vigorous (get new energy) close to the time we would normally wake up. . . . “owls” . . . “larks” . . . Like birds that are nocturnal (owls are an example), many younger adults ...
... feel most mentally confused and uncoordinated (groggiest) about halfway through the night. But we may feel more lively and vigorous (get new energy) close to the time we would normally wake up. . . . “owls” . . . “larks” . . . Like birds that are nocturnal (owls are an example), many younger adults ...
A comparison of the glutamate and dopamine
... to me because of all the mysteries and misunderstandings surrounding it; it is at the same time one of the most talked about, but also least understood mental disorders. It also belongs to the most complex and heterogenous illnesses of the nervous system. This heterogeneity is what makes schizophren ...
... to me because of all the mysteries and misunderstandings surrounding it; it is at the same time one of the most talked about, but also least understood mental disorders. It also belongs to the most complex and heterogenous illnesses of the nervous system. This heterogeneity is what makes schizophren ...
Neuro-Science Outline
... Cannabinoid receptors are present throughout the body, embedded in cell membranes, and are believed to be more numerous than any other receptor system. What are Receptors Receptors are binding sites for chemicals in the brain, chemicals that instruct brain cells to start, stop or otherwise regulate ...
... Cannabinoid receptors are present throughout the body, embedded in cell membranes, and are believed to be more numerous than any other receptor system. What are Receptors Receptors are binding sites for chemicals in the brain, chemicals that instruct brain cells to start, stop or otherwise regulate ...
Nervous System II: Development & Plasticity
... transdifferentiation? • Since brain injuries have been known to cause adult neurogenesis and transdifferentiation of astrocytes into neurons, we can study what happens in vivo. • In vivo, many chemicals are released following trauma, including: – Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) – Fibroblast Growth Fac ...
... transdifferentiation? • Since brain injuries have been known to cause adult neurogenesis and transdifferentiation of astrocytes into neurons, we can study what happens in vivo. • In vivo, many chemicals are released following trauma, including: – Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) – Fibroblast Growth Fac ...
File
... •Can be done at neuronal level, larger areas of brain tissue or at hemispheric level •Rerouting = an undamaged neuron that has lost a connection with an active neuron may seek a new active neuron and connect with it instead •Sprouting = the growth of new bushier nerve fibres with more branches to ma ...
... •Can be done at neuronal level, larger areas of brain tissue or at hemispheric level •Rerouting = an undamaged neuron that has lost a connection with an active neuron may seek a new active neuron and connect with it instead •Sprouting = the growth of new bushier nerve fibres with more branches to ma ...
Drug distribution and protein binding
... • Slight changes in the binding of highly bound drugs can result in significant changes in clinical response or cause a toxic response. Since it is the free drug in plasma which equilibrates with the site of pharmacological or toxic response, a slight change in the extent of binding, such as 99 to ...
... • Slight changes in the binding of highly bound drugs can result in significant changes in clinical response or cause a toxic response. Since it is the free drug in plasma which equilibrates with the site of pharmacological or toxic response, a slight change in the extent of binding, such as 99 to ...
Early treatment of psychosis
... • Active against psychosis of any origin: idiopathic, metabolic, drug-induced • More active against ‘positive’ symptoms • Antipsychotic drugs interfere with dopamine transmission, most block dopamine receptors • Drugs start to work relatively quickly, but it takes a few months to reach maximum effec ...
... • Active against psychosis of any origin: idiopathic, metabolic, drug-induced • More active against ‘positive’ symptoms • Antipsychotic drugs interfere with dopamine transmission, most block dopamine receptors • Drugs start to work relatively quickly, but it takes a few months to reach maximum effec ...
4Central Nervous System (CNS)
... Tract—bundle of central axons White matter—brain or cord tissue composed primarily of ______________________________ (tracts) Gray matter—brain or cord tissue composed primarily of ...
... Tract—bundle of central axons White matter—brain or cord tissue composed primarily of ______________________________ (tracts) Gray matter—brain or cord tissue composed primarily of ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
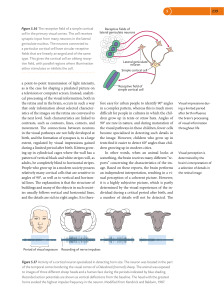
... of the temporal cortex bordering the visual cortex of a Dalesbred (horned) sheep. The animal was exposed to images of three different sheep heads and a human face during the periods indicated by blue shading. Recorded action potentials are shown as vertical deflections from the baseline. The head wi ...
... of the temporal cortex bordering the visual cortex of a Dalesbred (horned) sheep. The animal was exposed to images of three different sheep heads and a human face during the periods indicated by blue shading. Recorded action potentials are shown as vertical deflections from the baseline. The head wi ...
Unit II Practice Exam – Answer Key
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
Studying the concepts pg 344 1-7 Motor neurons are located in the
... Motor neurons are located in the central nervous system (CNS) they project their axons outside the CNS and directly or indirectly control muscles. A typical neuron is divided into three parts: the soma or cell body, dendrites, and axon. The soma is usually compact; the axon and dendrites are filamen ...
... Motor neurons are located in the central nervous system (CNS) they project their axons outside the CNS and directly or indirectly control muscles. A typical neuron is divided into three parts: the soma or cell body, dendrites, and axon. The soma is usually compact; the axon and dendrites are filamen ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Autonomic nervous system controls involuntary activities of smooth muscle, secretory glands and the visceral organs of the body such as the heart (involuntary activities of smooth muscle) Somatic nervous system innervates the skeletal muscles and controls voluntary ...
... Autonomic nervous system controls involuntary activities of smooth muscle, secretory glands and the visceral organs of the body such as the heart (involuntary activities of smooth muscle) Somatic nervous system innervates the skeletal muscles and controls voluntary ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... Movement of the Action Potential • Depolarization occurs as a wave along the membrane of the axon • The wave of depolarization is followed by a wave of re-polarization • The action potential moves along the axon by jumping from one node of Ranvier to another ...
... Movement of the Action Potential • Depolarization occurs as a wave along the membrane of the axon • The wave of depolarization is followed by a wave of re-polarization • The action potential moves along the axon by jumping from one node of Ranvier to another ...
This Week in The Journal - Journal of Neuroscience
... mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptors. In contrast, glutamine had no effect on Schwann cell proliferation or myelination. ...
... mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptors. In contrast, glutamine had no effect on Schwann cell proliferation or myelination. ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... Contains nuclei involved in the regulation of visceral activities such as breathing. Relays information to and from higher brain centers. The Midbrain. Contains nuclei involved in the integration of sensory information. Superior colliculi are involved in the regulation of visual reflexes. ...
... Contains nuclei involved in the regulation of visceral activities such as breathing. Relays information to and from higher brain centers. The Midbrain. Contains nuclei involved in the integration of sensory information. Superior colliculi are involved in the regulation of visual reflexes. ...
System Introduction to Sensory Physiology: Sensory- Motor
... 2) MRO1- slow adaptation- IK (Ca), Na/K pump! 3) MRO1 and MRO2 have similar generator potentials! 4) MRO2 adapts more quickly to depolarization! ...
... 2) MRO1- slow adaptation- IK (Ca), Na/K pump! 3) MRO1 and MRO2 have similar generator potentials! 4) MRO2 adapts more quickly to depolarization! ...
The biological basis of behavior
... The synapse • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. ...
... The synapse • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. ...
Basic Pharmacology of the Alpha
... 48 hours or longer). It is somewhat selective for α 1 receptors but also blocks α 2 receptors. The drug also inhibits reuptake of released NE and blocks histamine (H1),ACh, and serotonin receptors. Causes relatively little fall in blood pressure in the supine position, it reduces blood pressure when ...
... 48 hours or longer). It is somewhat selective for α 1 receptors but also blocks α 2 receptors. The drug also inhibits reuptake of released NE and blocks histamine (H1),ACh, and serotonin receptors. Causes relatively little fall in blood pressure in the supine position, it reduces blood pressure when ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and c ...
... about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and c ...
Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
Orexin-A excites rat lateral vestibular nucleus neurons and improves
... Orexin is a newly discovered peptide which is synthesized exclusively within the lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle ...
... Orexin is a newly discovered peptide which is synthesized exclusively within the lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle ...