Chapter 7 Linear Momentum and Collisions
... m1 = 5.001 kg is released from A. It makes a head–on elastic collision with a block of mass m2 = 10.0 kg at B, initially at rest. Calculate the maximum height to which m1 rises after the collision. Whoa! What is this problem talking about?? We release mass m1 ; it slides down to the slope, picking u ...
... m1 = 5.001 kg is released from A. It makes a head–on elastic collision with a block of mass m2 = 10.0 kg at B, initially at rest. Calculate the maximum height to which m1 rises after the collision. Whoa! What is this problem talking about?? We release mass m1 ; it slides down to the slope, picking u ...
ME33: Fluid Flow Lecture 1: Information and
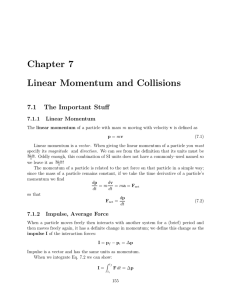
... The product of the mass and the velocity of a body is called the linear momentum. Newton’s second law the linear momentum equation in fluid mechanics The momentum of a system is conserved when it remains constant the conservation of momentum principle. Momentum is a vector. Its direction is the ...
... The product of the mass and the velocity of a body is called the linear momentum. Newton’s second law the linear momentum equation in fluid mechanics The momentum of a system is conserved when it remains constant the conservation of momentum principle. Momentum is a vector. Its direction is the ...