Chapter 14
... No light can escape a black hole => Black holes can not be observed directly. If an invisible compact object is part of a binary, we can estimate its mass from the orbital period and radial velocity. ...
... No light can escape a black hole => Black holes can not be observed directly. If an invisible compact object is part of a binary, we can estimate its mass from the orbital period and radial velocity. ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 18 Notes: Neutron Stars
... achieved briefly (using focused explosives) are around 107 gauss. Even a 106 gauss field cannot be created using conventional materials because the magnetic forces generated exceed the tensile strength of terrestrial materials, i.e. a 106 gauss electromagnet would crush itself because steel would no ...
... achieved briefly (using focused explosives) are around 107 gauss. Even a 106 gauss field cannot be created using conventional materials because the magnetic forces generated exceed the tensile strength of terrestrial materials, i.e. a 106 gauss electromagnet would crush itself because steel would no ...
Collisions: Momentum and Impulse
... A 100 kg fullback moving straight downfield with a velocity of 5 m/s collides head on with a 75 kg defensive back moving in the opposite direction with a velocity of -4m/s. The defensive back hangs on to the fullback, and the two players move together after the ...
... A 100 kg fullback moving straight downfield with a velocity of 5 m/s collides head on with a 75 kg defensive back moving in the opposite direction with a velocity of -4m/s. The defensive back hangs on to the fullback, and the two players move together after the ...
grains of
... tset with decreasing grain size (a) Micron-sized grains settle in about 105 years at 1 AU, although grains grow during their journey to the midplane => reduce the settling time-scale ...
... tset with decreasing grain size (a) Micron-sized grains settle in about 105 years at 1 AU, although grains grow during their journey to the midplane => reduce the settling time-scale ...
Impact and Momentum - definition and units
... In this leaflet the concepts of Impulse and Momentum will be introduced. Momentum If the mass of an object is m and it has a velocity v, then the momentum of the object is defined to be its mass multiplied by its velocity. momentum= mv Momentum has both magnitude and direction and thus is a vector q ...
... In this leaflet the concepts of Impulse and Momentum will be introduced. Momentum If the mass of an object is m and it has a velocity v, then the momentum of the object is defined to be its mass multiplied by its velocity. momentum= mv Momentum has both magnitude and direction and thus is a vector q ...
Sample problems
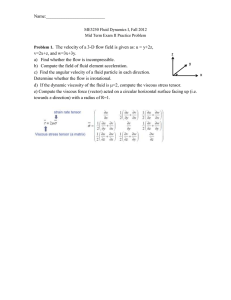
... height of H1=2m and the outlet has H2=4m. The velocity is uniform (u1 = 1m/s) at inlet. The flow at outlet is laminar and fully developed. Ignore gravity in this problem. (a) Write down the Navier-Stokes equation for the fully developed flow at the outlet in xdirection; simplify it to a solvable for ...
... height of H1=2m and the outlet has H2=4m. The velocity is uniform (u1 = 1m/s) at inlet. The flow at outlet is laminar and fully developed. Ignore gravity in this problem. (a) Write down the Navier-Stokes equation for the fully developed flow at the outlet in xdirection; simplify it to a solvable for ...
ASTRONOMY 5
... is actually accelerating. These are: a) The measurement of distances to certain galaxies and the observation that their radial velocities are increasing. b) The angular size of “measles” in the cosmic microwave background radiation and the upper limit to the baryon density (bary) set by nucleosynt ...
... is actually accelerating. These are: a) The measurement of distances to certain galaxies and the observation that their radial velocities are increasing. b) The angular size of “measles” in the cosmic microwave background radiation and the upper limit to the baryon density (bary) set by nucleosynt ...
Conservation of Linear Momentum Solutions
... 4. Is the conservation of linear momentum consistent with Newton’s first and third laws of motion? Explain. Yes. The first law states that an object’s motion is unchanged unless affected by a net external force; same with an object’s momentum. The third law states that when two object’s interact, th ...
... 4. Is the conservation of linear momentum consistent with Newton’s first and third laws of motion? Explain. Yes. The first law states that an object’s motion is unchanged unless affected by a net external force; same with an object’s momentum. The third law states that when two object’s interact, th ...