CHAPTER-IV LIPID METABOLISM BETA
... Beta-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids changes the ATP yield due to the requirement of two possible additional enzymes. Ketogenesis Ketogenesis is the process by which ketone bodies are produced as a result of fatty acid breakdown. Types of ketone bodies The three ketone bodies are: ...
... Beta-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids changes the ATP yield due to the requirement of two possible additional enzymes. Ketogenesis Ketogenesis is the process by which ketone bodies are produced as a result of fatty acid breakdown. Types of ketone bodies The three ketone bodies are: ...
Sequence, expression, and characterization of the first archaeal ATP
... were about 5 U/mg. The enzyme was specific for ATP as phosphoryl donor, but showed a broader spectrum of phosphoryl acceptors: in addition to F-6-P, glucose 6-phosphate, adenosine, fructose, ribose 5-phosphate, and ribose were accepted. Enzyme activity required divalent cations; Mg2+, which was most ...
... were about 5 U/mg. The enzyme was specific for ATP as phosphoryl donor, but showed a broader spectrum of phosphoryl acceptors: in addition to F-6-P, glucose 6-phosphate, adenosine, fructose, ribose 5-phosphate, and ribose were accepted. Enzyme activity required divalent cations; Mg2+, which was most ...
Vegetable origin latic acid bacteria
... more active through stomach and intestines. This plant origin lactic acid bacterium is active and still remained active in the intestines and so it worked as probiotic in the intestines and improved intestine flora. ○ Due to its homo type lactic acid bacterium, this produces lactic acid only, and as ...
... more active through stomach and intestines. This plant origin lactic acid bacterium is active and still remained active in the intestines and so it worked as probiotic in the intestines and improved intestine flora. ○ Due to its homo type lactic acid bacterium, this produces lactic acid only, and as ...
Nucleosomes released from oviduct nuclei during brief micrococcal
... glycine and alanine. HMGY has all these properties. Except for being smaller, HMGY is very similar to HMG17 in that it elutes just after the main peak of HMG17 on the CM-Sephadex column and elutes with HMG17 on the CM-cellulose column. HMGY does not appear to be a degradation product of HMG14 or HMG ...
... glycine and alanine. HMGY has all these properties. Except for being smaller, HMGY is very similar to HMG17 in that it elutes just after the main peak of HMG17 on the CM-Sephadex column and elutes with HMG17 on the CM-cellulose column. HMGY does not appear to be a degradation product of HMG14 or HMG ...
Isotope Fractionation: Why Aren`t We What We Eat?
... times the percent difference in the isotope ratio relative to a standard. Moreover, the ä values are far simpler to tabulate, compare and remember than the multidigited fractions listed in Table 1. The differences in the relative isotopic abundances of the elements that arise in two different molecu ...
... times the percent difference in the isotope ratio relative to a standard. Moreover, the ä values are far simpler to tabulate, compare and remember than the multidigited fractions listed in Table 1. The differences in the relative isotopic abundances of the elements that arise in two different molecu ...
Polymers - Yafi Zayyat
... between small units called monomer molecules to form a long chained macromolecule ( polymer ) and a small molecule ( usually water). For example: Dicarboxylic acid + Diamines ...
... between small units called monomer molecules to form a long chained macromolecule ( polymer ) and a small molecule ( usually water). For example: Dicarboxylic acid + Diamines ...
Evolutionary Patterns in the Sequence and Structure of
... ribosome [1,2]. Their acceptor arms charge specific amino acids through the activity of cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, while triplets of bases on their ‘anticodon’ arms recognize complementary ‘codon’ sequences in messenger RNA. These and many other molecular interactions define the identities ...
... ribosome [1,2]. Their acceptor arms charge specific amino acids through the activity of cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, while triplets of bases on their ‘anticodon’ arms recognize complementary ‘codon’ sequences in messenger RNA. These and many other molecular interactions define the identities ...
Summary of fatty acid synthesis
... the ER and mitochondria. 2. Certain cell types in the brain can add up to a total of 24 carbon units to an acyl chain 3. Enzymes present in the ER (mixed-function oxidases) are responsible for desaturating fatty acids using NADPH as a cofactor ...
... the ER and mitochondria. 2. Certain cell types in the brain can add up to a total of 24 carbon units to an acyl chain 3. Enzymes present in the ER (mixed-function oxidases) are responsible for desaturating fatty acids using NADPH as a cofactor ...
The nonenzymatic subunit of pseutarin C, a
... D prothrombin activators trocarin D (Tropidechis carinatus) and hopsarin D (Hoplocephalus stephensi).15,16 Both are glycoproteins and are homologous (62%-70% similarity) to FXa with identical domain architecture. The light chain consists of an N-terminal Gla-domain containing 11 gamma-carboxyglutami ...
... D prothrombin activators trocarin D (Tropidechis carinatus) and hopsarin D (Hoplocephalus stephensi).15,16 Both are glycoproteins and are homologous (62%-70% similarity) to FXa with identical domain architecture. The light chain consists of an N-terminal Gla-domain containing 11 gamma-carboxyglutami ...
Supplementary Notes - Word file
... replaced with a fragment derived from pGLf37-CM1 digested with the same enzymes to construct pTVLtS286N. method ...
... replaced with a fragment derived from pGLf37-CM1 digested with the same enzymes to construct pTVLtS286N. method ...
Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency: metabolic
... Glucose is the major source of energy for the fetus [1]. Immediately after birth free fatty acids are mobilized from adipose tissue stores. A rapid increase in the activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I and II and a rise in the capacity to oxidize fatty acids is found in liver [2] and in heart ...
... Glucose is the major source of energy for the fetus [1]. Immediately after birth free fatty acids are mobilized from adipose tissue stores. A rapid increase in the activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I and II and a rise in the capacity to oxidize fatty acids is found in liver [2] and in heart ...
The Complete Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of the Donkey and
... et al. 1996a), common chimpanzee (Horai et al. 1995; Arnason et al. 1996a), pygmy chimpanzee (Horai et al. 1995), gorilla (Horai et al. 1995; Xu and Arnason 1996), and Bornean orangutan (Horai et al. 1995); Rodentia, represented by the mouse (Bibb et al. 1981) and the brown rat (Gadaleta et al. 1989 ...
... et al. 1996a), common chimpanzee (Horai et al. 1995; Arnason et al. 1996a), pygmy chimpanzee (Horai et al. 1995), gorilla (Horai et al. 1995; Xu and Arnason 1996), and Bornean orangutan (Horai et al. 1995); Rodentia, represented by the mouse (Bibb et al. 1981) and the brown rat (Gadaleta et al. 1989 ...
Supplemental Text
... GSSG levels similar to or even higher than APAP alone. This indicated that the delayed GSH treatment did not prevent the mitochondrial oxidant stress, which is presumably initiated by binding of NAPQI to mitochondrial proteins.15 These data provided strong evidence that the delayed treatment with G ...
... GSSG levels similar to or even higher than APAP alone. This indicated that the delayed GSH treatment did not prevent the mitochondrial oxidant stress, which is presumably initiated by binding of NAPQI to mitochondrial proteins.15 These data provided strong evidence that the delayed treatment with G ...
INPS: predicting the impact of non-synonymous variations on protein
... residue substitution, (ii) predict whether a residue substitution promotes a DDG increase or decrease (two class predictors) and (iii) predict whether a mutation is stabilizing, destabilizing or not affecting the protein stability (three class predictors). Noticeably, it is also very difficult to fi ...
... residue substitution, (ii) predict whether a residue substitution promotes a DDG increase or decrease (two class predictors) and (iii) predict whether a mutation is stabilizing, destabilizing or not affecting the protein stability (three class predictors). Noticeably, it is also very difficult to fi ...
D - Clayton State University
... that is difficult to account for by conventional natural selection. • Kimura (1969, 1983) proposed an alternative model to Darwinian evolution at DNA level. – Observed that rate of AA substitution averages ~1 change per 28 × 106 years for proteins of 100 residues. – Corresponding rate of nucleotide ...
... that is difficult to account for by conventional natural selection. • Kimura (1969, 1983) proposed an alternative model to Darwinian evolution at DNA level. – Observed that rate of AA substitution averages ~1 change per 28 × 106 years for proteins of 100 residues. – Corresponding rate of nucleotide ...
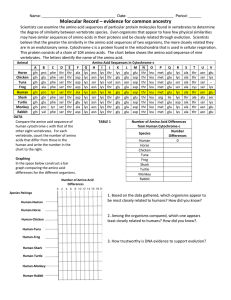
Molecular Record – evidence for common ancestry
... Molecular Record – evidence for common ancestry Scientists can examine the amino acid sequences of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between vertebrate species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequenc ...
... Molecular Record – evidence for common ancestry Scientists can examine the amino acid sequences of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between vertebrate species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequenc ...
2. Solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) - RSC Publishing
... 1). In particular, the posttranslational modifications are essential for protein activation: phosphorylation for signal transduction, ubiquitination for proteolysis, attachment of fatty acids for membrane anchoring or glycosylation for extending protein half-life, targeting, and cell-cell interactio ...
... 1). In particular, the posttranslational modifications are essential for protein activation: phosphorylation for signal transduction, ubiquitination for proteolysis, attachment of fatty acids for membrane anchoring or glycosylation for extending protein half-life, targeting, and cell-cell interactio ...
Application of Bruchin B to pea pods results in
... genome sequences revealed more than 600 P450 genes in ...
... genome sequences revealed more than 600 P450 genes in ...
as a PDF
... referred to as liquid secondary ionization (LSI)-is suitable for the rapid assay of specific components in complex biological samples (5). The basis for this type of analysis is the production of mostly intact molecular species from a complex mixture by use of a “soft” ionization technique, after wh ...
... referred to as liquid secondary ionization (LSI)-is suitable for the rapid assay of specific components in complex biological samples (5). The basis for this type of analysis is the production of mostly intact molecular species from a complex mixture by use of a “soft” ionization technique, after wh ...
The Nucleotide Sequence Determination of Catalases of Three
... a similar score (98%)in the topoisomerase II gene between the two species (Kanbe et al., personal communication). On the other hand, homology between a C. tropicalis clinical isolate (NUM 5076)and C. troplicalis Pk233 was 95%, even though both strains are thought to belong to the same species24). Ka ...
... a similar score (98%)in the topoisomerase II gene between the two species (Kanbe et al., personal communication). On the other hand, homology between a C. tropicalis clinical isolate (NUM 5076)and C. troplicalis Pk233 was 95%, even though both strains are thought to belong to the same species24). Ka ...
Gene Finding by Computational Analysis
... called nucleotides Francis Crick shows James Watson the model of DNA in their room number 103 of the Austin Wing at the ...
... called nucleotides Francis Crick shows James Watson the model of DNA in their room number 103 of the Austin Wing at the ...
genetic load and soft selection in ferns
... selection reduces the expressed load to zero under conditions of panmixia. The reduced selection against recessive lethals allows their accumulation, and populations are soon characterized by a high frequency of individuals heterozygous for recessive lethals. This leads to an increased expression of ...
... selection reduces the expressed load to zero under conditions of panmixia. The reduced selection against recessive lethals allows their accumulation, and populations are soon characterized by a high frequency of individuals heterozygous for recessive lethals. This leads to an increased expression of ...
The Urea Cycle
... fumarase enzyme which converts fumarate into malate. Malate can be transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane. There is also a cytostolic malate dehydrogenase which will convert malate into oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate can also be transported into the matrix of the mitochondria. Oxaloacetate ...
... fumarase enzyme which converts fumarate into malate. Malate can be transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane. There is also a cytostolic malate dehydrogenase which will convert malate into oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate can also be transported into the matrix of the mitochondria. Oxaloacetate ...
Document
... It is the most abundant trace element next to iron Rich sources of zinc include meat , fish, and dairy products. Typical diet supply 10-15 mg of zinc/day The body does not store zinc, the main route for excretion is through the gut • Along with magensium , zinc is the most frequently encountered met ...
... It is the most abundant trace element next to iron Rich sources of zinc include meat , fish, and dairy products. Typical diet supply 10-15 mg of zinc/day The body does not store zinc, the main route for excretion is through the gut • Along with magensium , zinc is the most frequently encountered met ...
Synthesis of RNA - Stamm revision
... solid-phase RNA synthesis is the choice of a suitable combination of orthogonal transient not clear what the orthogonal means, can you explain and put in glossary (R1) and permanent (R, R2, R3) protecting groups. It is of critical importance that the 2’-protecting groups remain completely intact unt ...
... solid-phase RNA synthesis is the choice of a suitable combination of orthogonal transient not clear what the orthogonal means, can you explain and put in glossary (R1) and permanent (R, R2, R3) protecting groups. It is of critical importance that the 2’-protecting groups remain completely intact unt ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.