Protein Synthesis Notes
... to a transfer RNA molecule. The tRNA molecule is a single strand of RNA that loops back on itself. At one end it has 3 bases called an ANTICODON, At the other end the corresponding amino acid is attached. The CODON of the mRNA attaches to the ANTICODON of the tRNA molecule. For example, if the mRNA ...
... to a transfer RNA molecule. The tRNA molecule is a single strand of RNA that loops back on itself. At one end it has 3 bases called an ANTICODON, At the other end the corresponding amino acid is attached. The CODON of the mRNA attaches to the ANTICODON of the tRNA molecule. For example, if the mRNA ...
Name: :______ Genetic Mutations—Online Model Go to: http
... 3. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids and breaks the bond between the first tRNA molecule and it’s amino acid. 4. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon. 5. The now empty tRNA molecule returns to the cytoplasm. 6. A complementary tRNA molecule bind ...
... 3. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids and breaks the bond between the first tRNA molecule and it’s amino acid. 4. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon. 5. The now empty tRNA molecule returns to the cytoplasm. 6. A complementary tRNA molecule bind ...
File - Kirkwall Grammar School
... 1. State the name of the small packets of information found on a chromosome? ...
... 1. State the name of the small packets of information found on a chromosome? ...
The Genetic Code
... Many questions have arisen about how the code as we see it right now came into being, as well as what is so special about this particular code -there could be other codes. I’ll go into some details in the next section. ...
... Many questions have arisen about how the code as we see it right now came into being, as well as what is so special about this particular code -there could be other codes. I’ll go into some details in the next section. ...
Mutations Can Change the Meaning of Genes
... How Mutations Affect Genes Mutation: any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
... How Mutations Affect Genes Mutation: any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
notes Protein_Synthe.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... How does a tRNA know which of the 20 amino acids to pick? It reads the codon (AKA triplet) which is a set of 3 nitrogenous bases that codes for a particular amino acid. What is translation? - creation of a polypeptide by a ribosome using the code from mRNA and individual amino acids from tRNA How d ...
... How does a tRNA know which of the 20 amino acids to pick? It reads the codon (AKA triplet) which is a set of 3 nitrogenous bases that codes for a particular amino acid. What is translation? - creation of a polypeptide by a ribosome using the code from mRNA and individual amino acids from tRNA How d ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations - Mr. Dalton
... What type of mutation occurred? • Original DNA Strand TAC AAG GCG ACT • Mutated DNA Strand TAC AAA GGC GAC T ...
... What type of mutation occurred? • Original DNA Strand TAC AAG GCG ACT • Mutated DNA Strand TAC AAA GGC GAC T ...
The genetic code and tRNA Biochemistry 302 February 15, 2006
... that AAG, AGA, and GAA must be codons for K, R, and E. ...
... that AAG, AGA, and GAA must be codons for K, R, and E. ...
Gene Expression
... As each new tRNA enters the ribosome, one leaves. Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
... As each new tRNA enters the ribosome, one leaves. Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
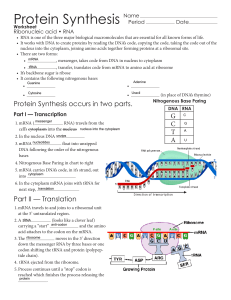
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
... DNA following the order of the nitrogenous bases 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
... DNA following the order of the nitrogenous bases 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
PBI 3 Student Handout 2
... bodies. The sequence of the 147 amino acids that comprise the precursor protein is encoded in a sequence of nucleotides that make up the β-Globin Gene. The first amino acid (Met) is later removed to produce a 146 amino acid protein. In this exercise, you are given a model of DNA. This model is a Map ...
... bodies. The sequence of the 147 amino acids that comprise the precursor protein is encoded in a sequence of nucleotides that make up the β-Globin Gene. The first amino acid (Met) is later removed to produce a 146 amino acid protein. In this exercise, you are given a model of DNA. This model is a Map ...
Quiz Next Tuesday (09/18) - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... The Coplanar Nature of the Peptide Bond Six atoms of the peptide group lie in a plane! ...
... The Coplanar Nature of the Peptide Bond Six atoms of the peptide group lie in a plane! ...
From Genes to Proteins
... gene for keratin is transcribed and translated by certain skin cells. The series of letters on the next slide represents the sequence of nucleotides in a portion of an mRNA molecule transcribed from the gene for keratin. This mRNA strand and the genetic code on page 211 can be used to determine some ...
... gene for keratin is transcribed and translated by certain skin cells. The series of letters on the next slide represents the sequence of nucleotides in a portion of an mRNA molecule transcribed from the gene for keratin. This mRNA strand and the genetic code on page 211 can be used to determine some ...
DNA and RNA Review
... 10. What does FIGURE 1 (picture on the right) show? 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
... 10. What does FIGURE 1 (picture on the right) show? 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
Transcription and Translation
... A tRNA molecule carries an amino acid tRNA nucleotides must be complementary to mRNA code ...
... A tRNA molecule carries an amino acid tRNA nucleotides must be complementary to mRNA code ...
DNA RNA
... Causes & Effects of Mutations • Causes: Mutagenesis can occur in many ways – Spontaneous mutations occur during DNA replication or recombination – Physical or chemical agents called mutagens may induce mutations (ex. High energy radiation from x-rays or UV light) ...
... Causes & Effects of Mutations • Causes: Mutagenesis can occur in many ways – Spontaneous mutations occur during DNA replication or recombination – Physical or chemical agents called mutagens may induce mutations (ex. High energy radiation from x-rays or UV light) ...
bio12_sm_07_3
... 3. There is not a specific tRNA molecule for each possible codon because several codons code for the same amino acid. If one tRNA recognizes each amino acid, then it can work efficiently by recognizing all the codons that code for it. There are many more codons than there are amino acids, but a uniq ...
... 3. There is not a specific tRNA molecule for each possible codon because several codons code for the same amino acid. If one tRNA recognizes each amino acid, then it can work efficiently by recognizing all the codons that code for it. There are many more codons than there are amino acids, but a uniq ...
12.3 Transcription and Translation PPT
... The genetic code is written in a language that only has four letters: A,U,G &C! These letters (nucleotides) combine in different ways to form the code for twenty different amino acids. The genetic code is read three letters (nucleotides) at a time in groups called codons. ...
... The genetic code is written in a language that only has four letters: A,U,G &C! These letters (nucleotides) combine in different ways to form the code for twenty different amino acids. The genetic code is read three letters (nucleotides) at a time in groups called codons. ...
Genetic Code
... As shown in Figure 1.1, the codon AUG codes for the amino acid methionine. This codon is also the start codon that begins translation. The start codon establishes the reading frame of mRNA. The reading frame is the way the letters are divided into codons. After the AUG start codon, the next three le ...
... As shown in Figure 1.1, the codon AUG codes for the amino acid methionine. This codon is also the start codon that begins translation. The start codon establishes the reading frame of mRNA. The reading frame is the way the letters are divided into codons. After the AUG start codon, the next three le ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... – Called hydrolysis (opposite of condensation) – Acid or base and heat required ...
... – Called hydrolysis (opposite of condensation) – Acid or base and heat required ...
Document
... RNA is similar to DNA in that it is also a nucleic acid composed of 4 nucleotides. Ways RNA is different from DNA: RNA contains Ribose, a 5-carbon sugar (instead of ...
... RNA is similar to DNA in that it is also a nucleic acid composed of 4 nucleotides. Ways RNA is different from DNA: RNA contains Ribose, a 5-carbon sugar (instead of ...
2.1 2 Translation - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... A What do you think the effect of cAMP is on the activity of the enzyme glycogen synthase and how do you think the effect is brought about? B What do you think the effect of G-6-P is on the activity of glycogen synthase? ...
... A What do you think the effect of cAMP is on the activity of the enzyme glycogen synthase and how do you think the effect is brought about? B What do you think the effect of G-6-P is on the activity of glycogen synthase? ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.