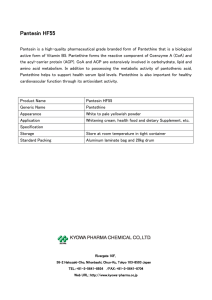
Pantesin HF55
... Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabo ...
... Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabo ...
Document
... Using mice and two strains of bacteria, he proved that it is possible for bacteria to take up genetic material from other bacteria and be transformed. ...
... Using mice and two strains of bacteria, he proved that it is possible for bacteria to take up genetic material from other bacteria and be transformed. ...
File
... Functions of Proteins: Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. We call these _______________. Some are used to grow and repair skin, ______________ and ______________. Others transport substances into or out of cells or help to _______________________. (this is ...
... Functions of Proteins: Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. We call these _______________. Some are used to grow and repair skin, ______________ and ______________. Others transport substances into or out of cells or help to _______________________. (this is ...
1. Proteins Are Informational and Functional Biological Polymers
... In Figure I.1.1 the observed frequencies of amino acids (last column of Table I.1.1) are plotted against what is expected from random permutations of nucleotides. The expected or random frequencies are calculated as follows: Let us consider tyrosine, for example. Two codons, UAU and UAC, code for ty ...
... In Figure I.1.1 the observed frequencies of amino acids (last column of Table I.1.1) are plotted against what is expected from random permutations of nucleotides. The expected or random frequencies are calculated as follows: Let us consider tyrosine, for example. Two codons, UAU and UAC, code for ty ...
S5. Untangling the central dogma- Extensions on
... Explain your reasoning. Indicate what the effect of the mutation would be on the protein synthesized from Liam’s gene. This change is in the promoter region. It could potentially affect transcription initiation, but since it states in the case that we should assume a protein product is synthesized, ...
... Explain your reasoning. Indicate what the effect of the mutation would be on the protein synthesized from Liam’s gene. This change is in the promoter region. It could potentially affect transcription initiation, but since it states in the case that we should assume a protein product is synthesized, ...
Bio-Macromolecules Worksheet.doc
... contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P). Nucleic acids carry the genetic information in a cell. DNA or deoxyribose nucleic acid contains all the instructions for making every protein needed by a living thing. RNA copies and transfers this genetic information so that prote ...
... contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P). Nucleic acids carry the genetic information in a cell. DNA or deoxyribose nucleic acid contains all the instructions for making every protein needed by a living thing. RNA copies and transfers this genetic information so that prote ...
DNA unit Summary
... If the two alleles in a pair are identical, then the trait is called homozygous. If the two alleles are different, then the trait is called heterozygous. Genetic crosses that involve one trait are called monohybrid crosses, while dihybrid crosses involve two traits. Outcomes of genetic crosses can b ...
... If the two alleles in a pair are identical, then the trait is called homozygous. If the two alleles are different, then the trait is called heterozygous. Genetic crosses that involve one trait are called monohybrid crosses, while dihybrid crosses involve two traits. Outcomes of genetic crosses can b ...
2017 - Barley World
... a. very generic, with each tRNA able to carry any of a number of amino acids. b. are coded for by sequences in introns. c. are very specialized, with each tRNA able to carry a specified amino acid. d. consists of 15S and 35S subunits. 7. The components of ribosomes are a. specific to each type of mR ...
... a. very generic, with each tRNA able to carry any of a number of amino acids. b. are coded for by sequences in introns. c. are very specialized, with each tRNA able to carry a specified amino acid. d. consists of 15S and 35S subunits. 7. The components of ribosomes are a. specific to each type of mR ...
A Guided Reading on Macromolecules
... acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functiona ...
... acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functiona ...
Organic Molecules - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
... 2. A very strong base might have a pH of ___. A. 3 B. 5 C. 9 ...
... 2. A very strong base might have a pH of ___. A. 3 B. 5 C. 9 ...
ap biology syllabus
... *I CAN describe the basic structure and function of DNA, mRNA, amino acids, polypeptides, and replication (e.g. replication, transcription, and translation). *I CAN describe the experiments of major scientists in determining both the structure and central dogma of DNA. *I CAN use mRNA codon charts t ...
... *I CAN describe the basic structure and function of DNA, mRNA, amino acids, polypeptides, and replication (e.g. replication, transcription, and translation). *I CAN describe the experiments of major scientists in determining both the structure and central dogma of DNA. *I CAN use mRNA codon charts t ...
Lectrure 9 - Columbus Labs
... Nature of Protein Sequences • Sequences and composition reflect the function of the protein • Membrane proteins have more hydrophobic residues, whereas fibrous proteins may have atypical sequences ...
... Nature of Protein Sequences • Sequences and composition reflect the function of the protein • Membrane proteins have more hydrophobic residues, whereas fibrous proteins may have atypical sequences ...
Topic 10 (From Genotype to Phenotype)
... A succession of tRNAs add their amino acids to the polypeptide chain as the mRNA is moved through the ribosome, one codon at a time. Codons mRNA ...
... A succession of tRNAs add their amino acids to the polypeptide chain as the mRNA is moved through the ribosome, one codon at a time. Codons mRNA ...
Chemical Composition of Living Cells
... There are four general classes of macromolecules within living cells: nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. These compounds, which have molecular weights ranging from 1 x 103 to 1 x 106, are created through polymerization of building blocks that have molecular weights in the range of ...
... There are four general classes of macromolecules within living cells: nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. These compounds, which have molecular weights ranging from 1 x 103 to 1 x 106, are created through polymerization of building blocks that have molecular weights in the range of ...
Introduction to Proteins
... Stabilize tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins Create an organic solvent-like environment in the interior ...
... Stabilize tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins Create an organic solvent-like environment in the interior ...
3 MoleculesCells
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
File
... Give a synonym for each: Producer – Autotroph or plant Consumer – heterotroph or herbivore/omnivore/carnivore ...
... Give a synonym for each: Producer – Autotroph or plant Consumer – heterotroph or herbivore/omnivore/carnivore ...
Document
... The Value of Intelligence • Motivation for Alteration - Desire for an Intelligent Child – intelligent individuals lead ‘better’ lives, have successful careers, and are perceived as being ‘superior’ – with the seeming availability of the technology to do so, why not? ...
... The Value of Intelligence • Motivation for Alteration - Desire for an Intelligent Child – intelligent individuals lead ‘better’ lives, have successful careers, and are perceived as being ‘superior’ – with the seeming availability of the technology to do so, why not? ...
Chapter Outline
... – messenger RNA (mRNA) is formed next to an activated gene – mRNA migrates to cytoplasm ...
... – messenger RNA (mRNA) is formed next to an activated gene – mRNA migrates to cytoplasm ...
Chapter 4 - Cellular Metabolism
... Messenger RNA can move out of the nucleus and associate with ribosomes in the cytoplasm where the protein will be constructed in a process called translation. d. In the cytoplasm, a second kind of RNA, called transfer RNA, has a triplet of nucleotides called the anticodon, which is complementary to ...
... Messenger RNA can move out of the nucleus and associate with ribosomes in the cytoplasm where the protein will be constructed in a process called translation. d. In the cytoplasm, a second kind of RNA, called transfer RNA, has a triplet of nucleotides called the anticodon, which is complementary to ...
02 B organic chemistry - macromolecules
... guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine, and uracil. Hey, that’s 5!... Uses: Information transformation We will have more detail later, when we study DNA replication (making sure that all cells get the same information), Transcription (DNA sequence directing RNA sequence), and Translation (RNA directing ...
... guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine, and uracil. Hey, that’s 5!... Uses: Information transformation We will have more detail later, when we study DNA replication (making sure that all cells get the same information), Transcription (DNA sequence directing RNA sequence), and Translation (RNA directing ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.























