Types and effects of protein variations. Vihinen
... interactions and other characteristics in several ways. List of the effects would be really long and include e.g. interactions, stability, electrostatic effects, protein packing, local and global structural changes and so on. Many deleterious variants are straightforward to explain, such as large de ...
... interactions and other characteristics in several ways. List of the effects would be really long and include e.g. interactions, stability, electrostatic effects, protein packing, local and global structural changes and so on. Many deleterious variants are straightforward to explain, such as large de ...
Sequence Alignment
... • exactly the same Amino Acid or Nucleotide in the same position Sequence similarity • substitutions with similar chemical properties Sequence homology • general term that indicates evolutionary relatedness among sequences • sequences are homologous if they are derived from a common ancestral sequen ...
... • exactly the same Amino Acid or Nucleotide in the same position Sequence similarity • substitutions with similar chemical properties Sequence homology • general term that indicates evolutionary relatedness among sequences • sequences are homologous if they are derived from a common ancestral sequen ...
Acid Base Balance
... the normal ranges, and the value that does not match the pH will be outside its normal range, indicating the body is attempting to get the pH back to normal. For example, if the pH (7.20) and CO2 (50) are acidotic, the HCO3 should be on the alkalotic side (27). ...
... the normal ranges, and the value that does not match the pH will be outside its normal range, indicating the body is attempting to get the pH back to normal. For example, if the pH (7.20) and CO2 (50) are acidotic, the HCO3 should be on the alkalotic side (27). ...
3. RESULTATS
... of CF with late-onset pancreatic sufficiency (PS) in 70% of cases (Vazquez et al. 1996). Although a larger number of cases should be analysed, it seems that the glycine change to valine has a more severe effect than that to glutamic acid at this position. 711 + 3A→T This splice mutation in intron 5 ...
... of CF with late-onset pancreatic sufficiency (PS) in 70% of cases (Vazquez et al. 1996). Although a larger number of cases should be analysed, it seems that the glycine change to valine has a more severe effect than that to glutamic acid at this position. 711 + 3A→T This splice mutation in intron 5 ...
Acid Base Balance
... the normal ranges, and the value that does not match the pH will be outside its normal range, indicating the body is attempting to get the pH back to normal. For example, if the pH (7.20) and CO2 (50) are acidotic, the HCO3 should be on the alkalotic side (27). ...
... the normal ranges, and the value that does not match the pH will be outside its normal range, indicating the body is attempting to get the pH back to normal. For example, if the pH (7.20) and CO2 (50) are acidotic, the HCO3 should be on the alkalotic side (27). ...
lncRNA in
... • Look for structural evidence – Structural possibility does not mean non-coding • Look for sequence binding motif – Could still be protein coding • Look for sequence similarity to known lncRNA – Not enough known about lncRNA and low evolutionary conservation ...
... • Look for structural evidence – Structural possibility does not mean non-coding • Look for sequence binding motif – Could still be protein coding • Look for sequence similarity to known lncRNA – Not enough known about lncRNA and low evolutionary conservation ...
An Abstract Description of Biological Evolution
... genotype (parthenogenesis) or a pair (sexual reproduction). In principle, multiple parents could be modelled if appropriate for particular social domains (like policies decided by committees) though this approach has not been used so far. 4) Mechanism of selection: A specification of all the process ...
... genotype (parthenogenesis) or a pair (sexual reproduction). In principle, multiple parents could be modelled if appropriate for particular social domains (like policies decided by committees) though this approach has not been used so far. 4) Mechanism of selection: A specification of all the process ...
NON-CANONICAL TRANSCRIPTION INITIATION: THE EXPANDING
... Attempts were made at establishing whether it is bacterial RNAP that could use NAD or CoA as initiation substrates but they failed (Chen et al., 2009; Kowtoniuk et al., 2009). Therefore, it was proposed recently for NAD that it may be the NAD synthetic machinery that attaches nicotinamide to the RNA ...
... Attempts were made at establishing whether it is bacterial RNAP that could use NAD or CoA as initiation substrates but they failed (Chen et al., 2009; Kowtoniuk et al., 2009). Therefore, it was proposed recently for NAD that it may be the NAD synthetic machinery that attaches nicotinamide to the RNA ...
Krogh, A., Brown, M., Mian, I.S., Sjolander, K., and Haussler, D. Hidden Markov Models in Computational Biology. J. Mol. Biol. , 235. pp. 1501-1531, 1994.
... time that we have been developing this approach. several related efforts hare come to our attention. One is that of \illite. Stu1t.z and Smith (Whiteet nl.. 1991: Stnltz et d.. 1993), who use HMMs to model protein superfamilies. This work is more ambitious to than our o w l . since superfamiliesareh ...
... time that we have been developing this approach. several related efforts hare come to our attention. One is that of \illite. Stu1t.z and Smith (Whiteet nl.. 1991: Stnltz et d.. 1993), who use HMMs to model protein superfamilies. This work is more ambitious to than our o w l . since superfamiliesareh ...
Multi-Organ Contribution to the Metabolic Plasma Profile Using
... each organ has to the metabolic profile of plasma samples. Metabolic profiles were obtained for gut, kidney, liver, muscle, pancreas and plasma samples, using GC-TOF MS. When applying PLS (partial least square projection to latent structures) and PCA modelling to complex data that includes multiple ...
... each organ has to the metabolic profile of plasma samples. Metabolic profiles were obtained for gut, kidney, liver, muscle, pancreas and plasma samples, using GC-TOF MS. When applying PLS (partial least square projection to latent structures) and PCA modelling to complex data that includes multiple ...
Document
... mutations that get accepted from a given set of proteins. 1 PAM refers to a change in position for an average of 1% of amino-acids residues. ...
... mutations that get accepted from a given set of proteins. 1 PAM refers to a change in position for an average of 1% of amino-acids residues. ...
Characterization of sparfloxacin-resistant mutants of Staphylococcus aureus Original article
... Topoisomerase IV [15–17]. Although, it has been suggested that the primary sparfloxacin target in Grampositive microorganisms might be the DNA-Gyrase [18,19]. However, a study using S. pneumoniae by Pan and Fisher [20] showed that this quinolone has a greater affinity to Topoisomerase IV than to DNA ...
... Topoisomerase IV [15–17]. Although, it has been suggested that the primary sparfloxacin target in Grampositive microorganisms might be the DNA-Gyrase [18,19]. However, a study using S. pneumoniae by Pan and Fisher [20] showed that this quinolone has a greater affinity to Topoisomerase IV than to DNA ...
The effect of different amino acid side chains on the stereospecificity
... cofactor. It has been argued that for optimal catalytic efficiency the α-carbon bond to be cleaved should be orthogonal to the plane of the imine-cofactor π-electron system [3]. The reaction catalysed will depend on whether the amino acid R-group, αcarboxylate or α-proton is orthogonal to the plane ...
... cofactor. It has been argued that for optimal catalytic efficiency the α-carbon bond to be cleaved should be orthogonal to the plane of the imine-cofactor π-electron system [3]. The reaction catalysed will depend on whether the amino acid R-group, αcarboxylate or α-proton is orthogonal to the plane ...
KAT6A Syndrome - Rarechromo.org
... happens before, or shortly after conception so they are found in all cells. Many of these changes seen in cancer are caused by a ‘translocation’ when part of the KAT6A gene is attached to part of another gene. This can cause lots of proteins to be produced as the new fusion protein has the ability t ...
... happens before, or shortly after conception so they are found in all cells. Many of these changes seen in cancer are caused by a ‘translocation’ when part of the KAT6A gene is attached to part of another gene. This can cause lots of proteins to be produced as the new fusion protein has the ability t ...
KAT6A Syndrome - Rarechromo.org
... happens before, or shortly after conception so they are found in all cells. Many of these changes seen in cancer are caused by a ‘translocation’ when part of the KAT6A gene is attached to part of another gene. This can cause lots of proteins to be produced as the new fusion protein has the ability t ...
... happens before, or shortly after conception so they are found in all cells. Many of these changes seen in cancer are caused by a ‘translocation’ when part of the KAT6A gene is attached to part of another gene. This can cause lots of proteins to be produced as the new fusion protein has the ability t ...
15. The Importance of Energy Changes and Electron Transfer in
... 19.5 Energetics and Control of the Citric Acid Cycle Control of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase ◈ Regulatory control (in citric acid cycle) 1) Citrate synthase is an allosteric enzyme inhibited by ATP, NADH, succinyl-CoA, and its product. 2) Isocitrate dehydrogenase reaction: ADP and NAD+ are allosteric act ...
... 19.5 Energetics and Control of the Citric Acid Cycle Control of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase ◈ Regulatory control (in citric acid cycle) 1) Citrate synthase is an allosteric enzyme inhibited by ATP, NADH, succinyl-CoA, and its product. 2) Isocitrate dehydrogenase reaction: ADP and NAD+ are allosteric act ...
Lec6 Fatty acid oxid..
... 3- Beta oxidation of fatty acids: It is the major pathway of oxidation (catabolism or breakdown) of saturated fatty acids in which two carbons are removed from activated fatty acid, producing acetyl CoA, NADH and FADH2 Site: in the mitochondria of all tissues particularly in the liver. So there is ...
... 3- Beta oxidation of fatty acids: It is the major pathway of oxidation (catabolism or breakdown) of saturated fatty acids in which two carbons are removed from activated fatty acid, producing acetyl CoA, NADH and FADH2 Site: in the mitochondria of all tissues particularly in the liver. So there is ...
Biochemistry - Wikimedia Commons
... biochemistry should generally be considered neither fully "biology" nor fully "chemistry" in nature. Biochemistry incorporates everything in size between a molecule and a cell and all the interactions between them. The aim of biochemists is to describe in molecular terms the structures, mechanisms a ...
... biochemistry should generally be considered neither fully "biology" nor fully "chemistry" in nature. Biochemistry incorporates everything in size between a molecule and a cell and all the interactions between them. The aim of biochemists is to describe in molecular terms the structures, mechanisms a ...
Co-translational Folding
... – formation of disulfide bridges and attachment of any of a number of biochemical functional groups, such as acetate, phosphate, various lipids and carbohydrates. – Removal of one or more amino acids from the amino end of the polypeptide chain, or cutting the polypeptide in the middle of the chain – ...
... – formation of disulfide bridges and attachment of any of a number of biochemical functional groups, such as acetate, phosphate, various lipids and carbohydrates. – Removal of one or more amino acids from the amino end of the polypeptide chain, or cutting the polypeptide in the middle of the chain – ...
Participation of DDDD and KPAR
... Mercuric reductase (MerA) is an essential enzyme for the survival of microorganisms that reside in environments containing mercuric compounds. The enzyme converts the extremely toxic mercuric ions (Hg2+) into the less toxic volatile elemental mercury form (Hg 0). A novel MerA molecule that has under ...
... Mercuric reductase (MerA) is an essential enzyme for the survival of microorganisms that reside in environments containing mercuric compounds. The enzyme converts the extremely toxic mercuric ions (Hg2+) into the less toxic volatile elemental mercury form (Hg 0). A novel MerA molecule that has under ...
The location and type of mutation predict
... further studies to delineate the deletion boundaries could not be performed. For the remaining 24 patients, direct sequencing detected five missense mutations, six splicing defects confirmed by RT–PCR analysis, five nonsense mutations and eight frameshift mutations (Fig. 2, Tables 1 and 2). Only two ...
... further studies to delineate the deletion boundaries could not be performed. For the remaining 24 patients, direct sequencing detected five missense mutations, six splicing defects confirmed by RT–PCR analysis, five nonsense mutations and eight frameshift mutations (Fig. 2, Tables 1 and 2). Only two ...
New insight into plant intramembrane proteases
... metalloproteases occurring widely in living organisms, from bacteria to humans, first identified in humans as protein involved in proteolysis of sterol-regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs; Rawson et al. 1997). S2P proteases comprise of at least four hydrophobic regions and their characterist ...
... metalloproteases occurring widely in living organisms, from bacteria to humans, first identified in humans as protein involved in proteolysis of sterol-regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs; Rawson et al. 1997). S2P proteases comprise of at least four hydrophobic regions and their characterist ...
- Wiley Online Library
... Enzymes: DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; CMS, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylD-erythritol synthase; CMK, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; MCS, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS, 1hydroxy-2-me ...
... Enzymes: DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; CMS, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylD-erythritol synthase; CMK, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; MCS, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS, 1hydroxy-2-me ...
Ch. 03 The Molecules of Life
... – more than twice as much energy as carbohydrate :The downside to this energy efficiency is that it is very difficult for a person trying to lose weight to “burn off” excess body fat ...
... – more than twice as much energy as carbohydrate :The downside to this energy efficiency is that it is very difficult for a person trying to lose weight to “burn off” excess body fat ...
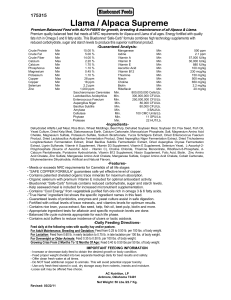
Llama / Alpaca Supreme
... - Contains “Cool Energy” from vegetable& purified fish oils rich in omega 3 & 6 fatty acids. -”True Name” ingredient list shows the specific ingredient names in this feed. - Guaranteed levels of probiotics, enzymes and yeast culture assist in safe digestion. - Fortified with critical levels of trace ...
... - Contains “Cool Energy” from vegetable& purified fish oils rich in omega 3 & 6 fatty acids. -”True Name” ingredient list shows the specific ingredient names in this feed. - Guaranteed levels of probiotics, enzymes and yeast culture assist in safe digestion. - Fortified with critical levels of trace ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.